短效胰岛素市场 规模与份额分析 - 成长趋势与预测 (2024 - 2031)
短效胰岛素市场按类型划分(胰岛素Lispro,胰岛素Aspart,胰岛素Glulisine),按指数划分(糖尿病1型,糖尿病2型),按地理划分(北美,拉丁美洲,亚太,欧洲,中东,非洲). 本报告为上述部分提供了价值(10亿美元)。....
短效胰岛素市场 趋势
市场驱动力 -- -- 全球糖尿病发病率上升
糖尿病在全球的发病率正在以惊人的速度增长。 根据专家的预测,到2030年,糖尿病将影响全世界约5.52亿人,发展中国家将承担大部分负担。 随着全世界人口的糖尿病率增加,对有效治疗和管理办法的需求也增加。 目前,2型糖尿病约占全球诊断糖尿病病例的90%。 由于现代生活方式基本稳定,肥胖症流行趋势日益恶化,二型糖尿病患者的人数在过去几十年里急剧增加。 由于这是一种慢性的终身疾病,目前还没有永久的治疗方法,病人依靠长期药物来控制血糖水平。
短效胰岛素仍然是管理食用后发现的妊娠后血糖突起的基石剂,尤其是在完全缺乏天然胰岛素生产的1型糖尿病患者中. 它通过模仿身体自身快速释放胰岛素在食物摄入后的作用. 它行动更快,在体内活动时间更短,因此对食前管理和控制食后高血糖非常有效。 随着全世界糖尿病人口的增加,需要强化胰岛素团(包括短效胰岛素)的病人人数激增。 获得保健的机会有限的国家正在面临负担得起的胰岛素供应严重短缺,加剧了全球疾病负担。 各国政府和非营利组织已加紧努力,向低收入群体患者广泛提供救生胰岛素类比。 然而,普遍获得糖尿病治疗和普及糖尿病治疗需要经过多年的时间才能成为所有国家的现实。 在此期间,持续增加的糖尿病患者人数将继续刺激所有类别胰岛素的需求,包括快速行动短胰岛素模拟。
市场驱动力 -- -- 胰岛素交付的技术进步
胰岛素疗法的技术创新在过去几十年中以快速的速度取得进展,领先的有胰岛素笔,胰岛素泵和新发明的智能胰岛素输送系统等进步. 创新的一个关键领域是开发更方便用户的设备,可以更密切地模仿胰岛素的自然胰岛素释放模式. 短效胰岛素类似物是这种先进的胰岛素送药机制的组成部分,通过精确的,按需的胰岛素剂量来进行更严格的葡萄糖控制.
例如,胰岛素笔作为餐前施用短效胰岛素的首选形式出现. 预先填充的一次性钢笔以易于使用的形式提供个别设定的胰岛素剂量,无需任何必要的混合步骤. 这提高了患者的坚持性和剂量的准确性. 同样,通过导管不断改变血糖水平的胰岛素泵使许多糖尿病患者的灵活性和生活质量发生了革命性的变化。 未来的"人工胰腺"系统使用自动算法,在零用户干预下,精确分分钟注入短胰岛素剂量,从而在自然目标范围内达到葡萄糖水平. 其它智能胰岛素投放创新如双激素泵,胰岛素补丁也高度依赖快速动作胰岛素特性. 技术突破将扩大获取这种以用户为中心的胰岛素解决方案的机会,将刺激今后几年对匹配短效胰岛素产品的需求激增。
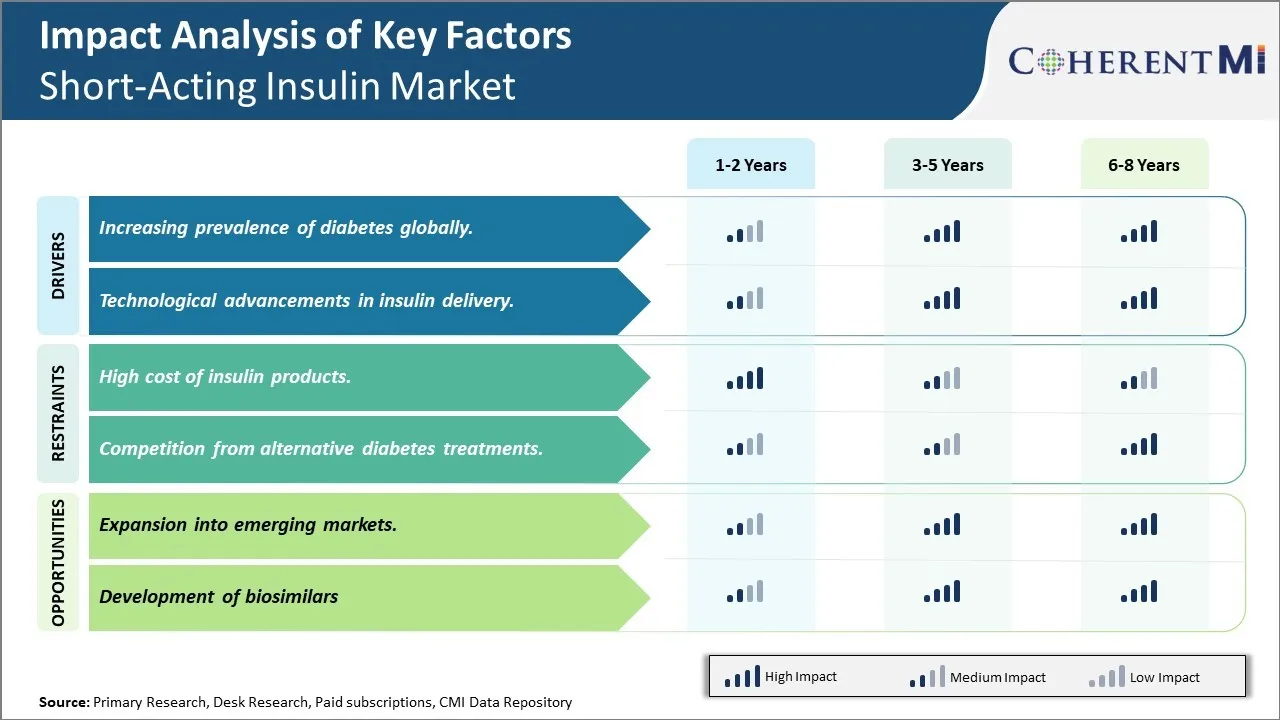
市场挑战 -- -- 胰岛素产品成本高
短效胰岛素市场面临的主要挑战之一是胰岛素产品成本高. 胰岛素是全世界数百万糖尿病患者的一种救命药物. 然而,多年来胰岛素费用增加,使许多患者难以负担并妥善管理其病情. 过去十年来,许多人喜欢的胰岛素类比的成本大幅上升,原因是其行动更快。 例如,自1996年上市以来,流行的胰岛素品牌Humalog的成本上升了1 000 %以上。 这种价格的急剧上涨对胰岛素的获得和承受能力产生了负面影响。 据报道,大约四分之一的糖尿病患者因费用高昂而配给胰岛素,这可能会造成严重的健康后果. 此外,高昂的药物费用对公共保健系统和私人保险的预算影响每年都在上升。 这给财政可持续性带来了挑战。 迫切需要解决胰岛素价格上涨的问题,以改善患者的结果,减轻糖尿病的社会经济负担。
市场机会----向新兴市场扩展
短期胰岛素市场的一个主要机会领域是向新兴经济体扩展。 据估计,全世界80%以上的糖尿病患者生活在中低收入国家。 印度、巴西、中国等新兴国家糖尿病发病率的上升,使大量病人需要治疗。 然而,由于保健基础设施低和负担不起等各种因素,这些地区的胰岛素使用率仍然很低。 如果胰岛素制造商能够为适应这些市场而作出适当的定价和分配策略的改变,就可以推动收入的大幅增长. 可以采取的一些战略包括开发低成本的瓶子和墨盒胰岛素产品,改善向偏远地区的供应链物流,与地方保健提供者和政府机构建立伙伴关系,以进行量计定价。 通过挖掘新兴市场的商业潜力,公司能够提高总的销售量,并发挥其在加强公共卫生方面的作用。