Inclusion Body Myositis Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Inclusion Body Myositis Market, By Treatment (Pharmacological Treatments, Non-Pharmacological Treatments), By Patient Population (Adult, Pediatric), B....
Inclusion Body Myositis Market Size
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR5.5%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 5.5% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Eli Lilly and Company, AbbVie Inc., Novartis AG and Among Others |
please let us know !
Inclusion Body Myositis Market Analysis
The inclusion body myositis market is estimated to be valued at USD 527.5 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 767.1 Mn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% from 2024 to 2031. The increasing prevalence of autoimmune disorders and rising geriatric population globally are expected to propel the market during the forecast period.
Inclusion Body Myositis Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Awareness and Diagnosis of Inclusion Body Myositis
As the condition is progressive and debilitating, awareness about its symptoms and the available diagnostic methods is crucial. Various non-profit patient advocacy groups and clinical communities have intensified their efforts towards educating the general population as well as healthcare providers. Several awareness campaigns are being run through multiple channels including social media, print media and community outreach activities. This is helping more individuals recognize the warning signs at an early stage and seek medical advice promptly. The number of patients approaching doctors with suspected symptoms of IBM has seen a steady rise over the last few years.
Clinical experts are also getting better at differentiating IBM from other types of inflammatory and muscular disorders based on patient history, physical examination and diagnostic tests. Advanced investigations such as muscle biopsy and protein analysis are playing an important role in confirming diagnoses that may have otherwise been difficult to identify with certainty. With growing experience and enhanced analytical capabilities, pathologists can now examine tissue samples more accurately under the microscope. This will boost growth of the inclusion body myositis market.
Market Drivers - Rising Healthcare Costs and Developments in Therapy Exploration
As the inflammatory condition leads to progressive weakening of muscles over time, patients often require long-term medical management and rehabilitative support. This translates to increased healthcare resource utilization and a rising economic burden on patients as well as national healthcare budgets.
The lack of an effective treatment also means that the condition is not easily arrestable or reversible currently. All these factors are driving higher spending on IBM annually.
At the same time, major pharmaceutical vendors and clinical research organizations are investing heavily in immunotherapy and gene therapy research for IBM.
Several candidate molecules are under pre-clinical and clinical evaluation for their safety and efficacy. stem cell therapy is another area attracting substantial research interests. Though finding a cure remains challenging given our limited understanding of the disease pathology, these efforts are expected to result in better treatment options and patient care standards going forward.
Some of the agents in the pipeline may even be able to modify the disease course if approved. This ongoing R&D focus on new drug development and alternative remedies is financed through growing industry investments and government grants for rare disease programs.
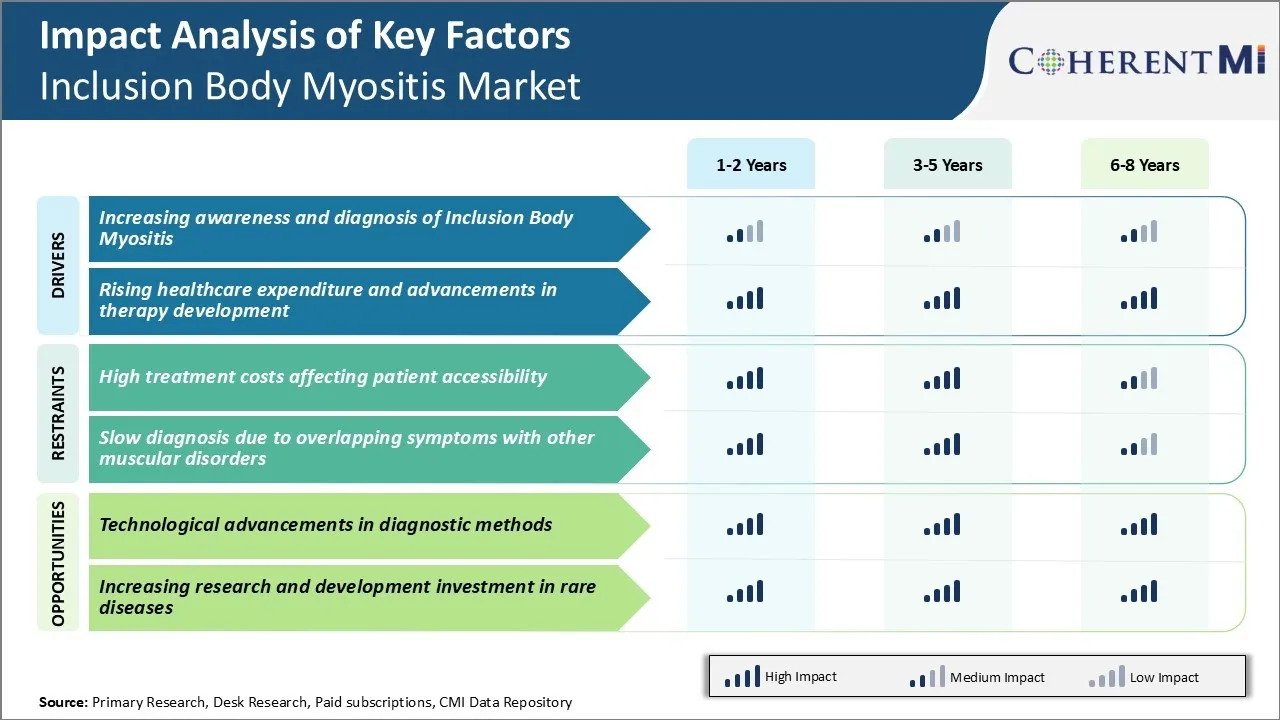
Market Challenge - High Treatment Costs Affecting Patient Accessibility
Inclusion body myositis is a rare muscle disease with no approved treatments available. Currently, the only options for patients are off-label corticosteroids or immunomodulatory drugs which have limited effectiveness. Developing new drugs specifically for IBM is challenging due to the rarity and heterogeneity of the disease.
Clinical trials needed to test new therapies require large sample sizes but recruiting sufficient numbers of eligible patients is difficult. This leads pharmaceutical companies to charge high prices to recoup extensive research and development investments. However, high treatment costs pose a major barrier to patient accessibility.
Many patients struggle to afford expensive medications, which can exacerbate the condition due to lack of proper treatment. Out-of-pocket costs also place a huge financial burden. To expand patient access, new drug development needs to be incentivized while also ensuring affordability and availability to those most in need. Alternative pricing and reimbursement strategies may need to be explored.
Market Opportunity - Technological Advancements in Diagnostic Methods for Market
Recent advances in neuroimaging and molecular diagnostics provide opportunities to enhance the understanding and diagnosis of IBM. New magnetic resonance imaging techniques allow visualization of muscle pathology with higher resolution. Advanced muscle biopsy analysis using immunoassays and DNA sequencing improves identification of diagnostic protein aggregates. Such technological improvements aid in differential diagnosis and earlier disease detection.
As diagnostic certainty and predictability increase, the IBM market is likely to expand. Pharmaceutical companies may feel more confident investing in drug development knowing the target patient population can be identified with greater accuracy.
More widespread use of objective diagnostic tools could also support clinical trial recruitment and enable evaluation of treatment responses. If incorporated into clinical guidelines and practice, new diagnostics change the landscape of IBM patient management and create ground for future market growth.
Prescribers preferences of Inclusion Body Myositis Market
Inclusion Body Myositis (IBM) is a progressive muscle disorder typically treated in a stepwise manner. For early stage IBM with mild symptoms, prescribers often recommend physical/occupational therapy and over-the-counter pain relievers.
As the disease advances to moderate stages with worsening muscle weakness, prescribers may prescribe corticosteroids such as prednisone to reduce inflammation. However, steroids can cause adverse effects with long-term use. Alternatively, immunosuppressants like methotrexate (Rheumatrex) may be tried.
For patients with significant functional impairment in late stages, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) treatments are commonly used. IVIg products prescribed include Gamunex-C, Gammagard, and Octagam. While IVIg provides symptom relief for some, it requires monthly infusions and is very expensive. As a result, cost is a major factor influencing prescribers' preferences here.
If IVIg proves ineffective, prescribers may recommend experimental therapies off-label. These include tumor necrosis factor inhibitors like Enbrel, which can help dampen the overactive immune response thought to underlie IBM pathology. However, side effects and lack of U.S. FDA approval remain concerns limiting widespread adoption. Overall, disease severity, safety, tolerability, cost and clinical evidence tend to be the primary determinants of prescribers' IBM treatment choices.
Treatment Option Analysis of Inclusion Body Myositis Market
Inclusion Body Myositis (IBM) is a progressive muscle disorder characterized by muscle inflammation and weakness. It is divided into three stages based on severity of symptoms:
Early stage (mild symptoms): Physical/occupational therapy is recommended to maintain muscle strength and flexibility. Symptoms can be managed with mild analgesics as needed.
Intermediate stage (moderate symptoms): As muscle weakness increases, immunotherapy may be considered. Low-dose corticosteroids (prednisone) or steroid-sparing immunosuppressants (azathioprine, methotrexate) are most commonly used, either alone or in combination. These aim to reduce muscle inflammation and slow disease progression.
Advanced stage (severe symptoms): Wheeled mobility may be required as walking becomes difficult. Stronger immunotherapy is necessary. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) treatments every 4-6 weeks is the preferred treatment. IVIg contains antibodies that counter abnormal immune system activity in IBM. Brands like Gamunex and Octagam are commonly used. For patients who don't respond adequately to IVIg, experimental mRNA therapies are being researched.
In summary, IBM treatment focuses on symptom management and controlling immune system overactivity. Treatment progresses from mild therapies to stronger immunotherapy as the disease advances from early to intermediate to advanced stages. Goals shift from maintaining strength to preserving function and quality of life.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Inclusion Body Myositis Market
Focus on clinical development for effective treatment options:
- Companies like BioMarin, KPI Therapeutics and Anthropic have focused on advancing their clinical pipeline of drugs to treat IBM. For example, BioMarin started two late-stage clinical trials (Pivot-IB-1 and Pivot-IB-2) in 2018 to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of BMN-250 in slowing disease progression in people with IBM. These Phase 3 trials are still ongoing.
License/acquire promising programs from smaller biotechs:
- In 2021, Roche acquired exclusive rights to a preclinical small molecule program (KPT-9274) from KPI Therapeutics to treat IBM. KPT-9274 showed promising results in preclinical models by reducing inflammation and protein aggregation. This allows Roche to further advance this asset in clinical trials. Such acquisitions allow big pharma companies to strengthen their IBM pipeline without spending on early research.
Establish collaborations for drug development expertise:
- Anthropic partnered with Toleranz Therapeutics in 2020 to leverage each other's capabilities in AI and drug development. This partnership will apply AI/machine learning tools to analyze molecular dynamics simulations and multi-omic datasets to identify potential drug targets for IBM. Successful collaborations help optimize resources and capabilities for productive R&D.
Segmental Analysis of Inclusion Body Myositis Market
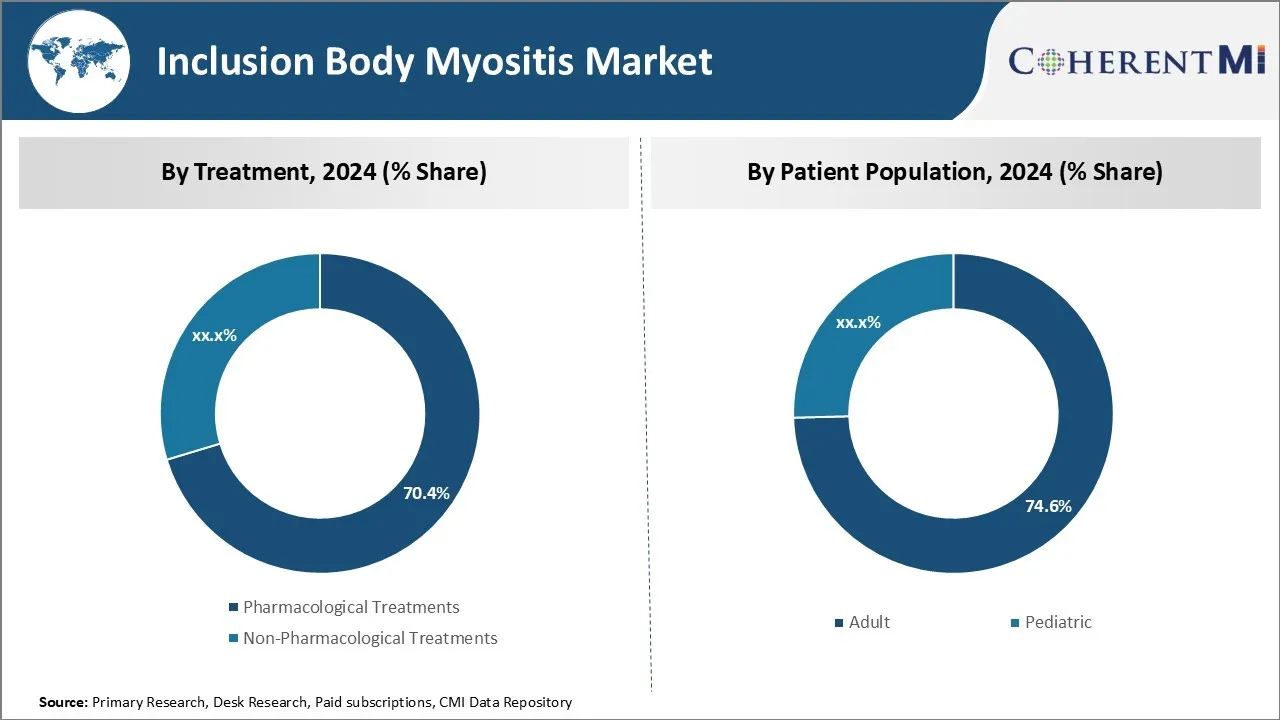
Insights, By Treatment: Pharmacological Treatments High in Demand with Growing Research on Developing Novel Medications
In terms of treatment, pharmacological treatments are expected to hold 70.4% share of the market in 2024, owning to continuous research and development activities focused on developing advanced and effective drug therapies for IBMyositis. While there is no approved drug for the disease currently, several pharmaceutical companies and research institutes are exploring various pharmacological options such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants.
The increasing clinical trials assessing the efficacy of novel molecular entities and biologics for the management of symptoms is a key factor bolstering the adoption of pharmacological treatments. Additionally, the growing awareness among physicians about drug therapies optimizing muscle strength and function is further supporting the demand for medication-based treatment regimens.
Insights, By Patient Population: Preference for Hospital-based Care
In terms of patient population, adult population is projected to account for 74.6% share of the market in 2024, due to their preference for seeking help from hospitals. As IBMyositis symptoms usually manifest among middle-aged and elderly patients, they tend to choose hospital-based treatment over other options.
The advanced care delivery capabilities, availability of specialized equipment and expertise, and patient comfort provided at hospitals make them a reliable treatment avenue for adult patients. Furthermore, complex healthcare requirements of adults with co-existing conditions warrant comprehensive treatment approaches commonly available at hospitals. These factors collectively account for the high concentration of adult patients within the hospital end-user segment.
Insights, By End User: Access to Multidisciplinary Teams
In terms of end user, hospitals contribute the highest share of the market owing to their ability to facilitate access to multidisciplinary healthcare teams. While single physician-led clinics may not have resources to form collaborations between specialists, hospitals bring together neurologists, rheumatologists, physiatrists, nutritionists, physical therapists, and other experts under one roof. This multimodal treatment methodology integrating different specialties has shown benefits in IBMyositis management.
The coordinated care approaches that leverage collective expertise deliver well-rounded support addressing medical, therapeutic, and psychosocial aspects of the disease. Therefore, hospitals are often the preferred choice as they offer consolidated treatment from multi-faceted perspectives, driving their attractiveness among end-users.
Additional Insights of Inclusion Body Myositis Market
- Inclusion body myositis is primarily seen in older adults and is characterized by progressive muscle weakness, particularly in the quadriceps and forearm muscles.
- The United States accounts for the highest diagnosed cases of inclusion body myositis in the 7MM (US, EU5, and Japan), and this trend is expected to increase over time due to aging populations.
- Patients with Inclusion Body Myositis often face delays in diagnosis due to the rarity of the disease and its symptom overlap with other conditions such as polymyositis. Awareness campaigns launched by several organizations aim to mitigate this challenge.
- The prevalence of Inclusion Body Myositis is increasing, particularly among the elderly population in North America and Europe. The U.S. alone accounts for nearly 40% of the total diagnosed cases globally.
Competitive overview of Inclusion Body Myositis Market
The major players operating in the Inclusion body myositis market include Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Eli Lilly and Company, AbbVie Inc., Novartis AG, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Orphazyme, Viela Bio, Sanofi, and Amgen.
Inclusion Body Myositis Market Leaders
- Pfizer Inc.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Eli Lilly and Company
- AbbVie Inc.
- Novartis AG
Inclusion Body Myositis Market - Competitive Rivalry

Inclusion Body Myositis Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Inclusion Body Myositis Market
- In June 2024, Pfizer Inc. initiated a clinical trial for a novel drug targeting muscle inflammation in Inclusion Body Myositis, aiming to improve mobility and reduce symptoms.
- In March 2023, GlaxoSmithKline plc announced a strategic partnership with smaller biotech firms to accelerate the development of innovative therapies for rare muscle disorders, including Inclusion Body Myositis. GSK has been active in various research areas related to rare diseases, and Inclusion Body Myositis is recognized as a rare inflammatory muscle disorder that continues to be a focus for potential therapeutic developments.
- In February 2023, Alexion Pharmaceuticals reported positive clinical trial data for a new monoclonal antibody targeting myositis-specific antigens, expected to reduce inflammation significantly. Furthermore, Alexion, a part of AstraZeneca's Rare Disease division, has been actively involved in developing monoclonal antibodies for rare diseases, particularly in complement system biology. Recent developments have focused on treatments for conditions such as paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and transthyretin-mediated amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM).
- Orphazyme had been conducting a Phase II/III clinical trial of arimoclomol, a drug designed to address protein aggregation, specifically for inclusion body myositis (IBM). This trial was initiated earlier and concluded before 2022. Unfortunately, by March 2021, the company announced that the trial did not meet its primary and secondary endpoints in IBM patients.
Inclusion Body Myositis Market Segmentation
- By Treatment
- Pharmacological Treatments
- Non-Pharmacological Treatments
- By Patient Population
- Adult
- Pediatric
- By End User
- Hospitals
- Clinics

Would you like to explore the option of buyingindividual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the inclusion body myositis market?
The inclusion body myositis market is estimated to be valued at USD 527.5 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 767.1 Mn by 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the inclusion body myositis market?
High treatment costs affecting patient accessibility and slow diagnosis due to overlapping symptoms with other muscular disorders are the major factors hampering the growth of the inclusion body myositis market.
What are the major factors driving the inclusion body myositis market growth?
Increasing awareness and diagnosis of inclusion body myositis and rising healthcare expenditure and advancements in therapy development are the major factors driving the inclusion body myositis market.
Which is the leading treatment in the inclusion body myositis market?
The leading treatment segment is pharmacological treatments.
Which are the major players operating in the inclusion body myositis market?
Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Eli Lilly and Company, AbbVie Inc., Novartis AG, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Orphazyme, Viela Bio, Sanofi, and Amgen are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the inclusion body myositis market?
The CAGR of the inclusion body myositis market is projected to be 5.5% from 2024-2031.