Acute Intermittent Porphyria 시장 규모 및 점유율 분석 - 성장 추세 및 예측 (2024 - 2031)
급성 간헐적 인 Porphyria 시장은 치료 (RNA 간섭 기반 치료, Givosiran, 증상 치료), 유통 채널 (Hospital 약국, 온라인 약국, 소매 약국), 지리 (북미, 라틴 아메리카, 아시아 태평양, 유럽, 중동 및 아프리카)에 의해 구분됩니다. 보고....
Acute Intermittent Porphyria 시장 트렌드
시장 드라이버 - 인식 증가 약 희귀 질환
기술 및 인터넷의 발전으로, 드문 질병에 대한 인식은 폭발적으로 상승합니다. 이 질병은 정보의 부족으로 숨겨져 있습니다. 의사와 연구원은 또한이 희소한 상태에 대해 더 보컬. 그들은 연구 논문을 출판하고 주류 매체에 인터뷰를 제공합니다. 국제 드문 질병의 날은 매년 다양한 국가에서 캠페인으로 표시됩니다.
침묵에서 고통받는 환자는 이제 목소리를 갖게되었습니다. 질병의 원인, 치료 및 관리와 관련된 그들의 질문은 신속하게 해결됩니다. 이 잎은 변형과 불필요한 불안에 대한 덜 범위. 인식 상승으로, 드문 질병에 초점을 또한 의료 및 간호 대학에서 증가. 새로운 의사와 의료 직원은 자신의 경력에 있는 그런 조건에 대해 배웁니다.
이러한 모든 결합 요인은 급성 간헐적인 사기그릇 시장의 성장에 크게 기여했습니다. 초기 감지는 적시 개입 기술 및 증상 관리가 채택 될 수 있습니다. 그것은 합병증과 악화 건강 상태를 방지합니다. 환자는 적절한 진단을 위해 endlessly 찾는 대신 적절한 치료를받을 수 있습니다. Awareness는 드문 질병의 주위에 stigma를 제거하고 다양한 이해 관계자로부터 더 많은 자금 및 더 깊은 연구 약속을 제공합니다.
Market Driver - RNA 기반 치료제 개발 대상 치료
RNA 기반 치료법은 급성 간헐적 인 사기그릇과 같은 유전적 장애에 대한 유망한 접근법을 제시하고 유전적 mutations를 병리학에 포함. 특히, RNA 간섭 (RNAi) 기술은 다른 중요한 세포 통로를 해치 없이 erring 효소의 지속적으로 구획 생산을 선택할 수 있는 연구됩니다. 이 독특한 힘의 대상 액션과 최소 부작용 RNAi 흥미로운 영역.
몇몇 biotechs는 급성 간헐적인 porphyria를 위한 RNAi 약의 임상 시험을 지휘하고 있습니다. 입증된 성공적인 경우, 그들은 현재 주어진 일반적인 약 치료에 경쟁적인 가장자리를 달성할 수 있습니다.
RNAi 외에도 유전자 치료는 새로운 형태도 희망을 제공합니다. 유전자 교체 또는 편집을 통해 루트에서 유전 적 발작을 수정하면 긴 실행을 통해 공격의 발생을 제거 할 수 있습니다. 초기 유전자 치료 연구 결과 및이 분야는 매년 급속하게 진행되고 있습니다. 벡터 엔지니어링 및 타겟팅 능력의 발전은 이러한 기술을 더욱 추진하고 있습니다.
따라서, RNA 기반 플랫폼에서 일어나는 획기적인 것은 급성 간헐적 인 사기그리아와 같은 유전 적 질환을 대상으로합니다. 그들은 직접 문제를 해결하고 증상이 없습니다. 이 차별화 된 접근 방식은 시장의 성장에 강한 영향을 미칠 것입니다.
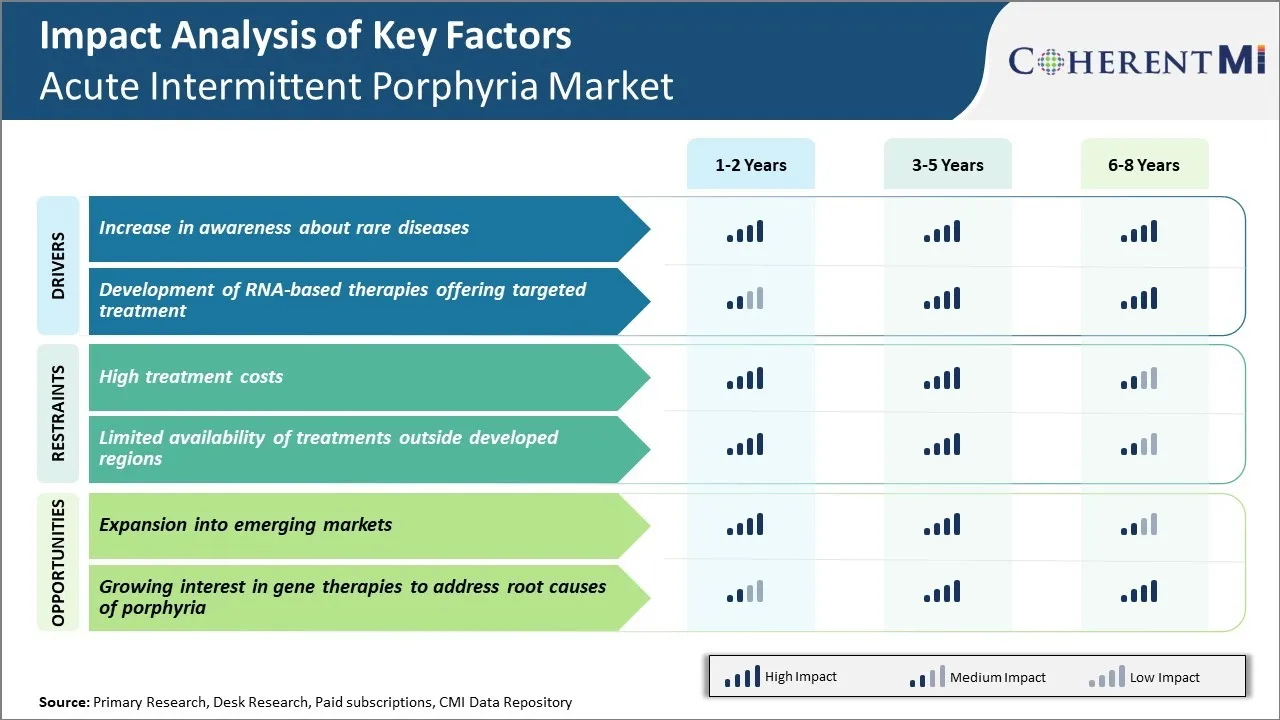
시장 도전 - 높은 reatment 비용
Acute Intermittent Porphyria 시장이 직면 한 주요 과제 중 하나는 상태 관리와 관련된 높은 치료 비용입니다. AIP는 공격과 잠재적인 합병증을 막기 위하여 costly 일생 관리를 요구합니다. AIP 공격에 대한 주요 치료에는 주입 당 수천 달러를 비용이 줄 수있는 정맥 분 주사가 포함됩니다.
또한 장기 치료 및 모니터링은 빈번한 실험실 테스트, 전문가 방문, 진단 테스트 및 약물을 통해 증상을 관리 할 수 있습니다. 이러한 모든 환자와 전반적인 의료 시스템에 무거운 경제 부담에 기여. 상태의 강렬은 상대적으로 적은 환자가 새로운 치료의 높은 고정 연구 및 개발 비용을 상쇄하는 데 도움이되는 것을 의미합니다.
약물 제조업체는 작은 잠재적 인 시장 크기로 인해 더 저렴한 치료 옵션을 개발하는 데 도움이됩니다. 무결성 및 적절한 진단은 크게 향상되며, 높은 비용은 AIP 시장의 성장에 대한 환자 접근을 제한하고 영향을 미칠 것입니다.
시장 기회 - Emerging Markets로 확장
Acute Intermittent Porphyria 시장의 주요 기회 중 하나는 신흥 시장으로 확장됩니다. 현재, 시장은 인식이 높고 진단 기능이 더 진보 된 북미 및 서유럽의 선진국에 의해 지배된다.
그러나, AIP는 세계적인 우선권이 있고 많은 개발 지구에서 근본적으로 남아 있습니다. 시장 성장 잠재력이 있고 라틴 아메리카, 아시아 태평양 및 중동 국가와 같은 신흥 시장에서 진단율과 접근을 증가하여 환자의 결과를 개선할 수 있습니다. 이 국가는 급속하게 성장하는 의료 분야를 가진 상승 소득 수준을 가진 감소시킵니다 치료 시간을 더 적당한.
AIP 시장에서 운영되는 기업은 의사 및 보조 치료 접근 모델에 대한 인식 캠페인을 실행하기 위해 지역 공급자, 환자 자문 그룹 및 정부와 파트너십을 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
신흥 시장에서 새로운 환자 인구로 확대함으로써, 회사는 차세대 치료법을 개발하는 장기 수익성과 투자를 돕기 위해 가늠자의 상당한 매출 성장과 경제를 달성할 수 있습니다.