Рынок лечения хронической идиопатической крапивницы (CIU) АНАЛИЗ РАЗМЕРОВ И ДОЛЕЙ - ТЕНДЕНЦИИ РОСТА И ПРОГНОЗЫ (2024 - 2031)
Рынок лечения хронической идиопатической крапивницы (CIU) сегментирован по маршруту администрирования (подкожная, внутривенная, пероральная), по типу ....
Рынок лечения хронической идиопатической крапивницы (CIU) Тенденции
Рыночный драйвер - растущая распространенность хронической идиопатической крапивницы (CIU) глобально
Хроническая идиопатическая крапивница, также известная как хроническая спонтанная крапивница, является распространенным состоянием, характеризующимся зудящими ульями или завязями на коже, которые длятся более шести недель. Хотя точная причина остается неизвестной во многих случаях, ее распространенность растет в течение последних нескольких десятилетий по всему миру. Многие факторы, такие как экологические триггеры, стрессовый образ жизни и пищевая аллергия, играют роль в развитии симптомов CIU. Поскольку все больше людей страдают от этого тревожного состояния, спрос на эффективные варианты лечения CIU значительно вырос.
Согласно имеющимся оценкам, CIU, по оценкам, затрагивает почти 1% мирового населения в какой-то момент их жизни, причем более высокие показатели зарегистрированы в развитых странах, где современные факторы риска более распространены. Состояние часто оказывает ухудшающееся влияние на качество жизни, поскольку постоянный зуд и заживление могут вызвать бессонницу, раздражительность, вялость и негативно повлиять на повседневную деятельность и социальные взаимодействия. С ростом осведомленности все больше людей обращаются за медицинской помощью для своих симптомов, а не рассматривают их как незначительные заболевания кожи. Это привело к росту числа рецептов на лекарства CIU за последние несколько лет.
Драйвер рынка - Достижения в области терапии моноклональных антител и биологических препаратов, которые обеспечивают целевые варианты лечения для CIU
Исследователи активно работают над разработкой новых подходов к лечению рефрактерной хронической идиопатической крапивницы, которая не адекватно реагирует на обычные антигистаминные препараты второго поколения. Это привело к значительным достижениям в лечении моноклональных антител и биологических агентов, которые точно нацелены на основные механизмы заболевания.
Например, омализумаб, гуманизированное моноклональное антитело, направленное против иммуноглобулина Е, было первым биологическим препаратом, успешно одобренным регулирующими органами для управления CIU. В клинических испытаниях омализумаб показал, что обеспечивает значительно большее облегчение от зуда, крапивницы и ангиодемы, чем плацебо.
Совсем недавно фариципимаб и лигелизумаб, оба нацеленные на сигналы иммунной системы, участвующие в CIU, вошли в клиническую оценку на поздней стадии. Их многообещающий профиль эффективности и безопасности, наблюдаемый до сих пор, указывает на то, что эти методы лечения могут стать основными факторами, влияющими на управление сложными для контроля случаями CIU.
Наличие таких целевых биологических препаратов, которые прерывают иммунологические пути, ведущие к заживлению и зуду, дает новую надежду пациентам, не оптимально реагирующим на варианты первой линии. Это ускорило исследования новых моноклональных антител для различных подтипов CIU. Разработка точных методов лечения позволит улучшить качество жизни для многих пациентов с CIU, способствуя более широкому внедрению этих передовых методов лечения в клиническую практику.
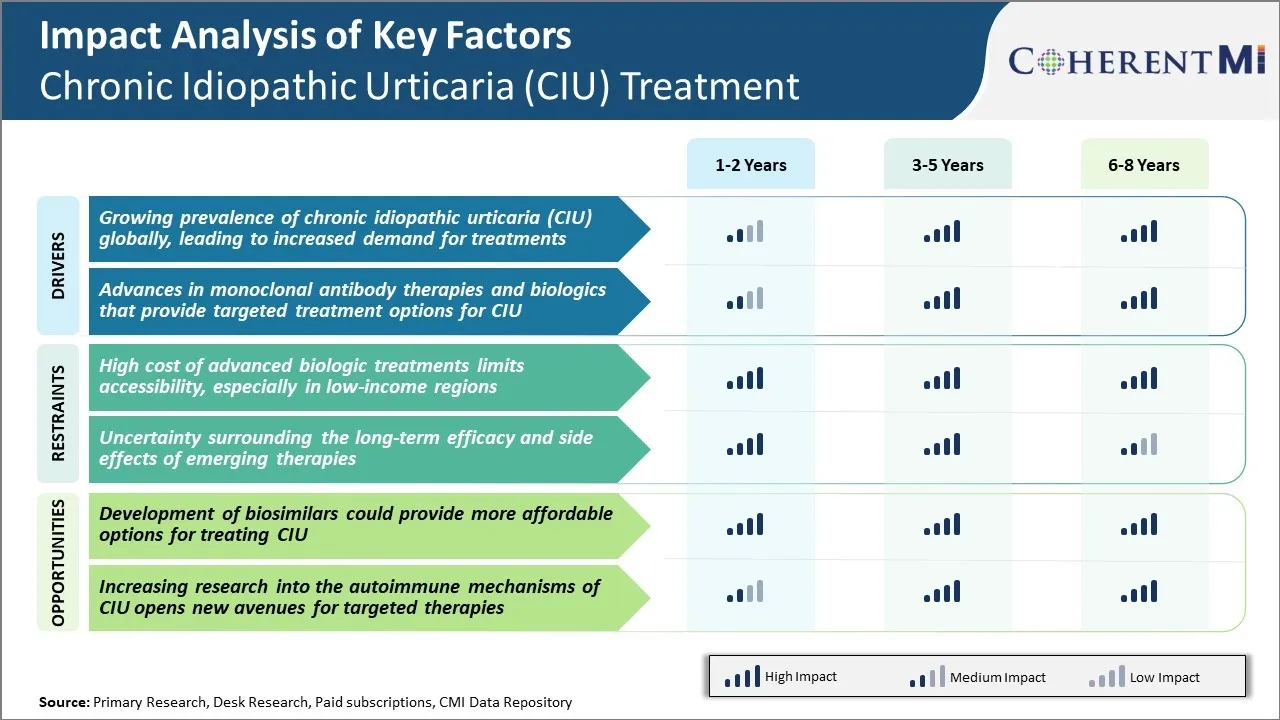
Вызов рынка: высокая стоимость современных биологических препаратов ограничивает доступность
Стоимость передовых биологических методов лечения хронической идиопатической крапивницы, таких как моноклональные антитела (mAbs), представляет собой серьезную проблему для широкого распространения во всем мире. Эти специальные биологические препараты, которые нацелены на иммуноглобулин Е (IgE) или его высокоаффинный рецептор FcεRI, очень эффективны в обеспечении быстрого контроля симптомов, но имеют высокую цену в диапазоне от 30 000 до 50 000 долларов США на пациента ежегодно.
Хотя они могут оказаться экономически эффективными за счет сокращения потребности в других медицинских услугах у респондентов, их высокая стоимость приобретения делает их недоступными для многих систем здравоохранения и отдельных пациентов в странах с низким и средним уровнем дохода. Даже на развитых рынках, расходы из собственных средств после страхового возмещения могут быть непомерно высокими для некоторых пациентов. Этот ценовой барьер ограничивает доступ к наиболее эффективным методам лечения, особенно для неимущих групп населения в развивающихся или ограниченных ресурсами регионах.
Если не будут доступны более доступные биоаналогичные или новые варианты перорального лечения, CIU, вероятно, продолжит негативно влиять на качество жизни многих пациентов, которые терпят неудачу в традиционной пероральной терапии из-за финансовых ограничений на дорогостоящие биологические препараты.
Рыночная возможность - Разработка биоаналогов может предоставить более доступные варианты лечения КИУ
Появление биоаналогов, ссылающихся на ведущие биологические методы лечения для CIU, предлагает потенциальную возможность решить их высокие затраты на лечение и расширить доступ к пациентам во всем мире. Биоаналоги, которые продемонстрировали сопоставимое качество, безопасность и эффективность своих эталонных продуктов, но продаются по сниженной цене, могут захватить значительную часть рынка после истечения срока действия патентной защиты для инновационных препаратов.
По прогнозам, глобальные расходы на биологические препараты CIU к 2025 году достигнут 2 миллиардов долларов США по мере увеличения поглощения, что сделает его привлекательным сегментом рынка для последующей конкуренции. Поскольку на крупных фармацевтических рынках стартует первая волна одобрения биоаналогов, со временем ожидается, что они значительно подорвут цены благодаря рыночным силам.
Более широкая доступность доступных биоаналогичных или биоаналогических эквивалентов биологических препаратов может позволить врачам оптимизировать лечение для многих пациентов с КИУ, особенно в чувствительных к цене регионах, где стоимость была препятствием для ухода.