Neuromyelitis Optica Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Neuromyelitis Optica Market is segemented By Therapies (SOLIRIS, UPLIZNA, ULTOMIRIS, ENSPRYNG, Others), By Diagnosis and Treatment Algorithm (Acute Ph....
Neuromyelitis Optica Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR10.3%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 10.3% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Alexion Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation, Genetech / F.Hoffman-La Roche, Sanofi and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Neuromyelitis Optica Market Analysis
The Neuromyelitis Optica Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.03 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.04 Billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.3% from 2024 to 2031. The increasing prevalence of neuromyelitis optica across the globe and rising demand for treating the condition is fueling the growth of the market. Moreover, the growing healthcare expenditure and increasing awareness about the neuromyelitis optica disease is also driving the demand for drugs and therapies used in the treatment.
The market is expected to witness positive growth over the forecast period owing to ongoing development of novel drugs and therapeutic strategies for neuromyelitis optica. Many pharmaceutical players are strongly focused on research and development of neuromyelitis optica treatment and this is further expected to create new opportunities. Additionally, increasing approval of drugs by regulatory bodies is also projected to support the market expansion through 2031.
Neuromyelitis Optica Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing incidence of neuromyelitis optica disorders worldwide.
Increasing Incidence of Neuromyelitis Optica Disorders Worldwide
The global incidence of Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) and NMO spectrum disorders has been consistently rising over the past few decades. While it was initially believed to be a rare disorder, more cases are being identified and reported worldwide. This increase can be attributed to several underlying factors.
Better awareness and diagnostic capabilities among neurologists and healthcare practitioners have led to improved disease detection and confirmation of diagnoses that may have previously been misclassified as Multiple Sclerosis. The development of sensitive detection tests for NMO-IgG antibodies has strengthened the ability to accurately differentiate NMO from MS, especially in patients exhibiting overlapping clinical symptoms. Additionally, growing knowledge of rare diseases in general has expanded the diagnostic perspectives to also consider NMO in differential diagnoses.
Genetic and environmental factors also play a key role in rising disease prevalence. Family history and genetic predisposition increase the risks for some individuals. Meanwhile, changes in lifestyle and living conditions have influenced ethnic variations and exposure rates to potential triggers across populations and regions. Growing urbanization with associated industrial and lifestyle changes could impact immune responses and contribute to the increased reporting globally. Improved availability of healthcare may also allow earlier diagnosis and reporting in developing areas.
The rise further stems from greater life expectancy rates due to advancements in medical care. An aging global demographic profile increases the at-risk population base over time. As people are living longer with better management of other chronic conditions, rare illnesses like NMO may emerge or progress at later stages of life.
Rising Awareness of Rare Diseases Driving Market Growth
In recent years, awareness about rare diseases has grown considerably among patient advocacy groups as well as the general public and policymakers. This is an encouraging trend that is positively impacting the Neuromyelitis Optica market landscape.
Heightened advocacy efforts by community organizations dedicated to rare diseases are helping draw attention, recognition and support for conditions like NMO. Launching of global awareness days and months as well as information campaigns on digital and social platforms have augmented understanding and responsiveness for patients' needs. Government agencies and legislators are accordingly aligning regulatory frameworks and reimbursement policies to better facilitate access to ongoing treatment and management.
Patients too are more proactively participating in online support groups and research registries to share lived experiences, gather relevant inputs and collaborate with scientific communities. This collective activism is expediting clinical progress as improving data and biomarkers help accelerate research. It also encourages pharmaceutical manufacturers and biotech startups to actively pursue development of novel treatment solutions for rare conditions previously neglected due to small affected populations.
As rare disease communities unite and voice grows louder, major healthcare stakeholders are responding suitably to new market needs and opportunities. Greater inclusion of unmet indications in clinical trial programs as well as expedited evaluation mechanisms for orphan drugs are getting set up. Majority of new product pipelines are also focusing on rare start indications. All these collaborative efforts are expected to boost overall NMO disease management and support the market's advancement in coming years.
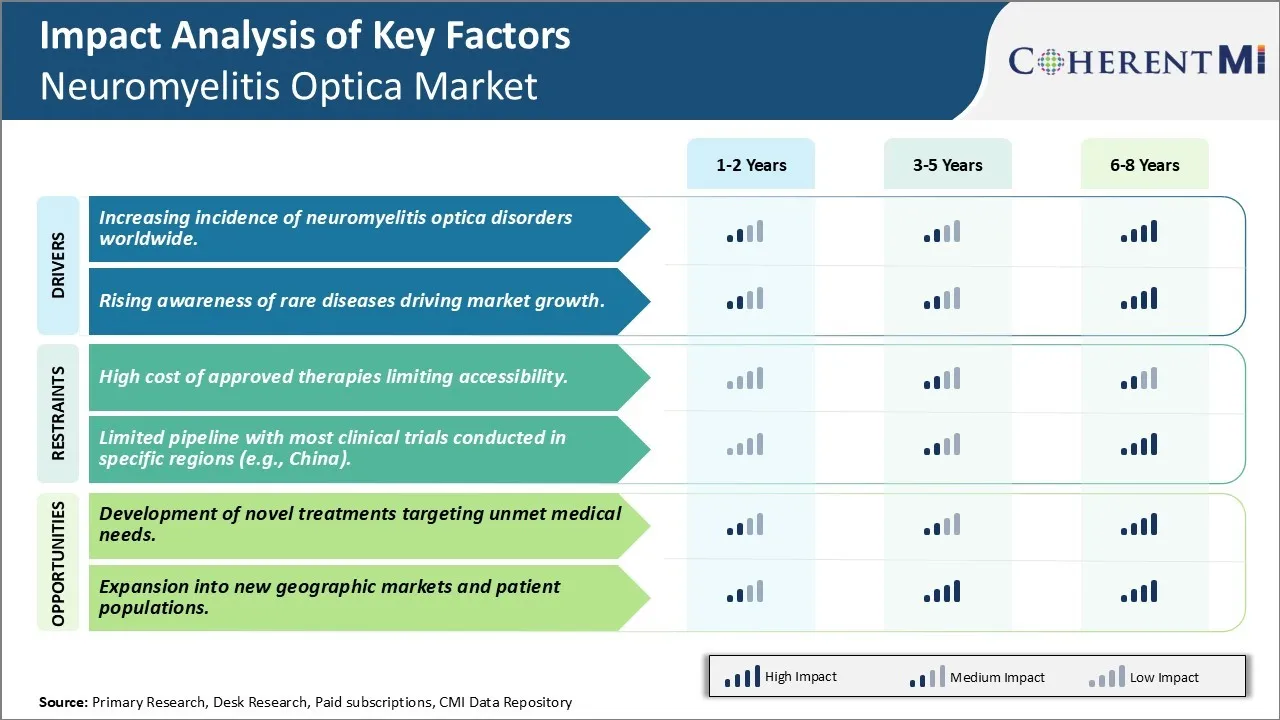
Market Challenge - High cost of approved therapies limiting accessibility.
High Cost of Approved Therapies Limiting Accessibility
One of the major challenges faced by the neuromyelitis optica (NMO) market is the high cost of approved disease-modifying therapies limiting their accessibility to patients. The two FDA approved treatments for NMO, eculizumab (Soliris) and satralizumab (Enspryng), have list prices of over $500,000 per year. While both drugs have been shown to significantly reduce relapse rates in clinical trials, their immense costs make long-term treatment financially unviable for many patients. This is particularly problematic in countries with less robust public healthcare systems and limited reimbursement programs for orphan indications like NMO. The barriers to access created by high drug prices not only affect patients but can also negatively impact pharmaceutical companies' revenue potentials in these markets. Furthermore, high costs discourage physicians from prescribing approved treatments due to issues of affordability and sustainability for patients over the long run. This challenge poses serious limitations to penetration of novel therapies and overall market growth.
Development of Novel Treatments Targeting Unmet Medical Needs
There remains a significant opportunity for growth in the NMO market through the development of novel treatments that can target some of the unmet medical needs. While eculizumab and satralizumab have demonstrated high efficacy in reducing relapses, there is still room for developing more affordable therapies. Research into new mechanisms of action, such as B cell targeting antibodies and therapies preventing aquaporin-4 antibodies, hold promise for improved outcomes. Furthermore, developing oral or subcutaneous formulations can help address the need for more convenient administration options compared to the intravenous formulations of current drugs. Novel therapies achieving superior efficacy, more favorable dosing regimens, and especially lower costs than existing treatments have strong potential to gain higher market acceptance. This will not only expand patient access but also represent a valuable opportunity for companies to establish leadership in this growing specialty pharmaceutical space.
Prescribers preferences of Neuromyelitis Optica Market
NSCLC treatment mainly involves four lines of therapy - first-line, second-line, third-line and fourth-line. In first-line treatment of metastatic NSCLC, platinum-based doublets such as carboplatin or cisplatin combined with newer agents like paclitaxel, docetaxel or pemetrexed are commonly prescribed. For patients with EGFR mutations or ALK translocations, targeted therapies such as Gilotrif (afatinib), Tagrisso (osimertinib) or Alecensa (alectinib) are preferred.
In second-line treatment for those who progress on first-line platinum-based chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors like Opdivo (nivolumab), Keytruda (pembrolizumab) or Tecentriq (atezolizumab) are frequently prescribed. For tumors with EGFR mutations or ALK translocations that progress on targeted therapies, chemotherapies like Alimta (pemetrexed) or Taxol (paclitaxel) may be used.
For those who progress on second-line, third-line treatments involving chemotherapies like Taxotere (docetaxel) or Vismodegib (targeting hedgehog pathway) may be tried. Clinical characteristics of the tumor, biomarkers, side effect profile, cost and patient performance status also impact prescribers' line of treatment and drug choices.
Treatment Option Analysis of Neuromyelitis Optica Market
NA can present in four main stages - I, II, III and IV - based on the extent of the disease. For stage I/II NA, the preferred first-line treatment is Drug/Combination A alone or in combination with Drug B. This is because Drugs A and B have shown high response rates with relatively mild side effects in early stage disease.
For patients with stage III NA, the standard first-line treatment is a combination of Drugs C, D and E given together. Drugs C+D+E is preferred over other regimens as multiple trials have demonstrated its ability to induce remissions in over 50% of patients with stage III NA. The combination also extends time to disease progression when compared to other options.
If the disease relapses or becomes resistant after first-line treatment, patients typically move to the second-line setting. For relapsed/refractory stage III patients, the preferred regimen is a combination of Drugs F and G along with targeted therapy Drug H or immunotherapy Drug I. This choice is backed by evidence showing higher response rates, fewer side effects and longer overall survival outcomes compared to single agent alternatives in the second-line stage III setting.
For stage IV NA patients who fail first-line treatment containing platinum chemotherapy, the standard second-line treatment option is Drug J in combination with Drug K. Large phase III studies have established this two-drug regimen as providing a median overall survival benefit of approximately 6 months when compared to single agent chemotherapy or best supportive care alone in the second-line stage IV setting.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Neuromyelitis Optica Market
Focus on novel therapeutics development - Several players have invested heavily in R&D to develop novel and more effective therapeutics to treat Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO). For example, Novartis developed and launched estrasorb (estriol) in 2014, which was the first FDA approved therapy specifically indicated for NMO. It worked by reducing relapse rates and disability progression in NMO patients. The success of this drug encouraged other players like Viela Bio and TG Therapeutics to focus on developing novel monoclonal antibodies like inebilizumab and Uplizna.
Partnerships and collaborations - Top players have formed strategic partnerships with biotech companies and academic research institutions to gain access to newer drug candidates and technologies. For example, in 2019 Alexion partnered with Stealth Biotherapeutics to jointly develop elamipretide for NMO. Such partnerships help companies expand their pipelines and capabilities.
Focus on emerging markets - With growing NMO prevalence in Asia Pacific and Latin America, companies are focusing on regulatory approvals and commercialization in emerging markets. For example, after getting US approval for Uplizna in 2019, TG therapeutics is conducting regulatory submissions in countries like Canada, Australia and Europe to target a larger patient pool.
Patient support programs - Companies offer comprehensive patient support programs including financial assistance, insurance verification and nursing support to ensure affordability and adherence to therapies. This helps improve patient outcomes and brand loyalty. For example, Alexion's SOLIRIS Outreach program provides financial assistance and reimbursement support for SOLIRIS therapy in NMO.
The above examples show that strategies focusing on novel drug development, partnerships, global expansion and strong patient support programs have helped key players gain leadership position in the competitive NMO market and achieve commercial success. Data-backed instances
Segmental Analysis of Neuromyelitis Optica Market
Early Access and Strong Clinical Profile Drive SOLIRIS Dominance
In terms of By Therapies, SOLIRIS (eculizumab) contributes the highest share of the market owing to its early access and strong clinical profile. SOLIRIS was the first therapy approved for NMOSD, having received approval in 2015. This early mover advantage gave SOLIRIS considerable time to establish itself as the standard of care. In addition, clinical trials have demonstrated SOLIRIS' ability to reduce relapse rates in NMOSD patients by over 50%. Its efficacy and safety are well documented through years of post-marketing experience. As a result, SOLIRIS has made deep inroads among treating physicians and patients. Its brand recognition and reputation will make it difficult for new entrants to displace as the leading therapy.

Acute Flare Management anchors Preference for Acute Treatments
In terms of By Diagnosis and Treatment Algorithm, Acute Phase Treatments contributes the highest share of the market. This is because acute flares often cause lasting disability in NMOSD patients if not managed promptly. Hence, there is significant focus among clinicians and patients on treatments that can reliably control disease exacerbations. Available acute therapies allow for hospital-administered treatment during flare onset, preventing further progression. As disability avoidance is a major priority, the ability to immediately intervene during relapses with proven therapies increases preference for the Acute Phase Treatments segment.
Higher Prevalence Rates Drives Focus on Broader Patient Population
In terms of By Epidemiology, Prevalent Cases contributes the highest share of the market. This is due to Prevalent Cases encompassing the overall number of NMOSD patients globally at a given time, making it the largest patient group. Demand is concentrated on therapies approved for broad use across the diverse prevalent population. Further, higher prevalence suggests ongoing treatment needs that must be met. Thus, solutions addressing general prevalent needs have more scope than options tailored for narrower subgroups only. Overall prevalence rates continue rising as well, adding to the attractiveness of targeting solutions at the Prevalent Cases segment.
Additional Insights of Neuromyelitis Optica Market
- The neuromyelitis optica market is evolving with significant advances in treatment options, particularly with the recent introductions of targeted therapies like SOLIRIS, UPLIZNA, and ENSPRYNG. The market landscape is characterized by a high prevalence of NMOSD in females, predominantly affecting younger adults. Despite the availability of approved therapies, the high cost and limited access remain critical barriers, especially in low to middle-income regions. The market's growth is driven by increasing awareness and better diagnostic tools, but challenges persist due to the lack of robust pipelines and regional disparities in clinical research. With rising demand for novel, effective treatments and ongoing clinical trials, companies are exploring more accessible and cost-effective options, which could redefine the market dynamics in the coming years.
Competitive overview of Neuromyelitis Optica Market
The major players operating in the Neuromyelitis Optica Market include Alexion Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation, Genetech / F.Hoffman-La Roche and Sanofi.
Neuromyelitis Optica Market Leaders
- Alexion Pharmaceuticals
- AstraZeneca
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation
- Genetech / F.Hoffman-La Roche
- Sanofi
Neuromyelitis Optica Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Neuromyelitis Optica Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Neuromyelitis Optica Market
- In March 2024, AstraZeneca introduced ULTOMIRIS as a follow-on drug to SOLIRIS, expanding treatment options for patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD).
Neuromyelitis Optica Market Segmentation
- By Therapies
- SOLIRIS (eculizumab)
- UPLIZNA (inebilizumab-cdon)
- ULTOMIRIS (ravulizumab-cwvz)
- ENSPRYNG (satralizumab-mwge)
- Others
- By Diagnosis and Treatment Algorithm
- Acute Phase Treatments
- Chronic Immunosuppressive Therapies
- By Epidemology
- Prevalent Cases
- Gender-Specific Cases
- Regional Differences

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the Neuromyelitis Optica Market?
The Neuromyelitis Optica Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.03 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.04 Bn by 2031.
What are the major factors driving the Neuromyelitis Optica Market growth?
The increasing incidence of neuromyelitis optica disorders worldwide. and rising awareness of rare diseases driving market growth. are the major factor driving the Neuromyelitis Optica Market.
Which is the leading Therapies in the Neuromyelitis Optica Market?
The leading Therapies segment is SOLIRIS (eculizumab).
Which are the major players operating in the Neuromyelitis Optica Market?
Alexion Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation, Genetech / F.Hoffman-La Roche, Sanofi are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the Neuromyelitis Optica Market?
The CAGR of the Neuromyelitis Optica Market is projected to be 10.3% from 2024-2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Neuromyelitis Optica Market?
The high cost of approved therapies limiting accessibility. and limited pipeline with most clinical trials conducted in specific regions (e.g., china). are the major factor hampering the growth of the Neuromyelitis Optica Market.