Bronchial Spasm Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Bronchial Spasm Market is segmented By Drug Type (Bronchodilators, Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Combination Therapies), By Route of Administration (Inhal....
Bronchial Spasm Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR6.1%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 6.1% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline plc, Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH, Novartis AG, Merck & Co., Inc. and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Bronchial Spasm Market Analysis
The bronchial spasm market is estimated to be valued at USD 14.1 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 21.7 Bn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% from 2024 to 2031. Driven by rising pollution levels and increasing cigarette smoking in emerging economies, the market is witnessing significant growth. Additionally, growing geriatric population susceptible to chronic respiratory diseases is anticipated to boost market revenue over the forecast period.
Bronchial Spasm Market Trends
Market Driver - Increase in Conditions Like Asthma and COPD is Leading to a Higher Incidence of Bronchial Spasms
According to recent studies, around 339 million people worldwide suffer from asthma, while over 329 million have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). These inflammatory lung diseases often lead to narrowing and blockage of the airways due to the bronchoconstriction of muscles. Bronchial spasms, also known as bronchospasms, are spontaneous contractions of the muscles in the walls of the bronchial tubes, which results in the obstruction of airflow.
The rising healthcare expenditures and improving access to diagnosis and treatment in developing Asian countries have also escalated the demand for bronchial spasm drugs. Furthermore, aging population profiles in North America and Europe imply a growing risk of respiratory illnesses. Older individuals suffering from recurrent or chronic respiratory diseases have a higher propensity of bronchial spasms. The presence of co-morbid conditions like heart diseases also aggravates bronchial spasms in elderly patients.
However, complete resolution of symptoms remains elusive for most patients due to the recurring nature of the underlying conditions. Therefore, long-term control medications for prevention and relief of bronchial spasms will continue to be prescribed. The widening patient pools of asthma and COPD and growing clinical emphasis on optimized bronchoconstriction management are fueling the demand for bronchial spasm pharmaceuticals globally.
Market Driver - Innovations in Inhalation Devices Improve Medication Efficacy and Patient Compliance
Inhalation has proven to be the most effective route of administration for bronchial spasm drugs due to its direct delivery of medications to the lungs. Technological advances in drug development along with novel propellant-free inhaler designs have augmented treatment successes in recent years.
Metered dose inhalers, dry powder inhalers and nebulizers utilizing innovative formulations are ensuring deeper lung penetration and higher drug concentrations for quick relief of bronchial spasms. Additionally, user-friendly features such as easy-breath activation and dose counter integration in new-age inhalers have greatly elevated patient comfort levels and compliance to pharmacotherapy regimens.
Recognizing the critical relationship between proper inhalation technique and therapeutic outcomes, device developers are focusing on fool-proof, intuitive functionalities. A number of smart inhalers are being launched which can record usage data and send reminders. Such connected devices aided by mobile health apps and respiratory monitoring sensors allow for remote monitoring and personalized advice from physicians.
Partnerships between device manufacturers and digital therapeutics companies are further strengthening medication adherence through remote therapeutic support on mobile platforms. Furthermore, single-dose dry powder inhalers dispensing month-long supplies are improving adherence to maintenance treatment schedules for long-term control.
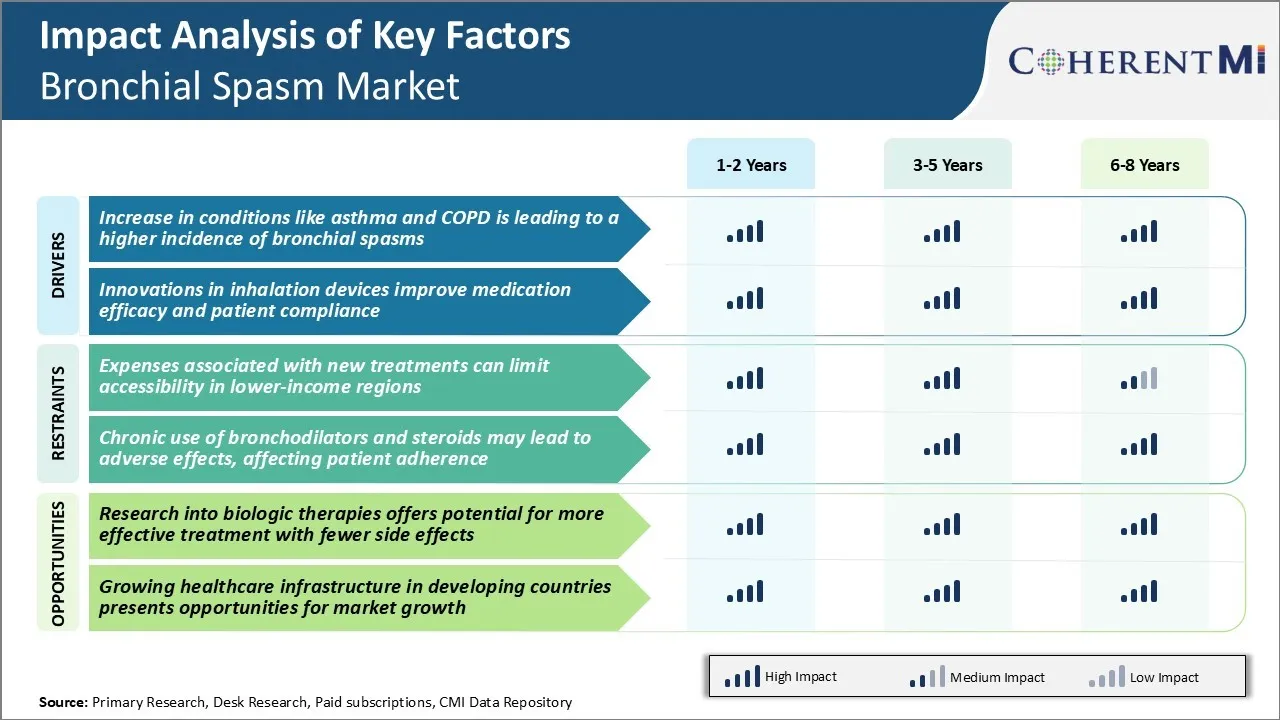
Market Challenge - Expenses Associated with New Treatments Can Limit Accessibility in Lower-Income Regions
One of the major challenges facing the bronchial spasm market is the expenses associated with new treatments, which can limit their accessibility in lower-income regions. Developing and bringing novel drug therapies to market requires massive investments in clinical research and regulatory approval processes.
As a result, the costs of these new drugs tend to be quite high once launched commercially. For populations in developing countries and underserved rural areas, these high drug prices can put life-changing treatments out of reach. Even in developed markets like the United States, the affordability of new specialty medications is a major public policy concern, as not all patients have comprehensive healthcare coverage or can afford high deductibles and co-insurance rates.
Unless generic alternatives emerge or governments take steps to subsidize costs, a sizable portion of patients worldwide may lack access to the latest medical innovations for bronchial spasms simply due to financial limitations. This disproportionately impacts those most in need, exacerbating global health inequities.
Market Opportunity - Potential of Biologic Therapies
One opportunity within the bronchial spasm market lies in ongoing research into biologic therapies. Scientists are working to develop more effective drugs that target the underlying inflammatory processes driving bronchial contractions, rather than just addressing symptom relief like many existing treatment options. Biologics derived from antibodies or cellular therapies offer the prospect of more precisely regulating the human immune system's misguided response in allergic asthma.
If successful, these new biologic treatments could provide corticosteroid-sparing options with fewer side effects compared to traditional bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids. Advances in biomanufacturing are also helping to drive down costs and facilitate greater accessibility of these highly customized medications over time. As the mechanistic understanding of bronchial spasms continues to evolve, research into biologics holds great potential to transform disease management and outcomes for affected patients worldwide.
Prescribers preferences of Bronchial Spasm Market
Bronchial spasm is generally treated through a step-wise escalation of therapies based on severity and persistence of symptoms. For mild intermittent symptoms, short-acting beta2 agonists (SABAs) like salbutamol (Ventolin) are prescribed as needed. These work within minutes to provide rapid relief from bronchospasm.
If symptoms occur more than twice a week or interfere with normal activity, controllers are added. Low-dose inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) like beclomethasone (Qvar) are preferred initially for their anti-inflammatory effects. As symptoms persist or severity increases, combinations of ICS and long-acting beta2 agonists (LABAs) such as fluticasone/salmeterol (Seretide) are prescribed for their synergistic dual action.
For patients with frequent exacerbations despite moderate ICS/LABA therapy, long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs) like tiotropium (Spiriva) are added to the regimen. LAMAs work via a different mechanism to provide 24-hour control.
Factors influencing prescriber preferences include severity/frequency of symptoms, adherence patterns, comorbidities, medication side effects, ease of use, availability of combinations and device type compatibility. Preferences also vary depending on guidelines, individual training and experiences with specific brands. Overall, a step-up approach is commonly adopted, seeking the optimal combination of safety, efficacy and convenience.
Treatment Option Analysis of Bronchial Spasm Market
Bronchial spasm can be treated differently depending on the severity and underlying cause. Treatment stages are as follows:
Mild Cases: Short-acting beta-2 agonists like salbutamol and terbutaline are usually prescribed. They work within 5-15 minutes to relax airway muscles. Ipratropium bromide metered dose inhalers may also be used alone or along with short-acting beta-2 agonists.
Moderate Cases: For more frequent or persistent symptoms, inhaled corticosteroids like fluticasone or budesonide are preferred. They reduce airway inflammation and prevent future bronchospasms when taken regularly over weeks. Long-acting beta-2 agonists such as salmeterol and formoterol are also prescribed for continual smooth muscle relaxation.
Severe Cases: In acute severe exacerbations requiring immediate relief, nebulized short-acting beta-2 agonists like salbutamol are given. For persistent symptoms despite above treatments, leukotriene receptor antagonists like montelukast tablets augment airway relaxation and reduce inflammation. Theophylline sustained-release tablets are another addition for their steroid-saving effects.
Refractory Cases: For life-threatening cases unresponsive to above, intravenous or subcutaneous administration of short-acting beta-2 agonists, anticholinergics, corticosteroids and magnesium sulfate provides urgent bronchodilation in critical care settings.
This multi-staged approach allows for effective control of bronchospasms through selective targeting of airway smooth muscles and inflammatory pathways.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Bronchial Spasm Market
Focus on developing innovative products to gain competitive advantage:
Developing innovative drugs and therapies has been a major winning strategy for top players in the bronchial spasm market. For example, in 2020, Teva Pharmaceutical introduced a generic version of nebulized levalbuterol HCl solution, which is used for treating bronchospasm associated with reversible obstructive airway disease. This allowed Teva to gain a significant share of the market.
Another example is Sunovion Pharmaceuticals who in 2018 launched a novel drug Xopenex HFA (levalbuterol tartrate) inhalation aerosol for the treatment of bronchospasm associated with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Focus on emerging markets for growth:
Players have focused on emerging markets like Asia Pacific and Latin America which are expected to offer higher growth opportunities over the coming years. For instance, Cipla launched reusable bronchodilator metered dose inhalers in India and other Asian countries in 2021 at competitive price points.
Partnerships and collaborations:
Establishing strategic partnerships has aided players in leveraging complementary strengths and expanding geographic reach. For example, Mylan partnered with Ferrer Therapeutics in 2017 for distribution and promotion of nebulized ipratropium bromide inhalation solution in Poland, Bulgaria, Romania and other European markets. This helped both companies increase sales and market penetration.
Segmental Analysis of Bronchial Spasm Market
Insights, By Drug Type: Growth of Bronchial Diseases Propels Bronchodilators Segment
In terms of drug type, bronchodilators contribute the highest share of the market owning to the increased prevalence of chronic respiratory diseases such as asthma and COPD across the globe. Bronchodilators work by relaxing and widening the airways of the lungs to provide immediate relief in bronchoconstriction. The rising geriatric population who are more susceptible to bronchial ailments further augments the demand for bronchodilators drugs.
Additionally, the development of novel bronchodilator formulations with improved efficacy and lesser side effects compared to existing drugs drives their preference among patients and physicians. Some of the key bronchodilator drugs include albuterol, ipratropium bromide, tiotropium, and others witnessing increased sales year-on-year.

Insights, By Route of Administration: Ease of Use Increases Preference for Inhalation Drugs
In terms of route of administration, inhalation contributes the highest share of the market owing to the non-invasive nature and immediate action provided via the pulmonary route. Inhalation drugs ensure direct delivery of the medication to the primary site of action in the lungs, allowing for better therapeutic response with a lower dose. This minimizes systemic side effects compared to oral and injectable formulations.
Among inhalation devices, metered-dose inhalers (MDIs) are highly popular due to their portability and ease of use. However, dry powder inhalers (DPIs) are gaining traction in the market as they require less coordination and are better suited for all age groups. Technological advancements in propellant-free inhalers will further support the growth of the inhalation drug segment in the bronchial spasm market.
Insights, By End User: Increased Healthcare Expenditure Favors Hospital Segment
In terms of end user, hospitals contribute the highest share of the market. This can be attributed to the increased healthcare spending by both governmental and private players to enhance hospital infrastructure and respiratory services. Most medical insurances and reimbursement schemes have provisions to cover hospital-based bronchial treatments. In severe bronchial attacks, patients prefer visiting hospitals equipped with emergency and critical care facilities.
Moreover, the presence of pulmonologists and respiratory therapists with latest diagnostic equipment aids in faster treatment and management of complex respiratory cases in hospitals. Although cost-effective, clinics and homecare settings have limited capabilities to treat critical conditions, which drives majority of patients towards hospitals.
Additional Insights of Bronchial Spasm Market
- Global Impact: Approximately 339 million people worldwide are affected by asthma, a major contributor to bronchial spasms.
- Healthcare Burden: Bronchial spasms account for a significant number of emergency room visits, emphasizing the need for effective long-term management strategies.
- Economic Cost: The global economic burden of asthma and related bronchial spasms is estimated to be over $50 billion annually due to healthcare costs and lost productivity.
Competitive overview of Bronchial Spasm Market
The major players operating in the Bronchial Spasm Market include GlaxoSmithKline plc, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH, Novartis AG, Merck & Co., Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Sanofi S.A., and Pfizer Inc.
Bronchial Spasm Market Leaders
- AstraZeneca
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH
- Novartis AG
- Merck & Co., Inc.
Bronchial Spasm Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Bronchial Spasm Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Bronchial Spasm Market
- In August 2023, GlaxoSmithKline plc launched a new triple combination inhaler that simplifies treatment regimens for patients with severe bronchial spasms, potentially improving adherence and outcomes. GSK has previously launched the Trelegy Ellipta, a triple combination inhaler for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, which combines an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS), a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist (LABA). This inhaler, approved in 2017 for COPD and expanded in 2020 to asthma, is designed to improve patient adherence by simplifying treatment regimens to a once-daily inhalation.
- In January 2024, AstraZeneca acquired a biotech firm specializing in biologics for respiratory diseases, aiming to enhance its pipeline with innovative treatments targeting bronchial spasms at a molecular level.
Bronchial Spasm Market Segmentation
- By Drug Type
- Bronchodilators
- Short-Acting Beta Agonists (SABAs)
- Long-Acting Beta Agonists (LABAs)
- Anticholinergics
- Anti-Inflammatory Agents
- Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS)
- Systemic Corticosteroids
- Leukotriene Modifiers
- Combination Therapies
- LABA/ICS Combinations
- LABA/LAMA Combinations
- Bronchodilators
- By Route of Administration
- Inhalation
- Metered-Dose Inhalers (MDIs)
- Dry Powder Inhalers (DPIs)
- Nebulizers
- Oral
- Injectable
- Inhalation
- By End User
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Homecare Settings
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the bronchial spasm market?
The bronchial spasm market is estimated to be valued at USD 14.1 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 21.7 Bn by 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the bronchial spasm market?
The expenses associated with new treatments in lower-income regions and chronic use of bronchodilators and steroids that can lead to adverse effects are the major factors hampering the growth of the bronchial spasm market.
What are the major factors driving the bronchial spasm market growth?
The increase in conditions like asthma and COPD is leading to a higher incidence of bronchial spasms. In addition, innovations in inhalation devices are also improving medication efficacy and patient compliance. These are the major factors driving the bronchial spasm market.
Which is the leading drug type in the bronchial spasm market?
The leading drug type segment is bronchodilators.
Which are the major players operating in the bronchial spasm market?
GlaxoSmithKline plc, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH, Novartis AG, Merck & Co., Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Sanofi S.A., and Pfizer Inc. are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the bronchial spasm market?
The CAGR of the bronchial spasm market is projected to be 6.1% from 2024-2031.