Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market is segmented By Treatment Type (Botulinum Toxin Injections (Xeomin, Myobloc), Oral Medications, Surgical Procedures....
Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market Size
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR5.30%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 5.30% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Merz Pharmaceuticals, US WorldMeds, NeuroHealing, Proveca, Eisai (via Sloan Pharma) and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market Analysis
The sialorrhea treatment market is estimated to be valued at USD 771 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1,110 Mn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.30% from 2024 to 2031. The increasing prevalence of neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and cerebral palsy is expected to drive the growth of this market during the forecast period.
Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Awareness and Diagnosis of Sialorrhea
With increased awareness about conditions like Parkinson's disease, motor neuron disease, and mental illnesses, the diagnosis of associated symptoms like excessive drooling or sialorrhea has also improved. Healthcare professionals are now able to better identify cases of sialorrhea compared to a few years ago. Several programs aimed at educating doctors as well as the public have played a key role in enhancing the understanding of this uncomfortable symptom. Patients who may have simply ignored excess saliva production in the past are now seeking medical help.
Besides patients, even caregivers are more watchful of changes in salivation and able to correlate it with the underlying condition. Support groups actively share their experiences in managing drooling which influences more people to report their cases to doctors. With rising education levels and digital connectivity, health information is easily accessible these days. People impacted by sialorrhea regularly search online forums and websites for solutions. This amplified knowledge about the causes and available remedies has spurred the identification and diagnosis rate of this long-ignored symptom. Even in developing countries, non-profit organizations are playing a part in disseminating guidance and raising recognition regarding sialorrhea.
Market Driver - Approval of Novel Therapies Like Myobloc and Xeomin
The approval of Botulinum toxin by the US FDA in 2011 was a landmark event in the sialorrhea treatment space. The novel therapy Myobloc, designed to treat chronic sialorrhea, offered patients and physicians an alternative to radiation therapy or surgery. It provided a minimally invasive and relatively well-tolerated option to control excess drooling. This approval inspired increased faith in pharmaceutical innovations and bolstered overall research efforts targeting sialorrhea. It has strengthened industry aspirations to enhance product pipelines and accelerate new launches.
Later, Myobloc's success paved the way for Xeomin, another Botulinum toxin approved in 2017 for this indication. Whereas Myobloc needed to be administered via electromyography, Xeomin delivered comparative results via clinical examination alone. This more convenient mode of administration amplified patient acceptance of pharmacotherapy.
Notwithstanding rare adverse effects, clinicians find Botulinum toxins as reliable treatments for adults and pediatric cases of sialorrhea. Their efficacy has mitigated the requirement for alternative methods and raised hope for discovering safer, targeted options. The therapeutic arrival has fueled momentum in clinical trials exploring other classes of molecules to manage this distressing condition. Patent expirations too will likely stimulate competition and price declines, improving accessibility in the coming years.

Market Challenge - High Costs of Approved Treatments and Therapies
One of the key challenges currently facing the sialorrhea treatment market is the high costs of approved treatment options such as botulinum toxin injections. These injections are an effective therapy for reducing saliva production in patients with conditions that cause excessive drooling such as cerebral palsy. However, each treatment session involves injecting minute doses of botulinum toxin into the salivary glands under local anesthesia. As botulinum toxin drugs like Botox and Dysport are biologics derived from living cells, the manufacturing process is complex and costs are high.
Insurers also often resist paying for repeated botulinum toxin injections which patients may require every 3-4 months to manage their sialorrhea symptoms. The high drug acquisition costs as well as costs of administering the injections each time in a clinical setting place a significant financial burden on patients and healthcare systems. This poses a major challenge to the long-term growth prospects of the sialorrhea treatment market.
Market Opportunity - Expansion of Xeomin and Myobloc into new markets
One of the key opportunities in the sialorrhea treatment market lies in the ongoing expansion of neuromodulator drugs Xeomin and Myobloc into new geographical markets and patient populations. Xeomin and Myobloc are two alternative botulinum toxin drugs to Botox and Dysport that are currently only approved for treating sialorrhea in a few countries. Both these drugs have demonstrated strong efficacy in reducing drooling with an improved safety profile over older drugs.
With Xeomin and Myobloc likely to get additional regulatory approvals in major pharmaceutical markets worldwide over the coming years, their manufacturer expects revenues from sialorrhea treatment to increase significantly. Furthermore, ongoing research aims to evaluate the benefit of these neuromodulators in younger patient groups beyond adults and the elderly. A potential expansion of approved age indications could substantially broaden the addressable patient pool and present promising growth prospects for players in this market.
Prescribers preferences of Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market
Sialorrhea, or excessive saliva production, is commonly seen in patients with neurologic conditions such as Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and cerebral palsy. Treatment approaches vary based on the severity and progression of symptoms.
For mild cases, prescribers typically recommend behavioral interventions like tongue holding methods and oral suction devices as the first-line approach. However, as symptoms worsen, medication becomes necessary.
For moderate sialorrhea, anticholinergic drugs that work peripherally are prescribed. Common options at this stage include brand names like Robinul (glycopyrrolate) and Kwells (orphenadrine). These work by reducing saliva secretion from salivary glands.
In severe, uncontrollable cases, central acting anticholinergics that cross the blood-brain barrier are used. Examples include controlled-release formulations like Robinul Forte and oral tablets like Robinul tablets. These block muscarinic receptors in the central nervous system to reduce drooling.
When medications prove ineffective or intolerable due to severe side effects like mental status changes or constipation, the next option is minimally invasive procedures like intraglandular botulinum toxin injections or radiotherapy. As a last resort, surgery to remove major salivary glands may be considered.
Other key factors affecting prescribers' choice include a patient's medication history, tolerance, compliance, and insurance coverage.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market
Drug development and innovation: Leading players like Lundbeck, GlaxoSmithKline, and Sun Pharmaceuticals have focused on developing innovative drug formulations and delivery methods for treating sialorrhea. For example, in 2017 Lundbeck received FDA approval for Naldemedine (Rotegrity) tablets for treating opioid-induced sialorrhea. The once-daily oral medication was found to significantly reduce excess saliva production compared to placebo.
Acquisitions and partnerships: Companies have made strategic acquisitions and partnered with smaller biotechs to gain access to new drugs and technologies. For instance, in 2015 Sunovion acquired Cynapsus Therapeutics to acquire rights to APD334 - an AMPA receptor antagonist in late-stage trials for neurodegenerative hypersalivation. Such deals helped expand product pipelines.
Geographic expansion: Market leaders have focused on expanding into high-growth regions like Asia Pacific and Latin America through new approvals, regional manufacturing plants and licensing agreements with local players. For example, between 2013-2018 GSK received aprovals for Glycopyrrolate tablet in over 15 countries, helping them become a top player in global markets.
Awareness programs: Pharma players regularly conduct awareness programs targeting healthcare practitioners and caregivers to educate about available treatment options and drive initial prescriptions. Clinical research establishing the negative impact of sialorrhea on patient quality of life has also helped promote early and effective management of the condition.
Segmental Analysis of Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market
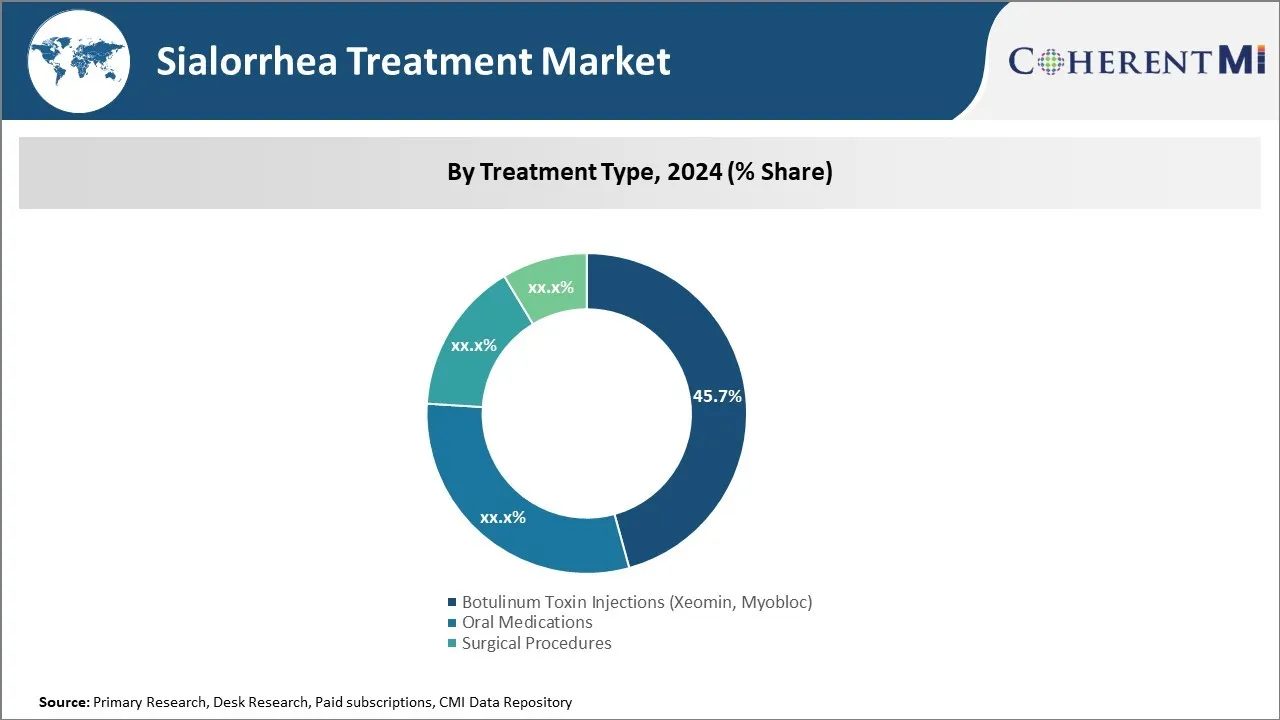
Insights, By Treatment Type: Botulinum Toxin Injections (Xeomin, Myobloc) Draw Attention in the Market
In terms of treatment type, botulinum toxin injections (Xeomin, Myobloc) contribute the highest share of the market owing to growing preference for minimally invasive procedures. Botulinum toxin injections represent a non-invasive and effective means for treating sialorrhea or excessive saliva production. The medications work by temporarily paralyzing the muscles responsible for saliva secretion, thereby reducing excess fluid flows. Compared to surgical and radiation-based alternatives, botulinum toxin procedures are associated with a significantly reduced risk of complications and side effects. This makes them better tolerated among patients, especially children and the elderly population who constitute a major part of those impacted by sialorrhea.
Additionally, botulinum toxin treatments offer advantages in terms of speed of action and reversibility of effects. Results are visible within 2-4 weeks of administration and symptoms typically resolve within 3-6 months as the muscles regain functionality. Meanwhile, effects of surgical gland removal or radiotherapy may persist permanently. The temporary paralytic impact also allows physicians to customize dosage for each patient until optimal symptom relief is achieved. Repeated injections can be administered safely as required.
Growing awareness about availability of minimally invasive options like botulinum toxins has pushed more patients and physicians to opt for them over alternative measures.
Additional Insights of Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market
- Myobloc was initially approved for cervical dystonia but later expanded its indication to treat Sialorrhea.
- XEOMIN became the first FDA-approved neuromodulator for treating Sialorrhea in children.
- In 2023, the United States recorded approximately 336,800 cases of chronic Sialorrhea in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
- Germany has the highest prevalence of Sialorrhea in the EU4 countries.
Competitive overview of Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market
The major players operating in the sialorrhea treatment market include Merz Pharmaceuticals, US WorldMeds, NeuroHealing, Proveca, and Eisai (via Sloan Pharma).
Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market Leaders
- Merz Pharmaceuticals
- US WorldMeds
- NeuroHealing
- Proveca
- Eisai (via Sloan Pharma)
Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market
- In August 2019, US WorldMeds received FDA approval for Myobloc (rimabotulinumtoxinB) for the treatment of chronic Sialorrhea in adults. This made Myobloc the first FDA-approved botulinum toxin for this condition. Myobloc works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, reducing saliva production, and its effects last up to three months. This approval created significant opportunities in the treatment landscape for Sialorrhea, especially for patients with neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease
- In December 2020, Merz Pharmaceuticals obtained FDA approval for Xeomin, expanding its use to children aged 2 years and older. This marked an expansion of its use, positioning Xeomin as a treatment for both pediatric and adult patients. This development strengthened Xeomin's standing in the treatment of Sialorrhea.
Global Sialorrhea Treatment Market Segmentation
- By Treatment Type
- Botulinum Toxin Injections (Xeomin, Myobloc)
- Oral Medications
- Surgical Procedures
- Radiation Therapy

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the sialorrhea treatment market?
The sialorrhea treatment market is estimated to be valued at USD 771 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1,110 Mn by 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the sialorrhea treatment market?
The high costs of approved treatments and therapies and limited awareness in some geographical regions are the major factor hampering the growth of the sialorrhea treatment market.
What are the major factors driving the sialorrhea treatment market growth?
The increasing awareness and diagnosis of sialorrhea and approval of novel therapies like myobloc and xeomin are the major factor driving the sialorrhea treatment market.
Which is the leading treatment type in the sialorrhea treatment market?
The leading treatment type segment is Botulinum Toxin Injections (Xeomin, Myobloc).
Which are the major players operating in the sialorrhea treatment market?
Merz Pharmaceuticals, US WorldMeds, NeuroHealing, Proveca, and Eisai (via Sloan Pharma) are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the sialorrhea treatment market?
The CAGR of the sialorrhea treatment market is projected to be 5.30% from 2024-2031.