Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market is segmented By Line of Treatment (Localized, Metastatic), By Drug Class (Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Dactinomycin, ....
Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market Size
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR6.12%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 6.12% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Salarius Pharmaceuticals, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, BioAlta and Among Others |
please let us know !
Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market Analysis
The Global Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market is estimated to be valued at USD 250.1 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 430.3 Mn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.12% from 2024 to 2031. New drug development and increased research funding is driving growth in this market. Better treatment options have improved survival rates of patients as well.
The market is witnessing positive trends. There is an increased focus on developing new targeted therapies and immunotherapies to treat Ewing sarcoma. Promising drug candidates in clinical trials can potentially enter the market in the coming years. Additionally, greater awareness levels about this rare cancer among people have led to early diagnosis and treatment seeking. This is expected to boost demand for improved Ewing sarcoma treatment options.
Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market Trends
Market Driver - Advancements in Treatment Methods, Such as the Adoption of VDC/IE Regimen (Vincristine, Doxorubicin, Cyclophosphamide/Ifosfamide, And Etoposide) For Localized Ewing Sarcoma.
The management of Ewing sarcoma has evolved over the years with the adoption of multimodal treatment regimens that combine chemotherapy with surgery and/or radiation therapy. Traditionally, first-line therapy comprised of vincristine, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and occasionally ifosfamide and etoposide (VDC/IE). While offering reasonable survival benefits, this conventional chemotherapy was often associated with significant treatment-related toxicities.
In recent times, the VDC/IE regimen has gained renewed interest owing to modestly improved progression-free and overall survival demonstrated by European and American clinical studies. Particularly, a European study reported a 5-year event-free and overall survival of 65% and 70% respectively with the VDC/IE regimen in patients with localized Ewing sarcoma. The reduced dose and duration of ifosfamide and etoposide in this regimen is thought to offer a relatively safer toxicity profile. Several medical centers have since adopted this modified VDC/IE protocol as the standard first-line therapy for patients with non-metastatic Ewing sarcoma based on its effectiveness.
Market Driver - Increasing Adoption of Targeted Therapies Boosts Industry Developments.
While multimodal treatment approaches have enhanced outcomes over the years, treatment resistance and relapse remain major challenges in Ewing sarcoma management. This has prompted continued research into novel targeted agents that act through non-classical mechanisms. In recent years, a few targeted therapies have emerged that offer patients more lines of treatment beyond traditional chemotherapy.
Notably, the antitumor antibiotic lurbinectedin has demonstrated promising anti-tumor activity against various types ofsoft tissue sarcoma in clinical trials. Based on a pivotal phase II study, lurbinectedin has received regulatory approvals in several countries for treating relapsed Ewing sarcoma. Meanwhile, early clinical studies of investigational drugs like seclidemstat, a novel reversible LSD1 inhibitor, have shown signals of anti-tumor response in refractory Ewing sarcoma. Such targeted agents that block specific molecular pathways driving tumor growth present new hope for patients with advanced or relapsed disease. Several ongoing combination studies aim to evaluate safety and efficacy of incorporating these targeted drugs with standard chemotherapy backbones. Their increasing adoption could potentially improve long-term outcomes over time.
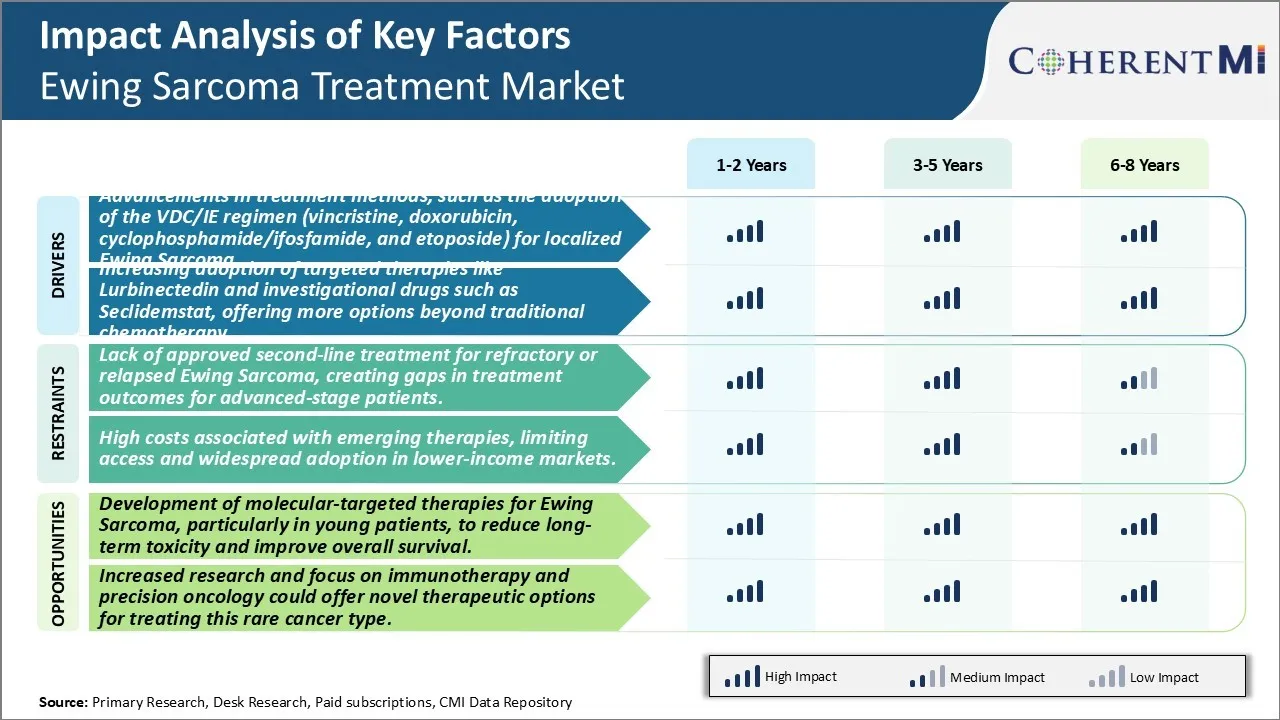
Market Challenge - Lack of Approved Second-Line Treatment For Refractory or Relapsed Ewing Sarcoma, Creating Gaps in Treatment Outcomes for Advanced-Stage Patients.
There is a significant unmet need for effective second-line treatment options for patients with Ewing sarcoma whose disease has become refractory or relapsed following first-line standard of care chemotherapy regimens. Current treatment protocols typically involve intense multi-agent chemotherapy consisting of vincristine, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, and etoposide. However, a sizable portion of patients will experience disease progression either during or following first-line treatment. For these patients, there are no approved or standardized second-line therapies available. Physicians are left with limited treatment options that consist mainly of pragmatic clinical trials evaluating new agents or combinations. This lack of an established standard of care protocol for relapsed/refractory disease leads to worse treatment outcomes and lower survival rates compared to patients able to achieve remission from front-line treatment. Developing an FDA-approved second-line treatment could help address this unmet need and reduce treatment gaps, improving outcomes for advanced-stage Ewing sarcoma patients.
Market Opportunity: Development of Molecular-Targeted Therapies for Ewing Sarcoma, Particularly in Young Patients, to Reduce Long-Term Toxicity and Improve Overall Survival.
There is significant potential to develop novel molecular-targeted therapies for Ewing sarcoma that improve upon conventional chemotherapy regimens. As the majority of Ewing sarcoma patients are children and young adults, reducing long-term treatment-related toxicities is paramount. Targeted therapies that inhibit specific molecular pathways driving cancer growth hold promise to deliver strong anti-tumor activity with more favorable safety profiles compared to traditional cytotoxic chemotherapies. Recent research has provided insights into recurring genetic mutations and dysregulated pathways in Ewing sarcoma, identifying new targets for drug development. Agents targeting programs like FGF/FGFR, IGF1/IGF1R, and PDGF/PDGFR pathways show early signs of clinical benefit. Continued investigation of targeted agents, especially in biomarkers-selected patient subgroups, could lead to options that are both more effective and better tolerated long-term than current standard of care regimens. This may help maximize quality of life outcomes which is especially important in younger patients.
Prescribers preferences of Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market
Ewing Sarcoma is an aggressive form of bone cancer that typically afflicts children and young adults. Treatment approaches vary depending on the stage of the disease and often involve a combination of therapies.
For localized disease, the standard first-line treatment is neoadjuvant chemotherapy with Vincristine, Doxorubicin, Cyclophosphamide, and Ifosfamide (VDC-IE). This is often followed by surgery to remove the tumor if possible. Examples of chemotherapy drugs prescribed include Vincristine (Oncovin), Doxorubicin (Adriamycin), and Ifosfamide (Ifex).
For patients with metastatic or recurrent disease, second-line treatment often involves high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell support. Prescribers commonly use Busulfan (Busulfex), Melphalan (Alkeran), and Etoposide (VePesid) as part of the conditioning regimen prior to stem cell transplantation.
Additional factors like tumor location, size, and response to initial treatment also guide treatment decisions. For tumors in difficult anatomical locations that are non-resectable, radiation therapy using proton beams may be considered as part of primary treatment or adjuvant therapy after chemotherapy. Prescribers also evaluate the patient's tolerance to treatment-related side effects and ability to undergo more intensive therapies.
Overall, Ewing Sarcoma requires a multimodal treatment approach combining chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation. Close monitoring of response and disease progression is important for determining patients’ eligibility for subsequent lines of therapy.
Treatment Option Analysis of Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market
Ewing Sarcoma typically has 4 stages - localized, regional, metastatic and recurrent. For localized disease, the standard first-line treatment is neoadjuvant chemotherapy with Vincristine, Doxorubicin, Cyclophosphamide and Ifosfamide/Etoposide, followed by definitive local therapy with surgery and/or radiation. This multifaceted approach aims to reduce the tumor size before aggressive local therapy and improve survival rates.
For regional or metastatic disease, intensive chemotherapy with additional drugs like Actinomycin D is recommended. The most commonly used regimen is VDC-IE (Vincristine, Doxorubicin, Cyclophosphamide, Ifosfamide, Etoposide). This multi-agent chemotherapy delivers high doses of potent drugs to eradicate any microscopic metastases while the combination helps lower resistance. Intensified treatment is crucial given the higher risk of systemic spread in these stages.
For recurrent/refractory disease, salvage therapy depends on prior treatment received and response. Options include high-dose regimens with Busulfan and Melphalan followed by stem cell rescue, oral Topotecan, Irinotecan or monoclonal antibodies like Nivolumab or Pembrolizumab. Topotecan is preferred for its favorable toxicity profile while antibodies showcase promise by leveraging the immune system. Overall, individualizing treatment per disease characteristics and tailoring multi-modality care is key to maximizing outcomes.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market
Collaboration for Drug Development: In 2021, Pfizer collaborated with Epizyme to develop tazemetostat for treating Ewing sarcoma. Tazemetostat is an EZH2 inhibitor approved for certain cancers. This partnership combines Epizyme's expertise in epigenetic targets with Pfizer's capabilities in clinical development and commercialization. Such collaborations accelerate development of new treatment options for patients.
Acquisitions of Firms with Promising Pipelines: In 2020, Lateral Oncology acquired the late-stage oncology company, Adimab. Adimab had developed drugs targeting Ewing sarcoma, including an antibody-drug conjugate ADI-2780. This acquisition strengthened Lateral's Ewing sarcoma portfolio and pipeline. Similarly, Lilly acquired ImClone in 2019, gaining access to its antibody pipeline including ramucirumab being tested for Ewing sarcoma.
Expanded Access Programs: In 2018, Roche began an expanded access program for their drug Meclorema, making it available for Ewing sarcoma patients before regulatory approval. This helped patients gain access to an experimental treatment while building researchers' understanding of outcomes. It also established Roche as a leader in developing new therapies.
Targeted Clinical Trials: Major players like Pfizer and Lilly have initiated targeted Phase 2 clinical trials for drugs like tazemetostat and ramucirumab in the orphan indication of relapsed Ewing sarcoma. Narrow focus on this hard-to-treat population addresses a major unmet need and regulatory incentives make drugs viable options even with small patient pools.
Segmental Analysis of Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market

Insights, By Line of Treatment, Localized Treatment Dominates Due to Access and Early Detection.
By Line of Treatment, the segment contributing the highest share to the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market is Localized treatment and is expected to account for 61.3% in 2024. This is primarily owing to greater access to early detection and localized treatment options. Ewing sarcoma commonly manifests in the bones or soft tissue of the legs, arms, chest, pelvis, or spine. When the cancer is detected early and confined to the localized area of origin, localized treatment protocols can be highly effective.
Advancements in medical imaging technologies have improved physicians' ability to detect tumors in their earliest stages before they have metastasized. Wide availability of X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans allow thorough examination of suspicious areas and confirmation of localized disease. Once localized Ewing sarcoma is identified, treatment typically involves surgery to remove the tumor along with a wide margin of healthy tissue surrounding it. For tumors developing in non-vital or removable bones, surgery may provide a cure on its own.
Adjuvant therapies are commonly administered before or after surgery to further eliminate any remaining cancer cells. Localized radiation therapy delivers high doses of radiation directly to the affected area to destroy any residual tumor while limiting exposure to other bodily regions. Some patients may undergo localized administration of chemotherapy through arterial or venous catheters threaded directly to the tumor site. This allows high concentrations of anti-cancer drugs to reach the local area while reducing systemic side effects.
Insights, By Drug Class, Cyclophosphamide's Proven Efficacy and Availability Fuels Market Share.
Among the drug classes utilized for Ewing Sarcoma Treatment, the segment contributing the highest market share is cyclophosphamide. It is expected to register 39.2% share in 2024. This alkylating chemotherapy drug has demonstrated efficacy against Ewing sarcoma in multiple clinical trials and has become incorporated as a backbone of various treatment regimens. Cyclophosphamide works by cross-linking DNA and preventing cell division, making it highly effective against the rapidly multiplying Ewing sarcoma tumor cells.
Decades of clinical usage has revealed cyclophosphamide's optimal dosing and side effect management when used alone or in combination with other drugs. Published studies support 2-3 year event-free survival rates exceeding 70% when multi-agent regimens incorporating cyclophosphamide are administered as part of primary treatment. Its off-patent status has also facilitated wide global availability at affordable prices. This accessibility is a major factor supporting cyclophosphamide's dominance in Ewing sarcoma management, especially in developing nations.
Additional Insights of Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market
Ewing Sarcoma is a rare but aggressive form of cancer that primarily affects children and young adults, often presenting in bones such as the femur and pelvis. The standard treatment approach involves a combination of chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy. However, for patients with metastatic disease, outcomes remain poor, with survival rates ranging between 30–40%. Traditional treatments like chemotherapy continue to dominate, but targeted therapies and immunotherapy are being explored as alternatives. The development of novel therapies, such as Seclidemstat (targeting LSD1) and Lurbinectedin (a transcription inhibitor), offer hope for patients who have failed first-line treatments. The market for Ewing Sarcoma is still underdeveloped, and there is significant unmet need, especially in second-line therapies. The focus on molecular-targeted treatments and the potential integration of precision medicine will likely drive future market growth. The Ewing Sarcoma market is expected to expand as more effective treatments gain approval, and patient outcomes improve, particularly for those with relapsed or refractory disease.
Competitive overview of Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market
The major players operating in the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market include Salarius Pharmaceuticals, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, BioAlta, Inhibrx, La Jolla Pharmaceuticals, Par Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical and Vivacelle Bio.
Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market Leaders
- Salarius Pharmaceuticals
- Jazz Pharmaceuticals
- Pfizer
- Eli Lilly and Company
- BioAlta
Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market - Competitive Rivalry

Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market
- In May 2023, Salarius Pharmaceuticals resumed its Phase I/II trial of Seclidemstat after a voluntary pause due to a SUSAR (suspected unexpected serious adverse reaction). The FDA approved the continuation of trials, with a focus on improving outcomes for refractory Ewing Sarcoma patients.
- In December 2022, Jazz Pharmaceuticals received approval for Lurbinectedin as a second-line treatment option for relapsed or refractory Ewing Sarcoma, marking a milestone in expanding therapy choices for patients with metastatic disease.
Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market Segmentation
- By Line of Treatment
- Localized
- Metastatic
- By Drug Class
- Cyclophosphamide
- Doxorubicin
- Dactinomycin
- Etoposide
- Infoposide
- Vincristine

Would you like to explore the option of buyingindividual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market?
The Global Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market is estimated to be valued at USD 250.1 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 430.3 Mn by 2031.
What will be the CAGR of the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market?
The CAGR of the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market is projected to be 6.12% from 2024-2031.
What are the major factors driving the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market growth?
The advancements in treatment methods, such as the adoption of the VDC/IE regimen (vincristine, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide/ifosfamide, and etoposide) for localized ewing sarcoma and increasing adoption of targeted therapies like lurbinectedin and investigational drugs such as seclidemstat, offering more options beyond traditional chemotherapy. are the major factor driving the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market?
The lack of approved second-line treatment for refractory or relapsed ewing sarcoma, creating gaps in treatment outcomes for advanced-stage patients. and high costs associated with emerging therapies, limiting access and widespread adoption in lower-income markets are the major factor hampering the growth of the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market.
Which is the leading Line of Treatment in the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market?
Localized is the leading Line of Treatment segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Ewing Sarcoma Treatment Market?
Salarius Pharmaceuticals, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, BioAlta, Inhibrx, La Jolla Pharmaceuticals, Par Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical, Vivacelle Bio are the major players.