Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market is segmented By Mutation Type (PKD1 mutations, PKD2 mutations), By Therapeutics (Vasopressin V2 Re....
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR6.2%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 6.2% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Reata Pharmaceuticals, Xortx Therapeutics (XRx-008), Sanofi, Janssen Pharmaceuticals and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market Analysis
The Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.56 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.25 Bn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2024 to 2031. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts in the kidneys which can lead to kidney failure at an early age if left untreated. The increasing prevalence of the disease along with rising healthcare expenditures is expected to primarily drive the market growth over the forecast period.
The market has witnessed some positive trends over recent years. Research into new drugs and treatment options has increased substantially. Several pharmaceutical companies have drugs in late-stage clinical trials that could slow cyst growth or progression to kidney failure if approved. Increased awareness about the genetic nature of the disease has led to more families undergoing genetic screening and early detection. Early treatment can help preserve kidney function longer.
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Awareness and Advancements in Genetic Testing, Leading to Early Diagnosis of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD).
With increasing awareness about genetic disorders and hereditary conditions, more and more people are opting for genetic testing to understand their risks of developing various diseases. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is one such hereditary condition where early genetic testing and diagnosis can help patients and their families understand the risks better and seek timely medical management.
Recent technological advancements have enabled improved genetic testing methods which can detect the genetic mutations responsible for causing ADPKD with higher accuracy. Next-generation sequencing and analysis of entire protein-coding genes has allowed for comprehensive scanning to pinpoint underlying gene defects. This is beneficial as in about 10–15% of ADPKD cases, genetic testing based on conventional Sanger sequencing may not be able to identify the causative mutations. The improved precision of modern genetic testing is encouraging more at-risk family members to opt for screening.
Early diagnosis through genetic testing can empower patients and physicians to have timely discussions around treatment planning and disease management. Lifestyle modifications and regular monitoring of kidney function and kidney size scans from a younger age can help slow progression in asymptomatic stages. It also assists in family planning decisions. Cascade genetic testing of family members allows testing of children, siblings and extended family members of known mutation carriers, leading to identification of more newly diagnosed early cases. In summary, growing knowledge about genetics and advancements in molecular diagnosis are positively impacting early identification of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease cases.
Market Driver - Availability of Tolvaptan Treatment to Boost Industry Developments.
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) has traditionally posed a big challenge for effective therapeutic management due to its inherited nature and lack of definite treatment options. In recent times, the FDA approval of the vasopressin receptor antagonist Tolvaptan in 2018 provided new hope. Tolvaptan acts by blocking the arginine-vasopressin receptors, reducing the rate of cyst formation and growth in the kidneys affected by ADPKD.
It is the first and only approved drug therapy shown to slow kidney function decline in patients with rapidly progressing ADPKD. Clinical trials established that Tolvaptan can significantly reduce the total kidney volume increase and the yearly decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) as compared to placebo groups. Given intravenously, it allows for easy administration and monitoring under physician care. The effectiveness has been seen across a range of ADPKD patient groups including those with low or preserved kidney function.
While Tolvaptan offers valuable symptom management, its availability has transformed the treatment landscape. Nephrologists now have an approved pharmacological intervention option to delay disease progression and buy time for transplant eligibility in suitable cases. Pharmaceutical companies marketing Tolvaptan are actively creating awareness about the new treatment paradigm amongst patients and doctors. Kidney patient advocacy groups globally are educating on its benefits. Reimbursement is being pushed for in both public and private healthcare programs. Overall, the market entry of Tolvaptan has provided much needed momentum to the growth of ADPKD treatment market.
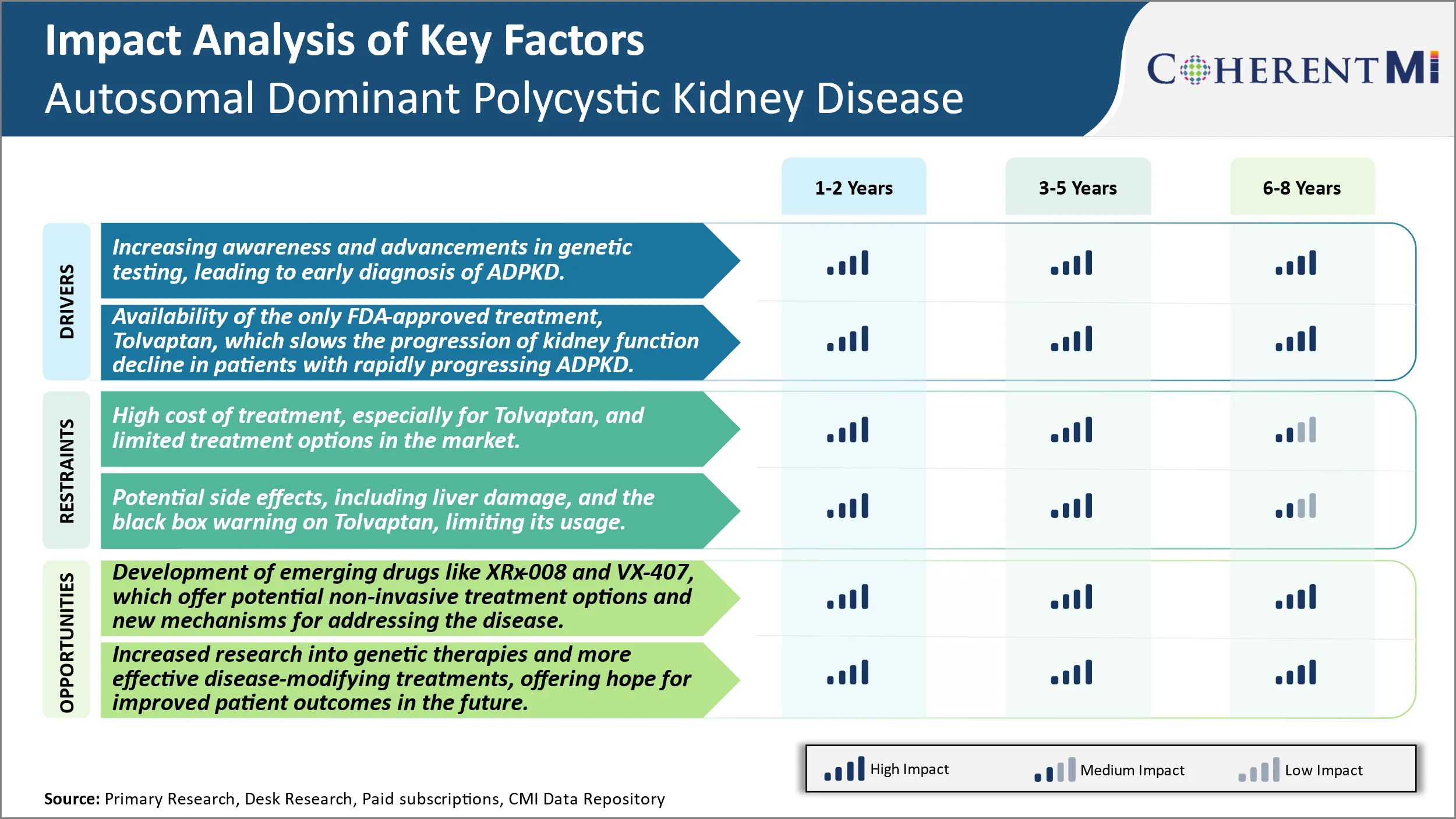
Market Challenge - High Cost of Treatment, Especially for Tolvaptan, And Limited Treatment Options in The Market.
The autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) market faces significant challenges due to the high cost of currently available treatments and limited treatment alternatives for patients. Tolvaptan, one of the only FDA-approved drugs for slowing cyst progression in ADPKD, can cost over USD100,000 per year. The financial burden of this treatment poses difficulties for healthcare systems and out-of-pocket costs may prevent many patients from accessing it. Furthermore, tolvaptan must be taken for life and can cause severe side effects such as liver damage. These risks and costs mean that tolvaptan may not be a viable option for all patients. Currently, the only other treatment choices are conservative measures like pain management rather than targeting the underlying cause of the disease. The lack of affordable and effective treatment alternatives presents major challenges in effectively addressing the needs of the large ADPKD patient population worldwide.
Market Opportunity: Emerging Drugs with Novel Mechanisms of Action
A key opportunity in the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease market involves the development of emerging drugs such as XRx-008 and VX-407. These drug candidates offer potential non-invasive treatment options and novel mechanisms of action that could help address some of the limitations of existing therapies. In particular, XRx-008 aims to inhibit the vasopressin V2 receptor without liver toxicity. Positive Phase 2 data demonstrated proof-of-concept for slowing cyst growth, representing an important step forward. Meanwhile, VX-407 works via a new mechanism involving inhibition of the secretory pathway calcium ATPase to reduce intracellular calcium levels and cystogenesis. Its early-stage trials have also yielded promising initial results. The potential availability of well-tolerated oral therapies targeting the underlying causes through different pathways could expand treatment choices and help many more ADPKD patients if approved. This presents a major opportunity for drug developers to address significant unmet needs in the market.
Prescribers preferences of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market
ADPKD is typically treated through a staged approach as the disease progresses. In early stages when kidney function is preserved, prescribers often recommend lifestyle modifications like dietary changes and regular exercise. Medications are usually not initiated unless glomerular filtration rate (GFR) declines below 60 ml/min/1.73m2.
Once GFR drops to this level, prescribers commonly start patients on Tolvaptan (brand name Jynarque). As a vasopressin V2-receptor antagonist, Tolvaptan helps slow cyst growth and renal function decline. It is typically the first-line pharmacologic therapy prescribed for slowing ADPKD progression in Stage 1-2 disease.
As ADPKD advances to Stage 3 with GFR 30-59 ml/min/1.73m2, prescribers may add an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) like Lisinopril (brand name Prinivil) or Losartan (brand name Cozaar). These control blood pressure and proteinuria, providing renal protection.
In Stage 4-5 disease with GFR 15-29 ml/min/1.73m2, prescribers commonly prescribe a combination of Tolvaptan, ACEi/ARB, and potentially vitamin D or phosphate binders if abnormalities arise. Prescribers closely monitor patients at this stage for risks of kidney failure and complications.
For end-stage renal disease, dialysis or transplant is recommended. Prescribers consider the patient's prognosis, support system, and preferences in determining the best treatment path.
Treatment Option Analysis of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) progresses through four stages - early (Stage 1), intermediary (Stage 2), late (Stage 3), and end-stage renal disease (Stage 4).
In Stage 1, lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes andexercise are recommended. As the disease progresses to Stage 2, treatment focuses on controlling blood pressure and slowing kidney function decline using angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). Medications such as Tolvaptan, a vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist, may also be prescribed to restrict cyst growth.
Stage 3 ADPKD involves significant kidney enlargement and decline in function. At this stage, treatments aim to curb disease progression through medications while preparing the patient for dialysis or transplantation. Tolvaptan continues to be a frontline therapeutic along with ACEi/ARBs. For patients who progress to Stage 4 or end-stage renal disease, dialysis is initiated to replace kidney function. The most common modalities are hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Kidney transplantation offers the best outcome for eligible Stage 4 patients. Immunosuppressants like tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil are prescribed post-transplant to reduce rejection risk. Close monitoring is needed long-term to manage transplant complications. By understanding disease stages and tailoring treatments appropriately, physicians can optimize patient outcomes at each stage of ADPKD.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market
Focus on Developing Novel Drugs - Companies like Otsuka Pharmaceuticals and Reata Pharmaceuticals have focused on developing novel drug therapies to slow cyst growth and kidney damage associated with ADPKD. Otsuka adopted an aggressive clinical trial strategy for their drug tolvaptan in the late 2000s. Their VAPOR trials from 2011-2015 evaluated tolvaptan's ability to slow cyst development and functional decline in over 1400 ADPKD patients. The trials showed clear benefits, with tolvaptan slowing the annual rate of total kidney volume increase by 25% compared to placebo. This was the first therapy to demonstrate a significant benefit in slowing ADPKD progression. Otsuka received FDA approval for tolvaptan in 2018, becoming the first approved drug specifically for ADPKD. Reata followed a similar pathway, advancing bardoxolone methyl through Phases 2 and 3 clinical trials from 2013-2019. Their landmark FALKON trial of 225 patients showed a statistically significant 30% reduction in estimated glomerular filtration rate decline and a 22% slowing of total kidney volume increase compared to placebo. This led to Reata filing for FDA approval in 2022.
Late-Stage Clinical Trials: By aggressively pursuing large, late-stage clinical outcomes trials, Otsuka and Reata generated strong data packages that convinced regulators of their drug's benefits - a key strategy for developing the first novel therapies for this rare disease. Their successes have spurred further research and established clinical proof of concept for targeting cyst growth and function decline in ADPKD.
In summary, developing drugs through well-designed late phase clinical trials focusing on clear outcomes like cyst growth, kidney function decline, and obtaining FDA approval has proven an effective strategy for companies to become leaders in the ADPKD treatment landscape.
Segmental Analysis of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market

Insights, By Mutation Type, PKD1 mutations is Expected to Register Remarkable Growth as Genetic Factors Determine Disease Severity.
By Mutation Type, PKD1 mutations is expected to contribute the highest share 52.2% in 2024 owing to its role in determining disease severity and earlier onset of end stage renal disease compared to PKD2 mutations. PKD1 mutations are implicated in around 85% of ADPKD cases and tend to cause a more severe form of the disease. Individuals with PKD1 mutations have an earlier age of diagnosis of hypertension and larger renal cyst burden by imaging criteria compared to those with PKD2 mutations. The rate of increase in total kidney volume is also faster among patients with PKD1 mutations. Due to the earlier manifestation of complications and end organ damage, patients with PKD1 mutations have a higher need for disease management therapies at an earlier stage.
Insights, By Therapeutics, Treatment Options Drive Therapeutic Segment Growth
By Therapeutics, Vasopressin V2 Receptor Antagonists is expected to contribute the highest share 41.1% in 2024 due to availability of treatment options and favorable efficacy and safety profile. Tolvaptan remains the only approved vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist for ADPKD, driving segment growth. It significantly lowers the rate of cyst growth and shrinkage and also slows the decline of kidney function. However, its use remains limited due concerns over side effects like thirst. The emergence of XRx-008, an investigational vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist, promises to expand treatment options in this segment. Positive phase 2 trial data suggests XRx-008 has comparable efficacy to tolvaptan but with better tolerability.
Insights, By End-User, Younger Population Prone to Early Disease Manifestations
By End-user, under 5 years contributes the highest share of the market owing to early disease manifestations in younger population. ADPKD is usually diagnosed during routine ultrasounds or scans conducted at younger ages unrelated to kidney issues. Renal cysts and abnormal kidney enlargement can be detected as early as during fetal development or in early childhood. Additionally, hypertension may manifest in childhood or adolescence. Younger patients are more likely to require regular screening and monitoring to manage early complications. Their overall disease severity also tends to be higher requiring costly long-term therapies pursued through adulthood. This drives higher healthcare utilization and spending in the under 5 years segment.
Additional Insights of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is the most common inherited kidney disorder, affecting millions worldwide. The condition is primarily driven by mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes, leading to the formation of cysts in the kidneys and, eventually, kidney failure. Currently, Tolvaptan is the only FDA-approved drug for ADPKD and is effective in slowing the progression of kidney function decline, although its use is limited by potential liver toxicity and high costs. Emerging therapies, such as XRx-008 and VX-407, are poised to address these unmet needs, offering hope for better and more accessible treatments. The disease burden is expected to grow as awareness increases and genetic testing becomes more common, leading to earlier diagnoses. However, the high cost of treatment, limited therapeutic options, and regulatory hurdles remain significant challenges in this space. With ongoing research and the anticipated introduction of new therapies, the market is set to expand rapidly over the forecast period.
Competitive overview of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market
The major players operating in the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market include Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Reata Pharmaceuticals, Xortx Therapeutics (XRx-008), Sanofi, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Galapagos NV, Palladio Biosciences, Regulus Therapeutics, Primerose Therapeutics, Exelixis Inc, Grupo Olmos and Bayer Healthcare.
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market Leaders
- Otsuka Pharmaceutical
- Reata Pharmaceuticals
- Xortx Therapeutics (XRx-008)
- Sanofi
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market
- In June 2024, VX-407 by Vertex Pharmaceuticals began its Phase I trials. This first-in-class small molecule targets PKD1 variants to stop kidney cyst growth and prevent progression to kidney failure.
- In December 2023, XRx-008 from Xortx Therapeutics is in Phase II trials for treating progressive kidney disease in ADPKD patients. The drug reduces uric acid production, thereby reducing systemic inflammation and improving kidney function.
- In May 2019, Tolvaptan (JYNARQUE) received FDA approval as the first treatment to slow kidney function decline in ADPKD patients. Despite being effective, the drug comes with a black box warning for potential liver damage.
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market Segmentation
- By Mutation Type
- PKD1 mutations
- PKD2 mutations
- By Therapeutics
- Vasopressin V2 Receptor Antagonists
- ACE inhibitors
- Angiotensin-Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
- Emerging Drugs (XRx-008)
- By End-user
- Under 5 years
- 5-14 years
- 15-24 years
- 25-44 years
- 45-64 years
- 65+ years

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market?
The Global Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.56 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.25 Bn by 2031.
What will be the CAGR of the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market?
The CAGR of the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market is projected to be 6.2% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the major factors driving the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market growth?
The increasing awareness and advancements in genetic testing, leading to early diagnosis of ADPKD and availability of the only FDA-approved treatment, tolvaptan, which slows the progression of kidney function decline in patients with rapidly progressing ADPKD are the major factor driving the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market.x
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market?
The high cost of treatment, especially for tolvaptan, and limited treatment options in the market and potential side effects, including liver damage, and the black box warning on tolvaptan, limiting its usage are the major factors hampering the growth of the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market.
Which is the leading Mutation Type in the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market?
PKD1 Mutation is the leading mutation type segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Market?
Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Reata Pharmaceuticals, Xortx Therapeutics (XRx-008), Sanofi, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Galapagos NV, Palladio Biosciences, Regulus Therapeutics, Primerose Therapeutics, Exelixis Inc, Grupo Olmos, Bayer Healthcare are the major players.