Diverticulitis Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Diverticulitis Market is segemented By Treatment (Medical Therapy, Surgical Procedures), By Diagnosis Method (Imaging Tests, Laboratory Tests), By End....
Diverticulitis Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR7.2%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 7.2% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, AstraZeneca PLC, Allergan (now part of AbbVie), Bayer AG, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer Inc. and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Diverticulitis Market Analysis
The diverticulitis market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.68 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 4.36 Bn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2024 to 2031. The aging population is more prone to develop diverticulitis, as it often occurs in older age groups. This increases the risk of complications associated with the disease.
Diverticulitis Market Trends
Market Driver - Rising Incidence of Diverticulitis Due to Aging Populations Boosts Market Growth
As population ages globally, the prevalence of diverticulitis is set to rise significantly in the coming years. Diverticulitis commonly occurs in aging population where diverticula tend to form in the weakened colon walls due to aging. People above 60 years of age have higher chances of developing diverticulitis compared to younger population. With worldwide average life expectancy increasing over time and percentage of elderly population growing rapidly, it is highly likely that cases of diverticulitis will surge exponentially.
In developed nations especially where life expectancy is highest, population over 65 years constitute over 15% of total population currently. This elderly segment is projected to grow over 35% in many European countries and North America by 2050. Higher life expectancy combined with poor lifestyle including lack of exercise and high processed food consumption makes aging population more susceptible to diverticulosis and diverticulitis. With nearly half of people over 60 years showing signs of diverticulosis, even a slight increase in elderly demographic can translate into massive patient pool for diverticulitis treatments.
Market Driver - Development of Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Enhances Patient Outcomes
Ever since laparoscopic colectomy was introduced for diverticulitis treatment in 1990s, it has gained widespread acceptance due to significant advantages over open surgeries. Minimally invasive procedures cause little damage to muscles and tissues compared to open surgery requiring large incisions. This results in less postoperative pain, quick recovery times, lesser hospital stay and lower risks of surgical site infections. Patients also benefit from smaller scars and improved cosmetic outcomes.
Newer advanced techniques like single port laparoscopy and robotic surgeries allow performing diverticulitis surgeries through just one tiny incision. This further reduces pain and improves cosmetic results. Such minimally invasive methods necessitate use of specialized surgical instruments, trocars and energy devices. Robotic systems offer additional benefits like increased precision, flexible instruments and 3D visualization helping surgeons perform even complex procedures with ease.
Constant innovation is underway to develop newer surgical robots with autonomous capabilities and augmented reality features. Surgical staplers, tissue graspers and energy devices are also becoming more compact and advanced and even start incorporating artificial intelligence. As minimally invasive surgeries for diverticulitis demonstrate continuously better clinical outcomes, adoption rates are accelerating. This rapidly evolving landscape provides ongoing momentum to diverticulitis treatment market.
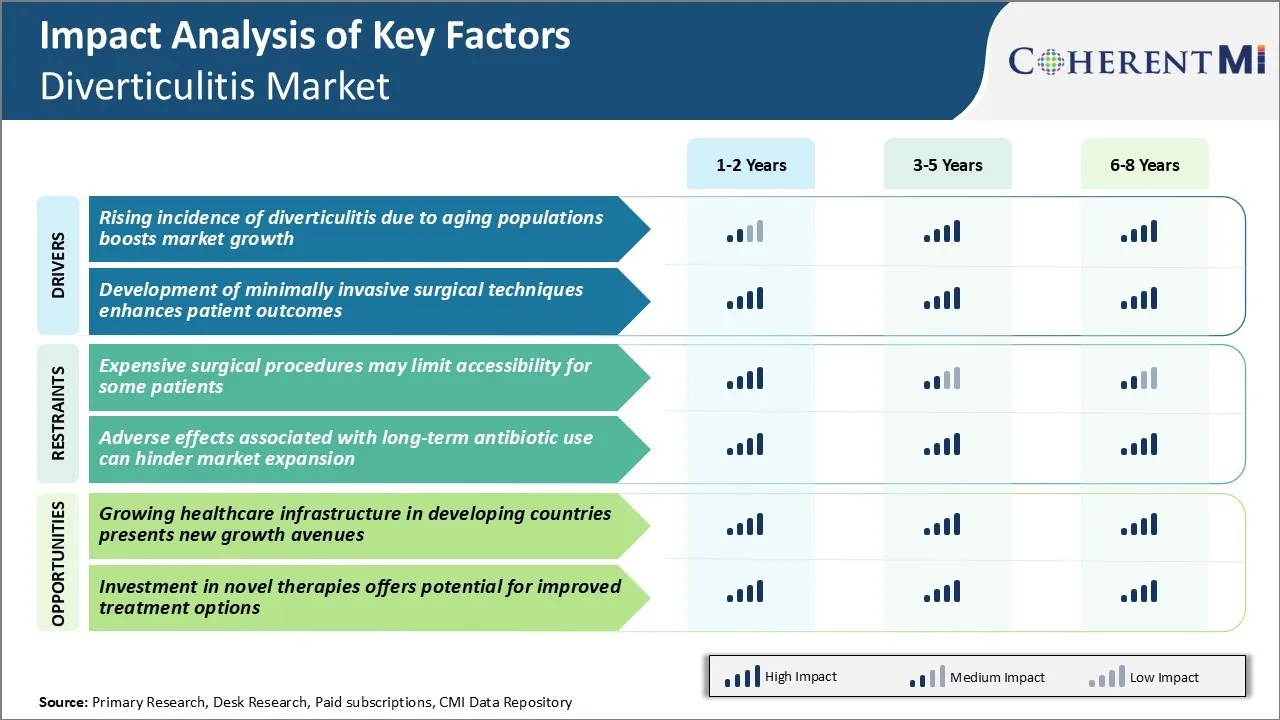
Market Challenge - Expensive Surgical Procedures May Limit Accessibility for Some Patients
Diverticulitis is a fairly common condition that often requires surgical intervention for treatment. While there have been advancements in minimally invasive techniques, many procedures still carry a high price tag. This represents a challenge as not all patients, especially those in developing nations or without adequate health insurance, may be able to afford the costs associated.
Hospital stays following surgery can be long and further drive up the bills. For those with acute diverticulitis, an emergency colectomy could easily run in the tens of thousands of dollars in the United States. The expense does not even factor in lost wages from time away from work for recovery.
As a result, some individuals may delay or avoid necessary interventions. This poses health risks and also impacts the potential patient pool for pharmaceutical manufacturers targeting this market. High procedure prices could impede broader market growth potential.
Market Opportunity - Growing Healthcare Infrastructure in Developing Countries Presents New Growth Avenues for Market
An opportunity for the diverticulitis market lies in the expanding healthcare infrastructure of developing nations. Countries in Asia, Latin America, Africa and elsewhere are investing heavily in modernizing facilities and improving access to care. As standards of living increase across emerging economies, rates of diseases like diverticulitis that have traditionally impacted wealthier areas are also rising.
A growing middle class has more disposable income available for healthcare spending. At the same time, biopharmaceutical companies and medical device manufacturers are paying greater attention to these regions as venues for sales and clinical trials.
A larger network of hospitals and clinics means more points of diagnosis and treatment of diverticulitis cases. It also presents the possibility of raising awareness of available options to manage this condition. This widening coverage in developing markets could open up major new channels for growth over the coming years.
Prescribers preferences of Diverticulitis Market
Diverticulitis is typically treated based on its stage and severity. For uncomplicated acute diverticulitis, prescribers commonly recommend oral antibiotics such as amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin) to treat the infection. If symptoms do not improve within a few days, or are severe, patients may be switched to intravenous antibiotics like piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn).
For patients with recurrent uncomplicated diverticulitis or those who do not respond to medical treatment, elective surgery such as colon resection is considered. Prescribers often prefer a laparoscopic approach (keyhole surgery) over open procedures to reduce recovery time. Post-surgery, antibiotics including metronidazole (Flagyl) or ciprofloxacin (Cipro) can help prevent infection.
For complicated diverticulitis with abscesses or bowel perforations, broad-spectrum IV antibiotics along with computed tomography (CT) scans are immediately used. Depending on CT findings, surgeons may drain or remove abscesses percutaneously using image-guidance. For non-resolving complications or those with bowel obstructions, sigmoidectomy (removal of the sigmoid colon) is commonly performed.
Other factors influencing prescriber decisions include age, co-morbidities, and severity/recurrence risk. Younger patients are offered more conservative options first.
Treatment Option Analysis of Diverticulitis Market
Diverticulitis has three main stages - mild, moderate, and severe. The treatment approach varies depending on the stage.
For mild diverticulitis, the preferred first-line treatment is antibiotics combined with a soft low-fiber diet. Commonly prescribed oral antibiotics include amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin), ciprofloxacin (Cipro), and metronidazole (Flagyl). Antibiotics help fight the infection and resolve inflammation.
In cases of moderate diverticulitis with abscess formation, antibiotics alone may not be sufficient. The standard treatment involves antibiotic therapy along with minimally invasive surgery such as CT-guided drainage of abscesses. Larger abscesses (>4cm) often require surgical drainage either laparoscopically or through small incisions.
For severe acute diverticulitis with perforation or obstruction, intravenous antibiotics and emergency surgery are required. The surgery typically involves resection of the infected bowel segment (sigmoidectomy) followed by reanastomosis or colostomy depending on the condition of the remaining colon.
Selecting the appropriate treatment depends on accurate staging. While antibiotics remain the first-line intervention for mild cases, drainage or resection becomes necessary for moderate to severe episodes to prevent complications like fistula or stricture formation. A multi-disciplinary approach combining antibiotics, radiology-guided procedures, and surgery achieves optimal outcomes.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Diverticulitis Market
Focus on innovative drug development
One of the major strategies adopted by pharmaceutical companies has been investing heavily in R&D to develop novel drugs for treating diverticulitis. For example, in 2019, Abbott Laboratories received FDA approval for their drug Entivyo (vedolizumab) for the treatment of mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis in pediatric patients.
Acquisitions and partnerships for pipeline expansion
Companies have strengthened their diverticulitis product portfolios through strategic acquisitions and partnerships. In 2020, Pfizer acquired Arena Pharmaceuticals to gain access to Arena's pipeline of gastroenterology assets including etrasimod.
Focus on emerging markets
Given the rising disease prevalence in developing nations, players are focusing on markets like Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa through tailored regulatory and commercial strategies. For instance, between 2015-19, Takeda Pharmaceuticals invested over $150 million in clinical trials and business development across Asia to prepare for launch of their IBD drug portfolio.
Adoption of new technologies
New diagnostic technologies are enabling early and accurate diagnosis of diverticulitis. Companies are partnering with diagnostic product innovators. For example, in 2021, Anthropic partnered with Robust AI to develop an AI-powered tool for analyzing CT scans to detect signs of diverticulitis.
Segmental Analysis of Diverticulitis Market
Insights, By Treatment: Rising Healthcare Expenditure Drives Medical Therapy as the Leading Treatment
In terms of treatment, medical therapy is estimated to hold 68.4% of market share in 2024, owing to increasing healthcare expenditure and better access to treatment options. Medical therapy is usually the first line of treatment for diverticulitis as it is non-invasive and has minimal risks. It involves antibiotics to treat infection, pain relievers to manage symptoms, and fiber supplements to regulate bowel movements.
As people are able to spend more on their health due to economic growth, they are opting for medical therapy to avoid risks of surgery. Additionally, advanced antibiotics and painkillers have improved treatment outcomes of medical therapy. Various government initiatives have also expanded health insurance coverage, making treatment affordable. All these factors have collectively increased uptake of medical therapy and grown its share of the diverticulitis treatment market over time.
Insights, By Diagnosis Method: Advancing Diagnostic Technologies Boosts Imaging Tests as the Leading Diagnosis Method
In terms of diagnosis method, imaging tests are estimated to account for 57.8% of market share in 2024, due to advances in diagnostic imaging technologies. CT scans and ultrasound have become highly effective in detecting diverticulitis by visualizing structures of the digestive system. CT scans provide detailed images of the abdomen allowing accurate diagnosis. Advancing CT scan technologies have automated processes, improved image quality, reduced radiation dosage and scan time.
Similarly, ultrasound equipment features higher resolution and portability. As a result, imaging specialists are readily able to diagnose diverticulitis at an early stage. This has popularized use of imaging tests among patients and clinicians to quickly diagnose the condition without needing invasive procedures or complex lab tests. Continuous innovations are further enhancing imaging diagnostics, consolidating its prominent position in the diverticulitis diagnosis market.

Insights, By End User: Infrastructure Expansion Drives Hospitals as the Prime End User
In terms of end user, hospitals contribute the highest share of the diverticulitis market owing to infrastructure expansion worldwide. Hospitals often own the most advanced diagnostic facilities and have specialized clinical experts to handle diverticulitis cases. Many governments focus on developing healthcare infrastructure to boost access to treatment. This has facilitated building and upgradation of hospitals especially in emerging nations.
An increasing number of beds, diagnostic centers and operating rooms in hospitals can effectively manage diverticulitis patients. Hospitals also provide round-the-clock emergency services for complicated cases. As patients increasingly rely on hospitals for quick and comprehensive care, their demand for diverticulitis services has grown the most within hospitals.
Moreover, favorable reimbursement policies have further encouraged patients to seek treatment from hospitals, making them the prime end user.
Additional Insights of Diverticulitis Market
- Studies indicate that about 25% of patients with diverticulosis may develop diverticulitis at some point in their lives.
- The adoption of high-fiber diets has been recommended as a preventive measure, influencing market trends toward dietary management products.
Competitive overview of Diverticulitis Market
The major players operating in the diverticulitis market include Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, AstraZeneca PLC, Allergan (now part of AbbVie), Bayer AG, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, GlaxoSmithKline PLC, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck & Co., Inc., AbbVie Inc., and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Diverticulitis Market Leaders
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- AstraZeneca PLC
- Allergan (now part of AbbVie)
- Bayer AG
- Johnson & Johnson
- Pfizer Inc.
Diverticulitis Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Diverticulitis Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Diverticulitis Market
- In July 2023, Takeda initiated a Phase III clinical trial for a novel oral therapy aimed at reducing inflammation in diverticulitis patients, potentially reducing the need for antibiotics and surgical interventions. Through the trial, the company primarily focuses on other therapeutic areas, such as chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) and colorectal cancer, without specific mention of diverticulitis or an associated Phase III trial for this indication.
- In April 2023, Pfizer announced the acquisition of a novel imaging technology company to enhance diagnostic accuracy in diverticulitis, aiming to reduce the rate of misdiagnosis and improve treatment outcomes.
- In April 2023, AbbVie Inc. launched a Phase III clinical trial for a new anti-inflammatory drug targeting diverticulitis, aiming to reduce recurrence rates. AbbVie has conducted Phase III trials of its drug RINVOQ (upadacitinib) for various conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
Diverticulitis Market Segmentation
- By Treatment
- Medical Therapy
- Antibiotics
- Pain Relievers
- Fiber Supplements
- Surgical Procedures
- Primary Bowel Resection
- Bowel Resection with Colostomy
- Medical Therapy
- By Diagnosis Method
- Imaging Tests
- CT Scans
- Ultrasound
- Laboratory Tests
- Blood Tests
- Stool Tests
- Imaging Tests
- By End User
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Specialty Clinics

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the diverticulitis market?
The diverticulitis market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.68 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 4.36 Bn by 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the diverticulitis market?
The expensive surgical procedures may limit accessibility for some patients. Also, adverse effects associated with long-term antibiotic use can hinder market expansion. These are the major factors hampering the growth of the diverticulitis market.
What are the major factors driving the diverticulitis market growth?
The rising incidence of diverticulitis due to aging populations boosts market growth. In addition, development of minimally invasive surgical techniques enhances patient outcomes. These are the major factors driving the diverticulitis market.
Which is the leading treatment in the diverticulitis market?
The leading treatment segment is medical therapy.
Which are the major players operating in the diverticulitis market?
Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, AstraZeneca PLC, Allergan (now part of AbbVie), Bayer AG, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, GlaxoSmithKline PLC, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck & Co., Inc., AbbVie Inc., and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the diverticulitis market?
The CAGR of the diverticulitis market is projected to be 7.2% from 2024-2031.