Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market is segmented By Therapy (Budesonide/Formoterol, Montelukast, N-acetylcysteine), By Drug Class (Macrolide Anti....
Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market Size
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR4.1%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 4.1% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Zambon Pharma, Incyte Corporation, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Altavant Sciences and Among Others |
please let us know !
Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market Analysis
The bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market is estimated to be valued at USD 60.37 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 79.93 Mn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% from 2024 to 2031. The prevalence of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) is increasing which is driving the demand for effective therapeutics. With no approved drug therapy currently available for BOS, the pipeline drugs in late-stage clinical trials holds significant potential to capture market share if approved.
Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Cases of BOS due to Lung Transplants and Graft-vs-Host Diseases
BOS involves scar tissue formation, known as fibrotic tissue growth, which narrows down the airways over the time and restricts the airflow due to rejection of transplanted lungs by body's immune system. Graft-vs-host diseases (GVHD) post hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is a major cause that increases the occurrence of BOS.
The number of patients undergoing lung transplant procedures continues to increase annually globally because lung failure has become a leading cause of mortality. While transplantation is a life-saving option for patients with end-stage lung diseases like cystic fibrosis, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension etc., the lifelong immune-suppressing therapy administered post-surgery has its share of risks.
According to latest data, BOS develops in nearly 30-50% of lung transplant recipients within 5 years of transplantation procedure majorly due to chronic rejection of transplanted organ. Persistent inflammation and scarring progressively destroys the small airways over time limiting air movement in and out of lungs. GVHD patients who receive stem cells from a living or deceased donor are also vulnerable to develop BOS as a long-term complication. The inflammatory destruction triggered by grafted immune cells against host tissues and organs may involve the air passages of lungs too.
Market Driver - Rising Awareness and Diagnostics for BOS, Leading to Early Treatment
Earlier, diagnosis was challenging as symptoms mimic other respiratory illnesses in the initial stages. However, improved lung function tests, high resolution CT scans and biopsy methods have enabled pathologists and doctors to detect early signs of obstruction and scarring in small airways caused by post-transplant complications.
At the same time, patient advocacy groups and support communities online are educating people about risk factors like chronic lung infections, non-adherence to medications, history of acute cellular rejection, obliterative bronchiolitis seen on transbronchial biopsy specimens.
Early diagnosis allows physicians to start treatment interventions in a timely manner before the damage to lungs becomes permanent and irreversible. Common therapeutic strategies followed include adjustment of immunosuppressive drugs, use of newer inhalers delivering steroid medications directly to small airways, photopheresis therapy, lung volume reduction surgeries. Research studies are ongoing to evaluate efficacy of drugs like Macitentan, Imatinib targeting fibrosis related pathways.
Overall, better awareness about recognizing symptoms and signs, enhanced diagnostic evaluations and availability of diversified management plan when BOS is diagnosed at initial stages are likely to improve treatment outcomes for those suffering from this lung condition. This also presents scope for avoided long term complications.
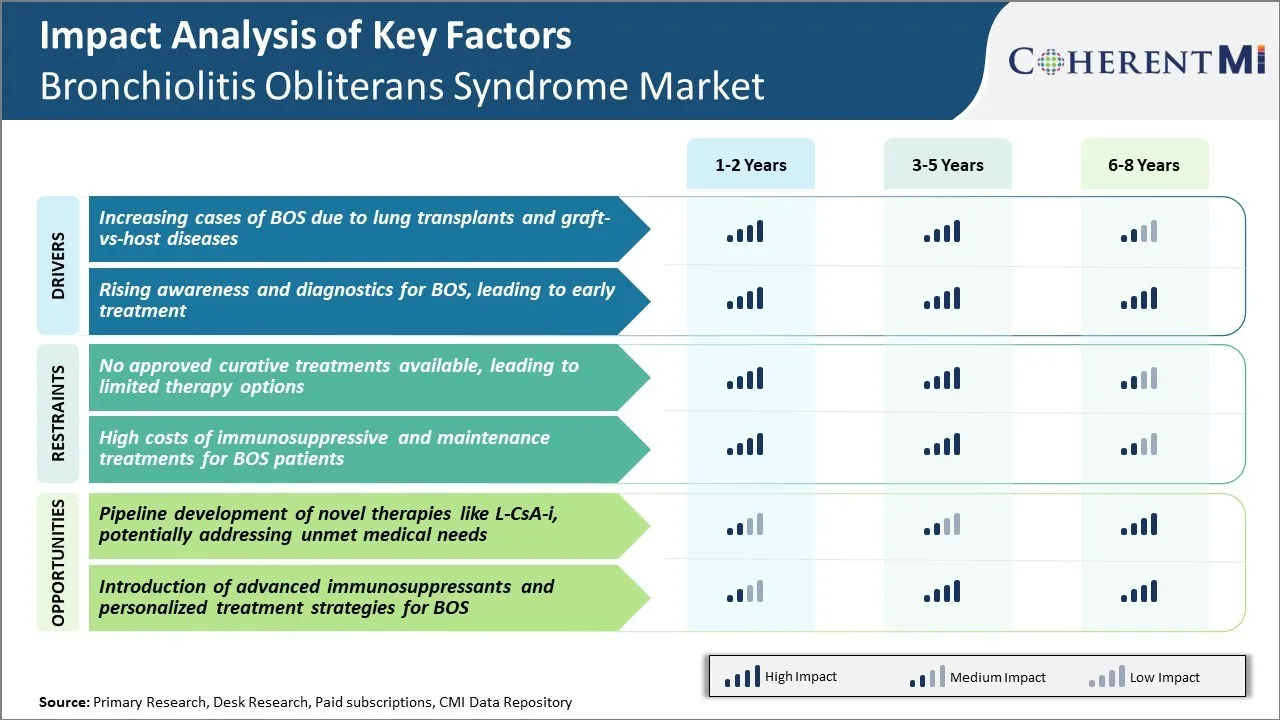
Market Challenge - No Approved Curative Treatments Available, Leading to Limited Therapy Options
There are currently no approved curative treatments available for BOS. Existing treatment options are limited and focus mainly on managing symptoms to slow disease progression. Lung transplantation is the only treatment that can potentially restore lung function, but it has a limited success rate and risks of post-transplant complications and graft rejection remain high.
The lack of effective pharmacological therapies that can directly target the underlying pathophysiology of BOS poses a major challenge for patients. It also means physicians have restricted options to choose from when treating patients at different stages of the disease. The unavailability of curative treatments is a key concern holding back the growth of the overall BOS market.
Market Opportunity - Potential of Novel Therapies
The pipeline development of novel therapies for BOS presents significant opportunities to address major unmet medical needs in the market. One promising candidate is inhaled cyclosporine A (L-CsA-i), which is being evaluated for its ability to potentially slow the progression of BOS by suppressing the immunological mechanisms involved.
Results from initial clinical studies have been encouraging, showing improvements in lung function parameters in patients receiving L-CsA-i compared to placebo. Its targeted pulmonary drug delivery approach may help achieve higher localized concentrations while reducing systemic exposure and side effects compared to oral immunosuppressants.
Success in late-stage trials could mean L-CsA-i becomes the first approved non-transplant therapy for BOS. This has the potential to transform treatment paradigms by providing physicians an effective option to manage the disease long-term. It also stands to vastly improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
This highlights the meaningful opportunities novel pipeline therapies present to significantly grow the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market in the upcoming years by addressing critical unmet medical needs.
Prescribers preferences of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market
BOS is a rare lung condition characterized by the narrowing of small airways in the lungs. Prescribers generally follow a step-wise approach based on the stage of the disease.
In mild cases categorized as stage 1 BOS, inhaled corticosteroids such as Pulmicort (budesonide) are usually prescribed to help reduce inflammation in the airways. Additionally, short-acting beta agonists like albuterol (Ventolin) provide temporary symptom relief via bronchodilation.
As the disease progresses to stage 2 BOS, oxygen therapy may be needed especially during exertion. Prescribers often add long-acting beta agonists such as Spiriva (tiotropium bromide) or Stiolto Respimat (tiotropium + olodaterol) to the treatment regimen for their 24-hour bronchodilation effect. Macrolide antibiotics like azithromycin (Zithromax) and roxithromycin (Rulide) are also prescribed for their immunomodulating properties.
In advanced stage 3 BOS, lung transplantation may be considered, as medications often provide limited relief at this stage. However, immunosuppressants like cyclosporine (Neoral) or tacrolimus (Prograf) are prescribed post-transplant as anti-rejection drugs. Mucolytic agents like acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) are also tried to reduce viscosity of respiratory secretions.
I hope this detailed report provides valuable insights into prescribers' approach towards treating different stages of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome. Please let me know if any part needs clarification or expansion.
Treatment Option Analysis of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market
BOS has three stages based on the severity of symptoms and degree of lung function decline. For stage 1 or mild BOS, physicians typically prescribe bronchodilators to help open airways and reduce coughing. These include inhaled beta-agonists like albuterol and inhaled corticosteroids like fluticasone. If symptoms persist, azithromycin may be added for its anti-inflammatory effects.
Stage 2 or moderate BOS sees a greater loss of lung function. In addition to bronchodilators and steroids, physicians may prescribe immunosuppressive drugs to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression. Common choices include macrolide antibiotics like azithromycin or cyclosporine. For patients who do not respond sufficiently, an antimetabolite called azathioprine may be used.
The most advanced stage 3 BOS has severe lung dysfunction that is rapidly progressive. At this stage, lung transplantation is often the only life-saving option as medical treatment has limited effectiveness. However, for patients who are not transplant candidates, augmented immunosuppression with both cyclosporine and prednisone provides the best option to preserve remaining lung function and minimize symptoms for as long as possible. Close monitoring of therapy response is essential in stage 3 to determine need for escalation of immunosuppression or pursuance of lung transplantation.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market
Product Innovation:
In 2021, United Therapeutics Corp gained FDA approval for Tyvaso therapy for the treatment of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) in patients who are not receiving recommended therapy. This was a major breakthrough as Tyvaso was the first-ever FDA approved treatment specifically for BOS. This gave United Therapeutics a significant competitive edge in the market.
Partnerships and Collaborations:
In 2020, Boehringer Ingelheim entered into a collaboration with FibroGen to develop novel treatment options for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and other forms of lung disease like BOS. Through this collaboration, the companies hope to identify new molecular targets and develop therapies to slow or halt the progression of lung diseases. Such partnerships allow companies to share resources and expertise to expedite drug development.
Geographic Expansion:
In 2016, Savara expanded its geographic footprint by establishing operations in Europe. The company began enrolling patients in its Phase 2 BOS clinical trial in Europe in addition to North America. This helped Savara reach more patients and investigators to accelerate trial enrollment. By 2022, Savara had over 60 active trial sites across 10 countries to support its BOS program. Geographic expansion is crucial for rare disease companies to build a global presence.
Segmental Analysis of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market
Insights, By Therapy: >Budesonide/Formoterol Maintain a Strong Efficacy Profile in Market
Budesonide/Formoterol combination therapy has emerged as the preferred treatment option for BOS owing to its potent anti-inflammatory and bronchodilation effects. As a glucocorticoid, budesonide works directly on the pulmonary inflammation that drives BOS progression. It achieves this through suppressing both innate and adaptive immune responses that cause fibrosis and obstruction in small airways. At the same time, formoterol provides crucial bronchodilation to open up constricted lungs and make breathing easier.
This dual mode of action makes budesonide/formoterol highly effective at alleviating BOS symptoms and slowing lung function decline. Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated its superiority over other therapies in parameters like forced expiratory volume and quality of life indices. The strong efficacy data has helped establish it as the first-line standard of care recommended in most treatment guidelines. Its ability to simultaneously reduce inflammation and dilate airways provides smoother, longer lasting relief to patients compared to monotherapies.
Overall, budesonide/formoterol has gained the largest market share in the BOS therapy segment owing to its clear efficacy benefits demonstrated via clinical evidence. Strong recommendation in guidelines, convenient dosing and high patient compliance have cemented its leadership position for this severe respiratory disease.

Insights, By Drug Class: Macrolide Antibiotics has Highest Market Share owning to its Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Properties
Within the drug class segment of the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market, macrolide antibiotics have emerged as a mainstay of treatment due to their unique non-antimicrobial characteristics. While bacterial infection is not the primary driver of BOS, macrolides like azithromycin and clarithromycin exert immuno-modulating effects that aid in controlling the immune mediated cascades damaging the lungs.
Specifically, macrolides inhibit neutrophil recruitment and activation, reducing their detrimental roles in generating oxidative stress and protease activity that destroys lung tissue over time. They also suppress production of various pro-inflammatory cytokines produced by macrophages and lymphocytes, tamping down the inflammatory response at its root. This dual mechanism of decreasing neutrophil-mediated injury and dampening cytokine storms proven to be central to BOS pathogenesis.
Additionally, macrolides stimulate phagocytosis and clearance of cellular debris by macrophages, helping remove dead and dying cells from inflamed airways. They even induce apoptosis of certain inflammatory cell types to actively regulate immune cell numbers at sites of disease.
The favorable risk-benefit profile and prolonged use enabled by lack of antibiotic resistance also give macrolides an edge over other immunosuppressive drugs in this chronic setting. Overall, macrolide's multi-targeted approach to modulating disregulated immunity positions it as the treatment of choice within the drug class segment for BOS.
Additional Insights of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market
- The total diagnosed prevalent cases of BOS in the U.S. were 17,000 in 2022, projected to increase by 2032
- The European Union's largest market, Germany, had approximately 3,900 diagnosed cases in 2022.
Competitive overview of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market
The major players operating in the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market include Zambon Pharma, Incyte Corporation, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, and Altavant Sciences.
Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market Leaders
- Zambon Pharma
- Incyte Corporation
- Genentech
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Altavant Sciences
Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market - Competitive Rivalry

Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market
- In September 2023, Zambon Pharma's Liposomal Cyclosporine A for Inhalation (L-CsA-i) has indeed received Fast Track designation from the U.S. FDA for the treatment of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome (BOS). This novel liposomal formulation aims to address the unmet need for BOS patients, particularly those who develop the condition post-lung or stem cell transplant.
- In July 2023, Genentech has indeed initiated clinical research focused on immunosuppressive therapy combinations to address bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) in patients following lung transplants. Immunosuppressive strategies, including novel therapies like aerosolized cyclosporine and adjustments in standard immunosuppressants such as tacrolimus, have shown promise in preventing or managing the progression of BOS in some studies.
Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Market Segmentation
- By Therapy
- Budesonide/Formoterol
- Montelukast
- N-acetylcysteine
- By Drug Class
- Macrolide Antibiotics
- Corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressive Drugs

Would you like to explore the option of buyingindividual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market?
The bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market is estimated to be valued at USD 60.37 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 79.93 Mn by 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market?
The no approved curative treatments available, leading to limited therapy options and high costs of immunosuppressive and maintenance treatments for BOS patients are the major factors hampering the growth of the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market.
What are the major factors driving the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market growth?
The increasing cases of BOS due to lung transplants and graft-vs-host diseases and rising awareness and diagnostics for BOS, leading to early treatment are the major factors driving the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market.
Which is the leading therapy in the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market?
The leading therapy segment is budesonide/formoterol.
Which are the major players operating in the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market?
Zambon Pharma, Incyte Corporation, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, and Altavant Sciences are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market?
The CAGR of the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome market is projected to be 4.1% from 2024-2031.