HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market is segmented By Treatment Type (Chemotherapy, Immunotherapy), By Route of Administration (Oral, Parenteral, Others)....
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR2.23%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 2.23% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Jiangsu HengRui Medicine Co., Ltd., Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Merus N.V., GeneQuantum, Roche and Among Others. |
please let us know !
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market Analysis
The HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market is estimated to be valued at USD 10.70 bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 12.03 bn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.23% from 2024 to 2031.
The market is witnessing positive growth trends over the past few years. The increasing prevalence of breast cancer worldwide due to growing obesity rates and lifestyle changes is expected to be a key factor driving the growth of this market. Additionally, rising awareness programs by governments and non-profit organizations regarding early screening and treatment is also contributing to the growth. The HER2-positive breast cancer market focuses on treatments targeting the overexpression of the HER2 protein, which promotes aggressive tumor growth. This type of cancer accounts for about 15-20% of all breast cancers. The market has grown significantly due to advancements in targeted therapies like trastuzumab (Herceptin), pertuzumab, and antibody-drug conjugates such as T-DM1 (Kadcyla) and trastuzumab deruxtecan. Increasing R&D investments, a rising global incidence of breast cancer, and the development of biosimilars are driving market expansion. However, high treatment costs and resistance to therapies remain challenges for patients and healthcare providers alike.
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Cases of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Globally.
One of the primary drivers for the HER2-positive breast cancer market is the increasing incidence of HER2-positive breast cancer cases across the world. This aggressive form of breast cancer accounts for approximately 15-20% of all breast cancers diagnosed globally each year. While breast cancer incidence rates in the United States and other Western nations have remained stable or decreased in recent years, the disease burden from HER2-positive breast cancer is rising. This is mainly attributed to lifestyle changes, increasing age of women, and other environmental risk factors.
In developing countries that are undergoing rapid social and economic transformations, there has been a surge in breast cancer cases, including the HER2-positive subtype. Factors such as later age of childbearing, obesity, physical inactivity, alcohol consumption and tobacco use are believed to be fueling this rise. Urbanization has also played a role, as women living in urban areas are more likely to adopt Western lifestyles associated with increased breast cancer risk. With women in low and middle-income countries tending to develop breast cancer nearly a decade earlier than in high-income countries, the burden from this disease is expected to escalate dramatically in the coming decades.
In addition, advances in diagnostic methods have led to improved detection of HER2-positive breast tumors. Wide availability of immunohistochemistry (IHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) tests for HER2 biomarker testing allows for more accurate identification of HER2-positive cancers worldwide. This growing patient pool diagnosis creates a compelling clinical need for improved HER2-targeted therapies.
Market Driver - The Introduction of Next-Generation HER2-Targeted Therapies, Including Bispecific Antibodies and ADCs
Another key driver fueling the HER2-positive breast cancer therapeutics market is the introduction of newer treatment modalities that provide more effective and personalized approaches to target this aggressive disease subtype. The last decade saw the approval of pivotal drugs such as ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla) and pertuzumab (Perjeta) that transformed outcomes for patients.
Building on this progress, pharmaceutical companies are now developing the next wave of innovative HER2-targeted agents. These include antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) that leverage proprietary linker technologies to deliver highly potent cytotoxic payloads directly to cancer cells. With their improved safety profiles and ability to cross the blood-brain barrier to target central nervous system metastases, the new generation of ADCs promise to advance treatment of both early and advanced HER2-positive disease.
Bispecific antibodies that can simultaneously bind two different epitopes are another class of novel agents under investigation. By enabling dual blockade of HER2 and other pathways critical to tumor growth, these multifunctional antibodies have demonstrated robust antitumor activity in early clinical trials. Their ability to redirect T-cells to kill cancer cells also makes bispecifics well-suited for combination therapy approaches.
These next-generation therapies have the potential to enhance clinical outcomes and quality of life for patients by addressing current unmet needs such as acquired or intrinsic resistance to standard agents. With many candidates in late-stage testing and some likely to be approved in the near future, they are anticipated to inject fresh momentum into the HER2-positive breast cancer therapeutic sphere.
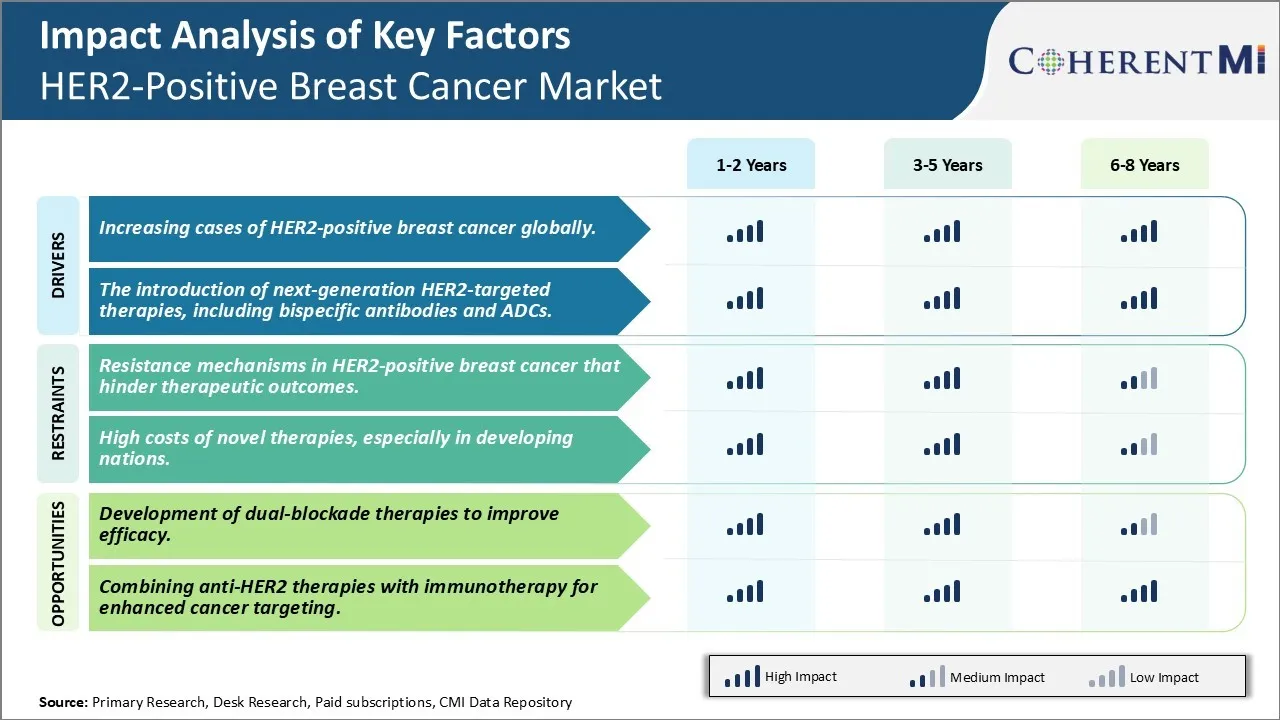
Market Challenge - Resistance Mechanisms in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer That Hinder Therapeutic Outcomes.
One of the major challenges in the HER2-positive breast cancer market is resistance mechanisms that can develop against existing targeted therapies over time. When cancer cells initially become dependent on the HER2 pathway for growth and survival, HER2-targeted therapies such as trastuzumab and pertuzumab can provide significant clinical benefit. However, there are several potential resistance mechanisms where tumor cells are able to alter signaling pathways and continue proliferating despite HER2 blockade. Primary resistance may occur before treatment begins if alternate pathways such as IGF1R or HER3 compensate for HER2 inhibition. Secondary or acquired resistance develops later on as cancer cells evolve new mutations that restore independence from HER2 or activate bypass tracks. Examples include upregulation of alternative HER family ligands, MAPK or PI3K pathway reactivation through receptor crosstalk, and phenotypic changes causing loss of HER2 expression. Identifying these resistance mechanisms and developing strategies to prevent or overcome them is critical for improving long-term treatment outcomes in HER2-positive breast cancer patients.
Market Opportunity- Development of Dual-Blockade Therapies to Improve Efficacy.
One major opportunity in the HER2-positive breast cancer market is the development of dual-blockade therapies that simultaneously target HER2 and other receptor tyrosine kinases or downstream signaling nodes. By combining HER2 inhibitors like trastuzumab with agents against complementary receptors like HER3 or IGF1R, it may be possible to achieve deeper and more durable responses than either drug alone. Dual blockade can not only prevent initial tumor growth driven by HER2, but also hamper the emergence of resistance. Several combination regimens are under clinical investigation, and preliminary results indicate these multi-pronged approaches can significantly improve progression-free and overall survival compared to standard of care HER2 monotherapy. Continued research and development of rationally designed dual-blockade therapies has strong potential to advance treatment standards and outcomes for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer.
Prescribers preferences of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market
Breast cancer treatment varies depending on the stage of the disease and other factors. For early-stage (I-II) hormone receptor positive breast cancer, the initial line of treatment typically involves endocrine therapy using aromatase inhibitors such as Arimidex (anastrozole) or Femara (letrozole). Tamoxifen brands like Soltamox are also commonly prescribed.
For patients with HER2 positive early breast cancer, targeted therapies are preferred. Trastuzumab brands like Herceptin are often prescribed alongside chemotherapy drugs like Taxol (paclitaxel). For more advanced local disease, prescribers may recommend neoadjuvant chemotherapy prior to surgery to shrink the tumor. Common regimens include AC (doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide) followed by a taxane such as paclitaxel or docetaxel.
For stage III/IV metastatic breast cancer, treatment depends on receptor status and disease progression. For hormone receptor positive recurrent/stage IV disease, endocrine therapies remain the standard first line. However, newer selective estrogen receptor degraders like Ibrance (palbociclib) are gaining favor when combined with letrozole as initial therapy due to superior outcomes over letrozole alone. For HER2+ metastatic breast cancer, dual anti-HER2 blockade using Herceptin and Perjeta (pertuzumab) is a preferred first line regimen. Physician expertise, lines of available therapies, tolerability, cost and patient preferences also impact treatment decisions.
Treatment Option Analysis of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market
Breast cancer treatment options vary depending on the stage of the disease. In early-stage breast cancer (Stage 0-II), the most common options are lumpectomy (surgical removal of the tumor plus some surrounding tissue), mastectomy (surgical removal of the breast), and radiation therapy. Chemotherapy is usually not required for early-stage disease but hormone therapy drugs like tamoxifen may be recommended for hormone receptor-positive cancers.
For locally advanced breast cancer (Stage III), in addition to surgery, chemotherapy is usually recommended before (neoadjuvant) or after (adjuvant) surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells that may have spread to other parts of the body. Common chemo regimens include AC (doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide) followed by taxane-based treatments like docetaxel or paclitaxel. Trastuzumab (Herceptin) is added for HER2-positive cancers.
For metastatic or Stage IV breast cancer that has spread to distant organs, chemotherapy remains the main treatment approach. The choice of chemo agents depends on the receptor status of the tumor - taxanes, capecitabine, gemcitabine, or carboplatin/protein-bound paclitaxel for triple-negative cancer, while hormonal therapies or HER2-targeted therapies like trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla) are preferred for receptor-positive metastatic disease. Immunotherapy drugs like atezolizumab (Tecentriq) in combination with nab-paclitaxel (Abraxane) also show promise.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market
Clinical Trials: Aggressive clinical trial programs testing new indications, combinations and sequencing of existing drugs have helped extend market opportunity. For example, Roche conducted large adjuvant studies of Herceptin in early 2000s demonstrating benefits in early-stage disease. This expanded the eligible patient pool worldwide and boosted sales. Similarly, Phase III studies led to approval of Kadcyla in metastatic and adjuvant settings. Such trials demonstrating value in sequential and combination regimens optimize treatment algorithms.
Business Development: Partnerships and M&A have allowed companies to leverage each other's strengths. For example, Roche licensed Kadcyla from Immunogen/Genentech after promising early data. This allowed both partners to share the commercial upside. Similarly, Daiichi Sankyo collaborated with AstraZeneca on Enhertu. Such deals accelerate development and commercialization of novel agents.
Advocacy: Building awareness through patient advocacy and engagement with providers has increased diagnosis and optimized treatment. For example, Roche spends over USD50M annually on HER2 patient advocacy to promote screening and guideline-compliant use of standards of care. This cements their leadership position and trust with physicians.
Segmental Analysis of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market
Insights, By Treatment Type, Cost Effectiveness Drives Growth of Chemotherapy.
By Treatment Type, Chemotherapy is expected to contribute the highest share 52.8% in 2024 owing to its relatively lower cost compared to other treatment options. Chemotherapy involves using potent drugs to destroy cancer cells, which makes it one of the most common and affordable first line treatments for HER2-positive breast cancer patients. The cost of chemotherapy drugs and administration is still much lower than targeted therapies or immunotherapy which typically involve biologics and require lengthy infusion sessions. This cost differential is a major factor influencing treatment decisions, as chemotherapy remains covered by most insurance plans while novel therapies often have high out-of-pocket costs for patients.
Due to its widespread affordability and availability across different settings, chemotherapy also sees high usage in developing nations where healthcare budgets are more constrained. Generic versions of chemotherapeutics further improve accessibility in price-sensitive markets. While side effects and short-term response rates may be better with newer targeted options, chemotherapy continues to dominate in the HER2 breast cancer segment owing to its established efficacy and minimal expense for both patients and healthcare systems. Recent drug discoveries aim to improve tolerability and outcomes of chemotherapy regimens through rational drug combinations and dose schedules. This progress helps maintain chemotherapy's positioning as the therapy of choice for early-line use.
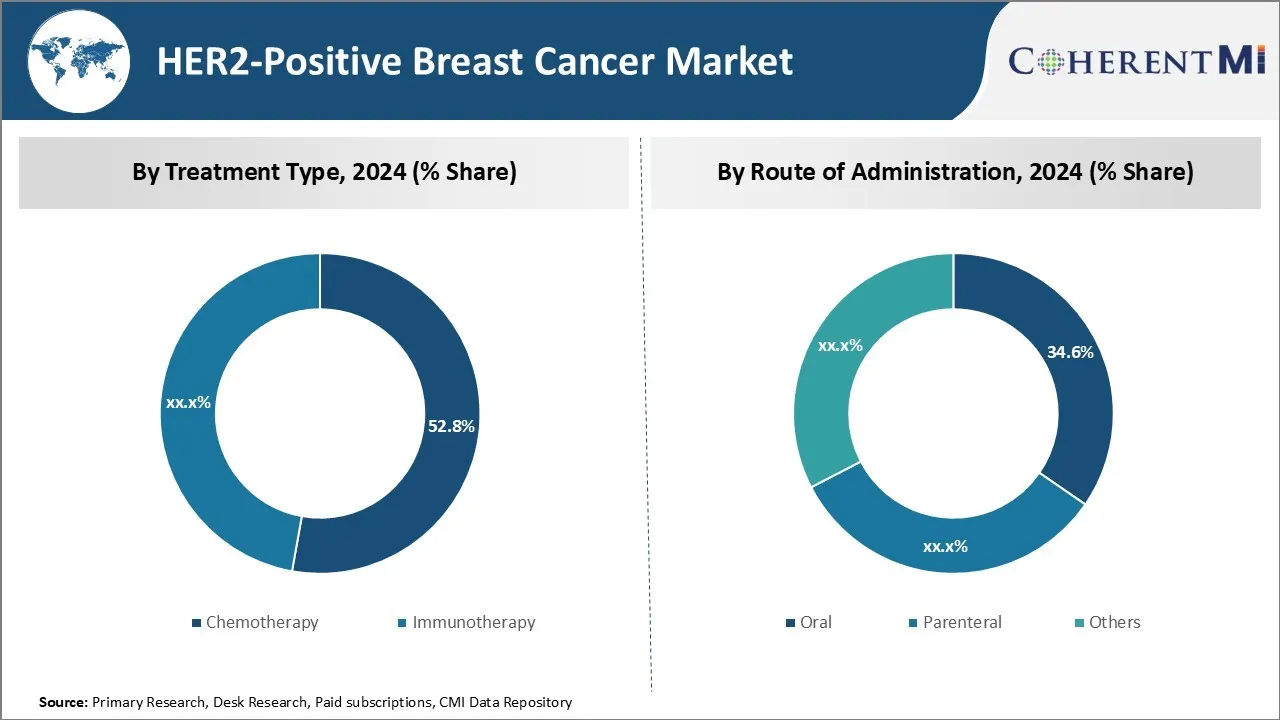
Insights, By Route of Administration, Ease of Self-Administration boosts Oral Treatment Demand.
Within the By Route of Administration segment, oral treatment is expected to contribute 34.8% in 2024 share due to advantages over parenteral therapies. Administering drugs through the oral route provides unmatched ease and convenience for patients as it eliminates the need for frequent hospital or clinic visits for infusions or injections. This leads to improved treatment compliance and satisfaction among individuals undergoing long-term HER2 breast cancer regimens that often span years. The comfort of self-administering pills at home ensures minimal lifestyle disruptions while undergoing cancer therapy.
Oral therapies also empower patients by giving them more control over their treatment schedule. Missed or delayed doses are less impactful for oral drugs compared to parenteral medicines with long half-lives requiring dedicated administration sessions. This dosing flexibility allows for better management of side effects and integration of treatment into daily routines. The non-medical setting of oral delivery further reduces health system resource burden and waiting times in clinics. With innovation bringing more drug entities to the oral delivery space, its popularity and share seems set to grow in the HER2 breast cancer segment going forward.
Insights, By End-user, Access to Multidisciplinary Support leads to Hospital Preference
Among the various end-user segment, hospital pharmacies have the dominant share as they continue offering a comprehensive set of services preferred by HER2 breast cancer patients. Advances in cancer care now demand multidisciplinary approach beyond just dispensing drugs, which hospitals are well-equipped to provide. They employ large oncology specialty teams including surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation therapists, dermatologists, and psychologists can easily coordinate appointments versus solo private practices.
This integrated care model ensures continuity throughout various treatment stages from biopsy to surgery to long-term drug therapy and surveillance. Hospitals also have sophisticated diagnostic technologies, extensive support staff and in-patient facilities to effectively manage complications. Their specialized cancer centers provide a nurturing environment with emotional counseling programs as well. For complex issues, hospitals facilitate rapid referrals to top experts elsewhere. This holistic one-stop support generates confidence among patients facing an aggressive disease like HER2 breast cancer and drives preference for hospital pharmacies to fill prescriptions. Their formulary coverage is usually robust as well.
Additional Insights of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market
The HER2-positive breast cancer pipeline is dynamic, with a mix of therapies targeting different mechanisms, such as inhibiting HER2 signaling, dual HER2/HER3 targeting, and overcoming drug resistance. Resistance to traditional HER2 therapies has necessitated the development of new approaches, including antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) like SHR-A1811, which carry a cytotoxic payload to selectively kill HER2-expressing tumor cells. Bispecific antibodies, such as Merus N.V.'s MCLA-128, are also gaining traction, as they offer a multi-targeted approach by blocking both HER2 and HER3 signaling pathways. The combination of HER2 therapies with immune checkpoint inhibitors, CDK4/6 inhibitors, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors represents a promising strategy for enhancing treatment efficacy. Furthermore, the emergence of the HER2-low category has expanded the patient population eligible for these therapies, underscoring the importance of accurate diagnostic tools and innovative treatment regimens in managing this aggressive cancer type.
Competitive overview of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market
The major players operating in the HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market include Jiangsu HengRui Medicine Co., Ltd., Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Merus N.V., GeneQuantum, Roche/Genentech, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Genetech, Johnson & Johnson, Cipla, Abbvie and Merck.
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market Leaders
- Jiangsu HengRui Medicine Co., Ltd.
- Shanghai Henlius Biotech
- Merus N.V.
- GeneQuantum
- Roche
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market
- In May 2024, Jiangsu HengRui Medicine Co. announced positive Phase III results for SHR-A1811, an antibody-drug conjugate that shows enhanced tumor cell death through HER2 targeting, which could revolutionize HER2-positive breast cancer treatment.
- In April 2024, Shanghai Henlius Biotech's HLX11, a pertuzumab biosimilar, completed Phase III trials, showcasing its potential in both early and metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer. This biosimilar could provide a more affordable treatment option for patients globally.
- In March 2024, Merus N.V. highlighted significant Phase II success with MCLA-128, a bispecific antibody that targets HER2 and HER3, showing promise in overcoming resistance to current HER2 therapies.
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market Segmentation
- By Treatment Type
- Chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy
- By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Parenteral
- Others
- By End-user
- Hospital Pharmacy
- Online Pharmacy
- Retail Pharmacy

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market?
The HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market is estimated to be valued at USD10.70 bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 12.03 bn by 2031.
What will be the CAGR of the HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market?
The CAGR of the HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market is projected to be 2.23% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market?
The resistance mechanisms in her2-positive breast cancer that hinder therapeutic outcomes and high costs of novel therapies, especially in developing nations are the major factor hampering the growth of the HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market.
What are the major factors driving the HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market growth?
The increasing cases of HER2-positive breast cancer globally and the introduction of next-generation HER-2 targeted therapies, including bispecific antibodies and ADCs are the major factor driving the HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market.
Which is the leading Treatment Type in the HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market?
Chemotherapy is the leading treatment type segment.
Which are the major players operating in the HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Market?
Jiangsu HengRui Medicine Co., Ltd., Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Merus N.V., GeneQuantum, Roche/Genentech, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Genetech, Johnson & Johnson, Cipla, Abbvie, Merck are the major players.