Optic Neuritis Treatment Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Optic Neuritis Treatment Market is segmented By Type (Oral Corticosteroids, Intravenous Corticosteroids, Others), By End-user (Hospitals, Research Fa....
Optic Neuritis Treatment Market Size
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR6.10%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 6.10% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | AbbVie Inc., Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Bausch Health, Merck & Co, Pfizer and Among Others |
please let us know !
Optic Neuritis Treatment Market Analysis
The Global Optic Neuritis Treatment Market is estimated to be valued at USD 250.1 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 320.4 Mn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.10% from 2024 to 2031.
The Optic Neuritis Treatment Market is witnessing positive trends in the recent years. With rising cases of optic neuritis diseases globally, driven by increasing inflammatory and viral disorders, the demand for effective optic neuritis treatment drugs and therapies is growing. In addition, several pharmaceutical companies and biotech startups investing heavily in R&D of novel drugs to treat optic neuritis more effectively. However, high costs of treatment and drugs remains a challenge for widespread adoption of treatment options. If drug development companies succeed in developing low-cost generic versions of existing high-priced drugs, it can boost the market in the coming years. Overall, the future looks positive for Optic Neuritis Treatment Market with technological advancements and growing healthcare investments in various countries worldwide.
Optic Neuritis Treatment Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Prevalence of Optic Neuritis Related to Autoimmune Diseases Like Multiple Sclerosis.
The increasing prevalence of optic neuritis globally, especially those associated with autoimmune diseases like Multiple Sclerosis (MS) has been a key driver augmenting the growth of optic neuritis treatment market. Optic neuritis is an inflammation of the optic nerve leading to temporal or permanent vision loss and pain in the affected eye. It is highly prevalent in patients affected with multiple sclerosis where it is one of the earliest and most common symptoms presenting in about 25-50% of MS patients.
With nearly 2.3 Mn people affected by multiple sclerosis worldwide, its prevalence has been rising gradually over the years. For instance, according to various studies and surveys, the prevalence rate of MS in North America and European countries such as United States, Canada, Germany and Italy have grown by 10-30% from the last three decades. This is mainly attributed to improved diagnostic capabilities and increased environmental risk factors in these regions. MS predominantly affects young adults in their 20s and 30s, so as this patient base continues to expand, so does the risk of optic neuritis. As there is no permanent cure available for MS, patients require long-term management of symptoms throughout their lives which further augments the need for effective optic neuritis treatment options.
While optic neuritis attacks associated with MS are usually unilateral, repeated attacks or bilateral involvement can severely hamper vision. Therefore, early diagnosis and timely intervention play a vital role in managing optic neuritis cases, restoring vision and preventing progression to functional blindness. With limited self-recovery possibility in chronic cases, pharmaceutical treatment gains more significance. This has propelled drug manufacturers to invest in developing more efficacious therapies targeting the underlying causes of optic neuritis like neuroinflammation and demyelination.
Market Driver - Advancements in Therapies Targeting Neuroprotection and Remyelination, Such as OCS-05 by Oculis.
One of the major drivers boosting the optic neuritis treatment market is the promising breakthroughs in pharmacological therapies that are centered on mechanisms of neuroprotection and remyelination. Among these, Paris-based Oculis' lead candidate drug 'OCS-05' holds huge potential as a first-in-class neuroprotective agent for optic neuritis as well as other ophthalmic and neurological diseases. OCS-05 acts by inhibiting Rho kinase (ROCK) which reduces axonal damage, inflammation and stimulates repair pathways like remyelination.
In preclinical studies, OCS-05 has demonstrated strong neuroprotective effects through substantial inhibition of axonal degeneration following acute optic nerve damage induced by various stimuli. It was also found to promote remyelination and enhance nerve conduction in mouse models of multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis. Encouraged by these results, Oculis has advanced OCS-05 into clinical trials where it has shown good safety and tolerability profile in healthy volunteers so far. The company is actively recruiting patients for Phase 2a randomized controlled trials in optic neuritis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder.
Positive outcomes from ongoing and planned clinical efficacy studies can validate OCS-05's role in neuroprotection, preventing permanent vision impairment and hastening recovery in optic neuritis. Its once-daily topical ocular formulation offers notable advantages over frequent invasive injections. If approved, OCS-05 is expected to get preference over existing treatments owing to its novel mechanism, improved efficacy and enhanced convenience. This makes it a promising drug candidate to disrupt the current optic neuritis management landscape and drive significant revenues in the global market in the upcoming years.
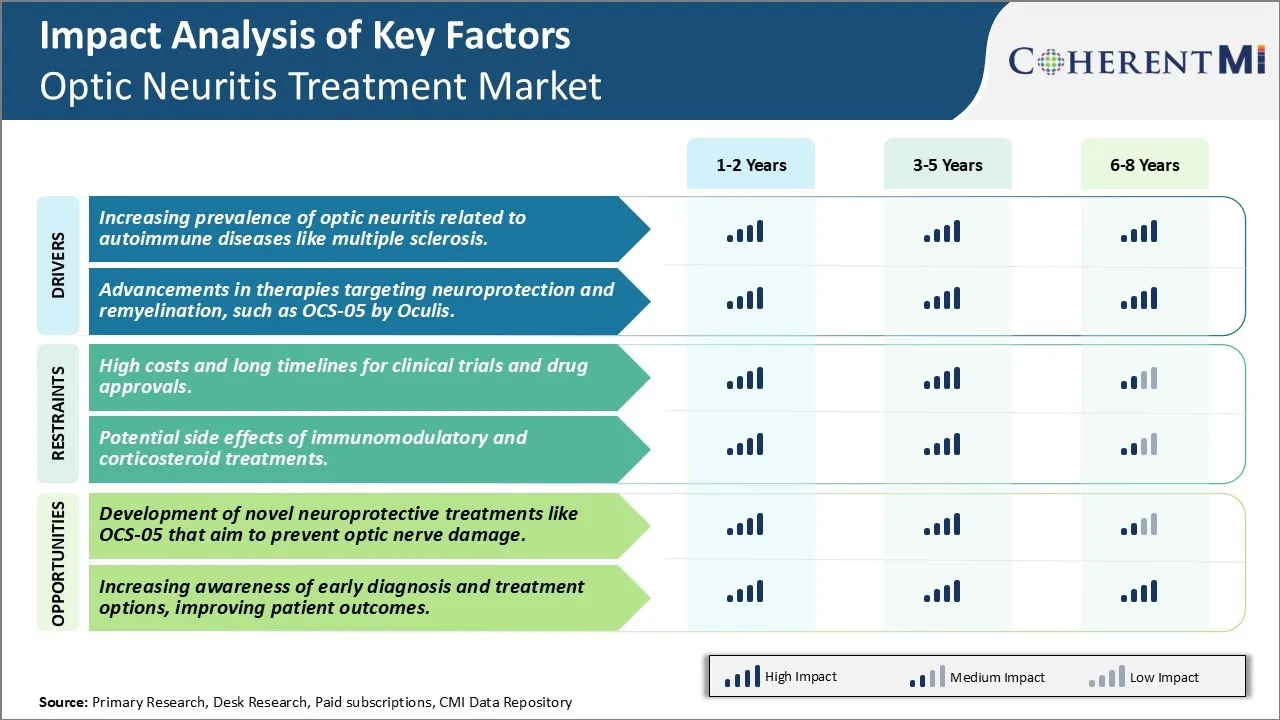
Market Challenge - High Costs and Long Timelines for Clinical Trials and Drug Approvals.
One of the major challenges faced by companies operating in the optic neuritis treatment market is the high costs associated with clinical trials and lengthy drug approval timelines. Developing a new drug and getting it approved is an expensive and time-consuming process. On an average, it takes 10-15 years for a drug to be developed, tested and approved for market after the initial discovery stage. Clinical trials involving human subjects are required to demonstrate safety and efficacy of new treatments. However, recruiting suitable participants and collecting meaningful clinical data takes significant time. Additionally, conducting multiple phases of clinical trials across different regions globally involves high costs related to staffing, monitoring, data collection and analysis. It is estimated that the total costs of developing and gaining approval for a new drug often exceeds USD 2.6 billion. The risks and investment requirements associated with clinical development discourage many pharmaceutical companies, especially small to mid-sized ones, from pursuing new optic neuritis treatments. The lengthy approval timelines also mean companies have to wait longer to generate returns from potential blockbuster drugs, increasing business uncertainties.
Market Opportunity- Development of Novel Neuroprotective Treatments Such as OCS-05 is Expected to Create New Avenues in the Industry.
One of the major opportunities in the optic neuritis treatment market is the development of novel neuroprotective therapies that can potentially prevent long-term optic nerve damage. Currently available treatment options like corticosteroids are focused on reducing inflammation and symptoms in the acute phase. However, there is no approved therapy that provides neuroprotection by preventing nerve cell damage and loss of vision over time. Researchers are exploring pathways like Ocular Compartment Syndrome (OCS) to develop novel therapeutics. For instance, OCS-05 is being evaluated as a potential neuroprotective treatment that aims to maintain optimal eye pressure and prevent compression injury to the optic nerve. Its development is seen as an opportunity to fundamentally change the treatment paradigm by protecting vision long-term rather than just managing symptoms. Such disease-modifying treatments could widen the eligible patient population beyond the acute phase. Their ability to provide lifelong neuroprotection is expected to yield much higher returns on investment compared to conventional therapies.
Prescribers preferences of Optic Neuritis Treatment Market
Optic Neuritis typically follows a stepwise treatment approach based on disease severity and stage. For mild, first-time episodes, prescribers commonly opt for corticosteroid medications such as oral prednisone to reduce inflammation in the optic nerve. Brand names include Deltasone and Medrol. If symptoms fail to improve within 7-10 days, a stronger corticosteroid like intravenous methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) may be administered in-clinic.
In cases of severe vision loss, chronic recurring episodes, or low response to initial steroids, prescribers often choose disease-modifying therapies. Popular first-line options include interferon beta-1a (Avonex, Rebif), which helps regulate the immune system, or glatiramer acetate (Copaxone), an immunomodulator. If insufficient response, prescribers may try rituximab (Rituxan), a B-cell depleting monoclonal antibody, or immunosuppressants like azathioprine (Imuran). Off-label use of natalizumab (Tysabri) has also shown promise.
In addition to medical history and symptom severity, several social factors could impact prescribing decisions. Age and lifestyle of the patient, side effect profiles of the various options, issues of accessibility, cost, and insurance coverage are all considerations for both prescribers and patients in selecting the most appropriate long-term treatment strategy. Close communication is required to develop a mutually agreeable management approach.
Treatment Option Analysis of Optic Neuritis Treatment Market
Optic neuritis typically follows one of three stages - mild, moderate, or severe. For mild cases, patients often opt for watchful waiting as the body's immune system usually resolves the inflammation on its own. However, corticosteroids are the standard first-line treatment for more advanced stages to quickly reduce inflammation and protect vision loss.
Prednisone is the most commonly prescribed oral corticosteroid. It works systemically to calm the overactive immune response causing the optic nerve swelling. Treatment typically involves a 1-week tapering course of Prednisone starting at 1 mg/kg daily. For moderate cases, intravenous steroids like methylprednisolone may be used instead via daily injections for 3-5 days. This delivers higher doses directly to reduce symptoms faster.
If steroids do not achieve complete resolution, neurologists may add immunomodulator drugs. The most effective is Rebif (interferon beta-1a), a disease-modifying therapy that modifies the immune system over the long run. Given via weekly self-injections, it can help prevent future attacks. For cases with incomplete visual recovery or frequent relapses, Tysabri (natalizumab) - an antibody injected monthly - sees high use as it more powerfully suppresses inflammation.
Overall, oral steroids remain first-line due to their strong efficacy reducing acute inflammation quickly with minimal side effects. Immunomodulators like Rebif provide valuable relapse prevention for moderate-severe cases. Timely treatment optimizes vision outcomes at each stage of this unpredictable condition.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Optic Neuritis Treatment Market
Innovation in Drug Development: Companies are focusing on developing targeted therapies, such as biologics (e.g., monoclonal antibodies), which can better control the immune response involved in optic neuritis. These therapies are particularly effective in treating optic neuritis associated with conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS) and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD). For example, Genentech’s ocrelizumab has been used successfully in MS patients with optic neuritis. Research and development into neuroprotective agents are gaining momentum. These agents aim to protect the optic nerve from further damage post-inflammation, thereby improving long-term visual outcomes for patients.
Partnerships and Collaborations: Pharmaceutical companies collaborate with academic institutions to advance clinical research. These partnerships help identify new biomarkers for early detection and prognosis of optic neuritis, which could lead to more personalized treatment approaches. Collaborations also aid in sharing knowledge and resources for faster drug development.
To facilitate early diagnosis, companies are forming partnerships with manufacturers of advanced diagnostic equipment such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) devices. Early detection is crucial in preventing irreversible optic nerve damage, and these collaborations help provide integrated care.
Geographical Expansion and Access to Treatment: Leading players are expanding their footprint in emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where rising healthcare expenditure and awareness of optic neuritis are driving demand. Companies are also working to improve access to advanced treatments and diagnostics in these regions.
To address the high cost of biologics and other advanced treatments, many companies are offering patient assistance programs. These programs help patients gain access to medications through financial support, especially in underinsured or low-income populations.
Focus on Comprehensive Care: Companies are adopting a holistic treatment approach by integrating medication with rehabilitative services such as vision therapy and counseling for patients experiencing vision loss. This strategy emphasizes patient well-being beyond just the pharmacological treatment.
Players are investing in physician education and patient awareness programs to ensure early diagnosis and timely intervention, especially for conditions like MS or NMOSD that are closely associated with optic neuritis. This also helps build strong relationships with healthcare providers.
Regulatory Approvals and Market Exclusivity: Since optic neuritis often overlaps with rare neurological diseases, companies are pursuing orphan drug designations from regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA. These designations offer market exclusivity for several years, giving companies a competitive advantage while also incentivizing further research and development.
Fast-Track Approvals: To capitalize on unmet medical needs, companies are applying for fast-track or breakthrough therapy designations to accelerate the development and approval process for new treatments.
By focusing on drug innovation, partnerships, geographical expansion, holistic patient care, and leveraging regulatory incentives, companies in the optic neuritis treatment market position themselves to better meet growing demand and improve patient outcomes.
Segmental Analysis of Optic Neuritis Treatment Market
Insights, By Type, Oral Corticosteroids are the Leading Segment in the Forecast Period.
By Type, the oral corticosteroids dominate the type segment of the optic neuritis treatment market owing to their convenience of oral administration over intravenous forms. The market share is projected to grow at 61.3% in 2024. As optic neuritis causes sudden vision loss or pain during eye movement, patients prefer treatment options that do not require visiting hospitals or clinics for intravenous injections or infusions. The oral forms can be self-administered at home, saving time and avoiding additional costs related to clinical visits.
Furthermore, oral corticosteroids have a well-established safety profile backed by decades of clinical usage. Patients are comfortable with the oral route as side effects are relatively mild when administered for short durations to treat optic neuritis episodes. The ease-of-use boosts compliance for the recommended course of therapy. With self-administration, oral corticosteroids also empower patients to start treatment immediately without delays.
The ubiquitous availability of generic oral corticosteroids also makes this segment the most affordable option for patients. Strong demand from the cost-conscious patient population further increases market share for oral forms. Accordingly, oral corticosteroids will continue dominating the type segment as long as they demonstrate safety and convenience benefits over alternatives.
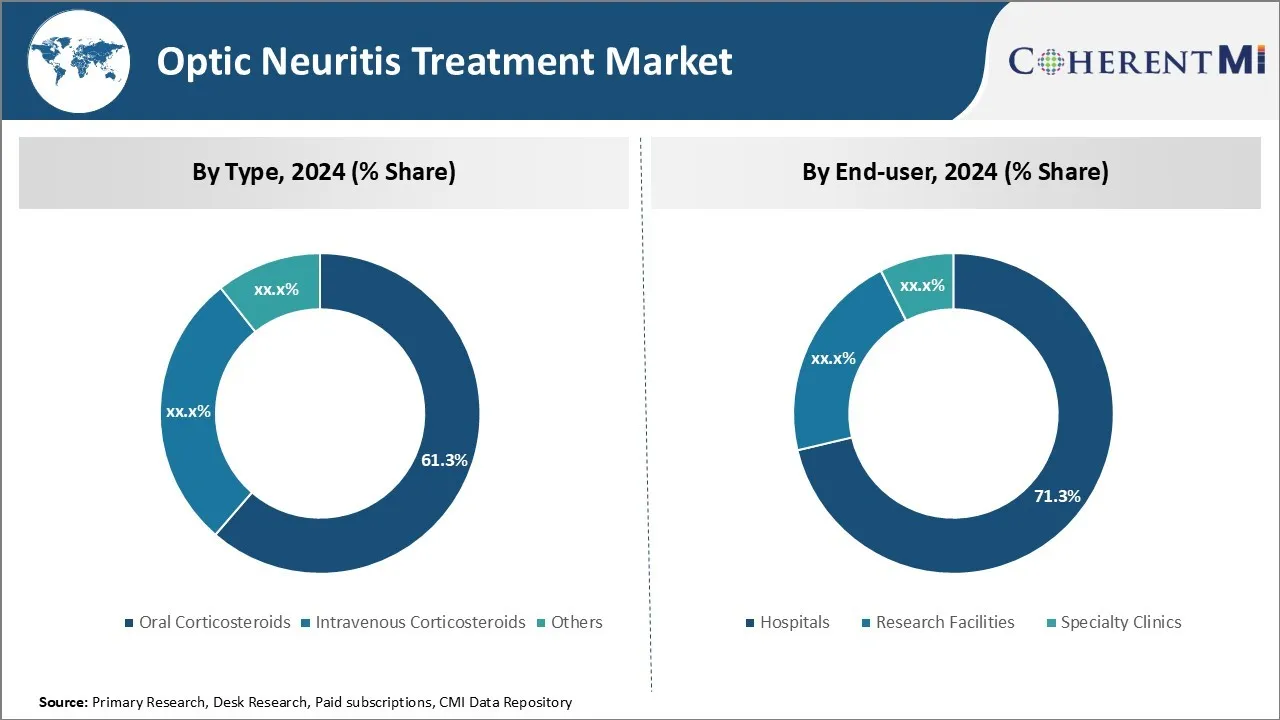
Insights, By End-User, Hospitals Drive the Highest Share of the End-User Segment Owing to Specialized Expertise and Diagnostic Capabilities.
Among the end-user segments, hospitals account for a share of 71.4% in 2024. This is because hospitals have specialized ophthalmology and neurology departments with staff and facilities to conduct tests needed to accurately diagnose optic neuritis. Diagnosis may involve MRI scans, lab tests, lumbar punctures etc. which require sophisticated equipment available only in hospitals.
Additionally, in severe or untreated cases where vision loss is extensive, hospitals can provide in-patient monitoring and care. They have highly skilled ophthalmologists and neurologists who can administer treatments intravenously if oral medications fail or are not suitable. Such specialized treatments and intravitreal therapies also take place in hospitals under expert supervision.
Hospitals also have the means to manage any potential treatment complications or adverse reactions in a timely manner. With a centralized location, patients also prefer hospitals to get a definitive diagnosis and coordinate any further management of their condition conveniently. These advantages continue attracting majority of the optic neuritis patient pool to hospitals, sustaining their commanding share in the end-user market.
Additional Insights of Optic Neuritis Treatment Market
Immunomodulatory treatments have gained prominence as first-line options for managing optic neuritis, particularly when associated with conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS). Corticosteroids, such as methylprednisolone, remain a standard treatment, as they help reduce inflammation and accelerate recovery. However, the long-term management of underlying conditions like MS is now being increasingly targeted through therapies like interferon-beta and natalizumab, which aim to prevent future relapses and nerve damage. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for preserving vision in optic neuritis patients. Advances in optical coherence tomography (OCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have enhanced the ability of clinicians to diagnose optic neuritis more effectively. This has led to a push for increased awareness among healthcare professionals regarding the importance of early intervention to reduce long-term visual impairment.
The development of biologics is another promising area in optic neuritis treatment. Monoclonal antibodies, such as ocrelizumab and rituximab, have shown potential in treating optic neuritis, especially when associated with neuromyelitis optica (NMO), a rare but severe autoimmune disorder. These therapies work by targeting the immune system and reducing inflammation that causes damage to the optic nerve.
Competitive overview of Optic Neuritis Treatment Market
The major players operating in the Optic Neuritis Treatment Market include AbbVie Inc., Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Bausch Health, Merck & Co, Pfizer, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Amorphex Therapeutics, Kubota Vision Inc, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc, Ellex Medical, Astellas Pharma Inc and Acorn Biomedical Inc.
Optic Neuritis Treatment Market Leaders
- AbbVie Inc.
- Aerie Pharmaceuticals
- Bausch Health
- Merck & Co
- Pfizer
Optic Neuritis Treatment Market - Competitive Rivalry

Optic Neuritis Treatment Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Optic Neuritis Treatment Market
In 2024, Oculis advanced its OCS-05 drug into Phase II trials. This drug has a novel mechanism of action, targeting SGK-2 pathways to support neuronal development and repair. The clinical trial named ACUITY is testing the drug in patients with acute optic neuritis of demyelinating origin. This development could significantly impact the treatment landscape for optic neuritis.
Optic Neuritis Treatment Market Segmentation
- By Type
- Oral Corticosteroids
- Intravenous Corticosteroids
- Others
- By End-user
- Hospitals
- Research Facilities
- Specialty Clinics

Would you like to explore the option of buyingindividual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the Optic Neuritis Treatment Market?
The Global Optic Neuritis Treatment Market is estimated to be valued at USD 250.1 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 320.4 Mn by 2031.
What will be the CAGR of the Optic Neuritis Treatment Market?
The CAGR of the Optic Neuritis Market is projected to be 6.10% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Optic Neuritis Treatment Market?
The high costs and long timelines for clinical trials and drug approvals and potential side effects of immunomodulatory and corticosteroid treatments are the major factors hampering the growth of the Optic Neuritis Treatment Market.
What are the major factors driving the Optic Neuritis Treatment Market growth?
The increasing prevalence of optic neuritis related to autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and advancements in therapies targeting neuroprotection and remyelination, such as ocs-05 by Oculis. These are the major factors driving the Optic Neuritis Treatment Market.
Which is the leading Type in the Optic Neuritis Treatment Market?
Oral Corticosteroids is the leading type segment.
Which are the major players operating in the Optic Neuritis Treatment Market?
AbbVie Inc., Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Bausch Health, Merck & Co, Pfizer, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Amorphex Therapeutics, Kubota Vision Inc, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc, Ellex Medical, Astellas Pharma Inc, Acorn Biomedical Inc are the major players.