Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market is segmented By Type of Treatment (CT-scan, MRI, Angiography, ECG), By Patient Type (Geriatric, Middle-Age Adults, You....
Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR5.23%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 5.23% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | GNT Pharma, ZZ Biotech LLC, JIXING Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Meridigen Biotech Co., Ltd. and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market Analysis
The Global Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.41 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.21 Billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.23% from 2024 to 2031. The increasing geriatric population who are more prone to strokes, rising prevalence of risk factors such as obesity, high blood pressure and smoking are expected to drive the demand for new treatment options and bolster the growth of this market during the forecast period.
The market is witnessing positive trends such as increasing research and development activities in this field. Many pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in developing new drugs and treatment options to treat ischemic strokes. Also, growing awareness among people about treatment options and early diagnosis is helping patients seek medical help in time. This is further supporting the growth of this pipeline market. The ischemic stroke pipeline market is expanding with innovative therapies aimed at improving outcomes for patients who suffer from strokes caused by blood clots. Current treatments include thrombolytics like tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and mechanical thrombectomy. However, ongoing research is focused on developing novel drugs that target neuroprotection, inflammation reduction, and clot-busting mechanisms. Stem cell therapies and gene therapies are also being explored. The pipeline is driven by increasing stroke incidence, aging populations, and unmet clinical needs. Despite promising developments, challenges include regulatory hurdles, high costs, and the need for faster treatment delivery to improve patient survival and recovery.
Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market Trends
Market Driver - Growing Global Prevalence of Ischemic Stroke and the Need for Novel Neuroprotective Therapies.
The global burden of ischemic stroke continues to rise each year. As per the World Health Organization, stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide and a leading cause of disability. The ageing population coupled with increasing prevalence of risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and obesity has contributed significantly to the growing incidence of ischemic stroke in recent times. It is estimated that more than 17 million people suffer a stroke each year and over 33 million people are living with the effects of stroke globally.
Currently, the only FDA approved therapy for acute ischemic stroke is alteplase (recombinant tissue plasminogen activator). However, it has a very narrow therapeutic window of just 4.5 hours from symptom onset. Many patients do not get to the hospital in time to receive this thrombolysis therapy. Additionally, alteplase is not completely effective and around 30-40% of patients do not achieve reperfusion after treatment. There remains a huge unmet need for effective neuroprotective therapies that can reduce brain injury in stroke patients and improve long term functional outcomes, even in the absence of reperfusion.
Several biopharmaceutical companies and research institutions are investing heavily in developing novel agents targeting neuroprotection in ischemic stroke. Some of the promising new treatment approaches in clinical trials include drugs modulating inflammatory response, excitotoxicity, apoptosis, oxidative stress pathways and upstream regulators of these cascades.
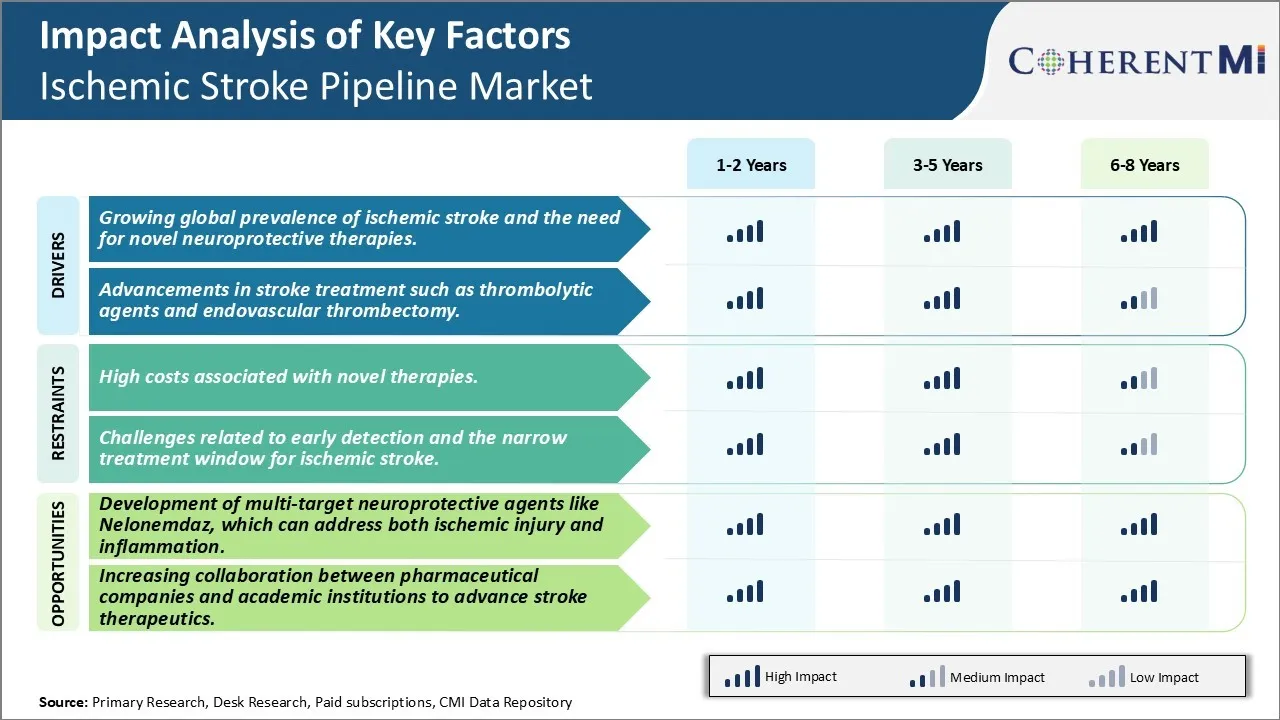
Market Driver - Advancements in Stroke Treatment to Boost Industry Developments.
Over the past few decades, major improvements have been made to the management of acute stroke. The introduction of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase revolutionized the treatment paradigm over two decades ago. More recently, endovascular thrombectomy has emerged as a very effective mechanical option for clearing blood clots, especially for large vessel occlusions. Multiple randomized controlled trials have demonstrated the superiority of thrombectomy in improving functional outcomes when performed within 6-24 hours of stroke onset in carefully selected patients.
As interventional technologies progress, stent retrievers and aspiration catheters now allow more rapid, complete and safer recanalization compared to older devices. Several trials are also evaluating extending the treatment window for mechanical thrombectomy up to 24 hours or using imaging to select patients beyond conventional guidelines. There is also a shift towards using direct aspiration first pass techniques which have demonstrated higher recanalization rates. Such advances continuously help improve treatment rates and outcomes in the modern endovascular era.
Furthermore, a few combination therapies evaluating thrombolysis followed by thrombectomy are ongoing. Preliminary results indicate such an integrated approach may optimize revascularization. Additionally, adjunctive neuroprotective agents are being investigated as part of combination strategies to potentially improve functional recovery. Overall, continuous improvements to reperfusion therapies as well as development of neuroprotective drugs hold promise to further transform the management landscape for acute ischemic stroke going forward.
Market Challenge - High Costs Associated with Novel Therapies Might Hinder Market Growth.
The ischemic stroke pipeline is currently facing significant challenges related to the high costs associated with novel therapy development and commercialization. Stroke therapeutics often target complex biological pathways involved in neuroinflammation, excitotoxicity, and neuronal cell death following ischemia. Developing drugs that can safely and effectively modulate these pathways requires extensive research and clinical testing. This lengthy and expensive R&D process has resulted in novel stroke therapies having extremely high price tags. For example, the novel thrombectomy devices used for minimally invasive mechanical clot retrieval have an average hospital procedure cost of over USD 30,000. Likewise, biologic therapies such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) also used for acute ischemic stroke treatment have an average list price of over USD 4,500.
Such high costs have made these novel therapies inaccessible or unaffordable for many patients. This has significantly limited their clinical utilization and penetration into the potential target patient population. It has also put pressure on healthcare systems and private insurers to cover the costs. Addressing these challenges of prohibitive pricing will be important for the long-term viability and growth of the stroke therapeutics pipeline. Developers will need to explore novel mechanisms to recoup R&D investments while also ensuring affordability and accessibility of future approved products.
Market Opportunity- Development of Multi-Target Neuroprotective Agents Like Nelonemdaz, Which Can Address Both Ischemic Injury and Inflammation.
Significant opportunities exist within the stroke therapeutics pipeline with the development of novel multi-target neuroprotective agents. Drugs that can safely and effectively modulate multiple biological pathways involved in ischemic injury hold promise to provide more effective options for stroke patients. Nelonemdaz is a prime example of such a promising multi-target candidate currently in clinical trials. Nelonemdaz is thought to provide neuroprotection through a combination of anti-inflammatory and anti-excitotoxic effects. It targets glutamate release, blocks NMDA receptors, and reduces inflammation following ischemia. In preclinical models, Nelonemdaz administered up to 12 hours post stroke onset demonstrated significant reductions in infarct volume. If ongoing phase 2/3 studies demonstrate Nelonemdaz's safety and efficacy in patients, it could emerge as an important new treatment option. More broadly, its multi-target mechanism represents an opportunity for developers to address the core pathologies of stroke more comprehensively compared to prior single target agents. This may finally enable shifting the treatment paradigm beyond the narrow window currently possible with thrombolytics alone.
Prescribers preferences of Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market
The primary line of treatment for ischemic stroke involves reducing damage to brain cells and minimizing long-term disability. In the acute stage (within 4.5 hours of onset), prescribers prefer administering tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) such as Alteplase to break up blood clots. This is the only FDA-approved medication for disrupting clots in the acute phase.
During the subacute recovery stage (4.5 hours to 10-14 days), managing secondary complications like edema and neuroinflammation is key. Antiplatelet drugs like Clopidogrel (Plavix) and Aspirin are widely prescribed to prevent additional clots from forming. For severe edema, short-term steroids like Dexamethasone are utilized. Minimizing neuroinflammation is tackled using drugs such as Minocycline.
In the post-acute stage (after 2+ weeks), preventing recurrence and reducing disability are priorities. Antihypertensives and statins like Atorvastatin (Lipitor) are routinely recommended for long-term secondary prevention. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) like Fluoxetine (Prozac) may be prescribed to treat post-stroke depression and anxiety. For motor deficits, dopamine agonists like Pramipexole are becoming increasingly favored.
Comorbidities, severity of initial deficits, and age heavily influence prescribers' decisions across different stages. Patient compliance also impacts medication choices, favoring once-daily oral options over frequent injections when possible.
Treatment Option Analysis of Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market
Ischemic stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is blocked by a clot. Treatment depends on the stage and severity of the stroke. Immediately after onset, the goal is restoring blood flow. For mild cases within 4.5 hours, a single drug such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA, alteplase brand) may be given intravenously to dissolve the clot. For more severe strokes, mechanical thrombectomy—surgically removing the clot—is best. This involves inserting a catheter with a retriever stent into the blocked artery. Studies show better outcomes with prompt thrombectomy plus tPA compared to tPA alone.
After the acute period, prevention of future strokes is key. For non-cardioembolic strokes, antiplatelet drugs like aspirin or clopidogrel (Plavix brand) are usually continued long-term. For cardioembolic strokes due to atrial fibrillation, anticoagulants such as warfarin (Coumadin brand) or a direct-acting oral anticoagulant like apixaban (Eliquis brand) reduce risk. Statins are also prescribed to lower cholesterol. Patients may need lifestyle changes like quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure, and managing other vascular risk factors.
Rehabilitation with physical/occupational/speech therapy aims to regain lost functions and prevent disabilities in activities of daily living. For residual neurological deficits, nimodipine (Nimotop brand) may aid recovery in the subacute period. Depression is also common, treated initially with SSRIs. Long-term management focuses on secondary prevention to avoid recurrence.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market
Focus on Developing Novel Therapies: Companies are investing heavily in R&D to develop novel, first-in-class drugs that can effectively treat ischemic stroke with minimal side effects. For example, Biohaven Pharmaceuticals is developing rimegepant, a CGRP receptor antagonist, for treatment of acute ischemic stroke. If approved, it will be the first drug approved for acute treatment.
Targeting Multiple Mechanisms: Given the complex pathogenesis of ischemic stroke, players are developing drugs that target multiple pathways involved in the disease. For example, Daiichi Sankyo's mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) aims to promote neuronal survival via multiple mechanisms such as anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammation. Targeting multiple pathways can offer more comprehensive treatment.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships: Companies are partnering or acquiring firms that have promising drug candidates to strengthen their pipeline. For example, in 2020 Roche acquired Athira Pharma to gain access to Athira's lead compound ATH-1017, a small molecule therapeutic targeting HGF/MET neuroprotective signaling pathway in ischemic stroke.
Focus on stroke subtypes: Rather than treating all strokes alike, companies risk-stratify patients and develop therapies for well-defined subgroups. For instance, Amgen is evaluating AMG901/KY1044 in large vessel occlusion strokes, which account for nearly 20% of all ischemic strokes. Targeting subtypes allows for more personalized care.
These strategies have helped companies gain significant first-mover advantage and achieve key clinical and regulatory milestones ahead of competition. For example, Roche/Genentech's Avagacestat was the first drug in over 25 years to show positive Phase-3 results for acute ischemic stroke, demonstrating the success of its large R&D investments.
Segmental Analysis of Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market
Insights, By Type of Treatment, CT-scan Early Detection & Diagnosis Facilitate Targeted Treatment.
By Type of Treatment, CT-scan is expected to contribute the highest share 51.2% in 2024 owing to its ability to effectively detect ischemic stroke at an early stage. CT-scans produce detailed images of the brain and surrounding structures which helps identify areas of dead or damaged tissue resulting from a blockage or burst blood vessel. The high-resolution images provided by CT-scans enable physicians to quickly determine the exact location and size of clots or bleeds. This early detection allows for timely administration of clot-busting drugs such as tPA which must be given within 3-4.5 hours of symptom onset to be effective. CT-scans also help rule out hemorrhagic strokes which require different medical management compared to ischemic strokes. Overall, the rapid diagnostics and accurate localization of clots facilitated by CT-scanning aids targeted clinical intervention and improves treatment outcomes for ischemic stroke patients.

Insights, By Patient Type, Increased Susceptibility with Age Drives Higher Prevalence in Geriatric Population.
By patient type, geriatric patients are expected to contribute the highest share 55.4% in 2024 due to age-related risk factors that elevate their susceptibility to ischemic strokes. The chance of having a stroke approximately doubles every decade after age 55. As people age, their arteries tend to narrow and harden from accumulation of plaque, increasing the likelihood of clots or restricted blood flow. Other common conditions in older adults such as high blood pressure, diabetes, atrial fibrillation and lifestyle habits like smoking further compound the risks. Physiological weakening of arteries also makes them more prone to ruptures as one grows older. With improved healthcare and lifestyle, life expectancy has risen globally but aging populations mean greater proportions will suffer from age-related diseases including strokes. This demographic trend continues propelling the geriatric segment.
Insights, By End-user, Hospitals at the Forefront of Stroke Management
By end-user, hospitals account for the largest share owing to their round-the-clock emergency facilities and specialized stroke units. Most ischemic stroke cases experience sudden onset of symptoms requiring immediate medical attention. Hospitals are optimally equipped with emergency departments, diagnostic technologies, stocks of thrombolytic drugs, neuro-intervention suites and trained stroke teams that can promptly attend to patients. They also have the infrastructure for long-term care of patients with residual deficits including rehabilitation therapies. Post-stroke care coordination is also more robust in hospitals with multidisciplinary teams of neurologists, physiatrists, nurses, therapists overseeing recovery. As the frontlines of stroke treatment, hospitals play a pivotal role right from emergency response and acute intervention to management of long-term health issues. This positions them at the core of ischemic stroke case management.
Additional Insights of Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market
The ischemic stroke market is witnessing significant advancements in therapeutic options, particularly with the development of neuroprotective agents that aim to reduce the extent of brain damage following a stroke. One such promising agent is Nelonemdaz, a multi-target drug being developed by GNT Pharma. This drug not only inhibits NMDA receptors but also scavenges free radicals, addressing both excitotoxicity and oxidative stress, two critical factors in stroke-induced brain damage. Similarly, ZZ Biotech’s 3K3A-APC focuses on protecting the integrity of the brain’s microvasculature, reducing the risk of hemorrhage during thrombolytic treatment. Another notable development is AbbVie’s Elezanumab, which targets nerve regeneration by inhibiting repulsive guidance molecule A (RGMa), promoting recovery in stroke patients. These drugs, in combination with existing thrombolytic treatments and mechanical thrombectomy, represent a shift toward comprehensive stroke care. The market is also characterized by a growing number of collaborations and partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and academic research institutions, highlighting the importance of collective efforts in addressing the unmet needs of stroke therapy.
Competitive overview of Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market
The major players operating in the Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market include GNT Pharma, ZZ Biotech LLC, JIXING Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Meridigen Biotech Co., Ltd., Athersys Inc., Novartis, Biogen, Ferrer Internacional and Boehringer Ingelheim.
Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market Leaders
- GNT Pharma
- ZZ Biotech LLC
- JIXING Pharmaceuticals
- AbbVie
- Meridigen Biotech Co., Ltd.
Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market
- In May 2024, GNT Pharma's Nelonemdaz, a neuroprotective agent, showed promising results in Phase III trials for treating ischemic stroke. The drug aims to reduce brain damage by inhibiting calcium influx and scavenging free radicals, thus preventing stroke-related neuronal injury.
- In April 2024, ZZ Biotech announced that its drug 3K3A-APC entered Phase III trials for ischemic stroke. 3K3A-APC aims to improve outcomes by protecting the brain’s microvascular integrity and preventing hemorrhage.
- In March 2024, AbbVie's Elezanumab (ABT-555) completed Phase II studies targeting nerve growth inhibition pathways in ischemic stroke patients, aiming to promote neuroregeneration and recovery.
Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market Segmentation
- By Type of Treatment
- CT-scan
- MRI
- Angiography
- ECG
- By Patient Type
- Geriatric
- Middle-Age Adults
- Young Adults
- Pediatric
- By End-user
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Clinics
- Home Care Settings
- Emergency Medical Services (EMS)

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market?
The Global Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.41 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.21 Billion by 2031.
What will be the CAGR of the Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market?
The CAGR of the Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market is projected to be 5.23% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market?
The high costs associated with novel therapies and challenges related to early detection and the narrow treatment window for ischemic stroke are the major factor hampering the growth of the Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market.
What are the major factors driving the Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market growth?
The growing global prevalence of ischemic stroke and the need for novel neuroprotective therapies and advancements in stroke treatment such as thrombolytic agents and endovascular thrombectomy are major factors driving the Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market.
Which is the leading Type of Treatment in the Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market?
CT-scan is the leading type of treatment segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Ischemic Stroke Pipeline Market?
GNT Pharma, ZZ Biotech LLC, JIXING Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Meridigen Biotech Co., Ltd., Athersys Inc., Novartis, Biogen, Ferrer Internacional, Boehringer Ingelheim are the major players.