Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market is segmented By Treatment(Topical Treatments, Oral Medications, Surgical Procedures), By Disease Type (Non-Progressive....
Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR2.5%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 2.5% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | LEO Pharma, Novartis AG, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), AbbVie and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market Analysis
The palmoplantar keratoderma market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.21 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1.44 Billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.5%. This growth can be attributed to the rising prevalence of palmoplantar keratoderma, which leads to thickening of skin on the palms and soles.
Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market Trends
Market Driver - Rising Awareness of Palmoplantar Keratoderma
With increasing efforts towards patient education and advocacy, awareness about rare skin conditions like palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) has been gradually rising. Several non-profit organizations and advocacy groups focused on genodermatoses are actively working to spread knowledge about different types of PPK and their signs and symptoms. Dermatologists and genetic counselors too are playing a role in enhancing public understanding. This empowers patients to understand the risk of passing on the condition to future generations and make plans accordingly.
With growing conversations around PPK online and offline, more cases are coming to light that may have otherwise gone unnoticed or diagnosed late. Awareness is translating to timely medical interventions in many situations.
It allows patients to understand diagnostic procedures, available treatment protocols and management strategies better. It reassures them about proven therapies in mitigating PPK symptoms. This in turn positively impacts their psychological wellbeing and motivation levels in self-care. Greater consciousness in society about genetic dermatological conditions like PPK is undeniably expanding the potential for drugs and therapies in palmoplantar keratoderma market.
Market Driver - Incremental Healthcare Spending Worldwide
Across the globe, economic development and rising income levels are consistently driving up healthcare budgets of nations. With improved affordability, people today are able to spend more on their medical needs than ever before.
As emerging economies continue to progress financially, their citizens develop higher expectations of quality medical care.
Vast untapped potential is attracting many large pharmaceutical companies and medical device manufacturers to expand product availability to palmoplantar keratoderma market. For PPK, it means more patients in the developing world can avail cost-effective drugs, gene therapies and other inventions introduced every year.
Wealthier patients worldwide are also inclined to spend on novel drugs and technology promising enhanced outcomes. In the case of chronic conditions with no cure, they may willingly bear high costs if it provides symptomatic relief or halts progression of the disease. This opens doors for premium brand PPK products targeting such segments where price is not a determining approval factor.
With budgets for medical innovation rising consistently across healthcare systems, research in neglected diseases is receiving enhanced funding support. Overall, exponential worldwide growth projected in healthcare consumption indirectly fuels the palmoplantar keratoderma market too.
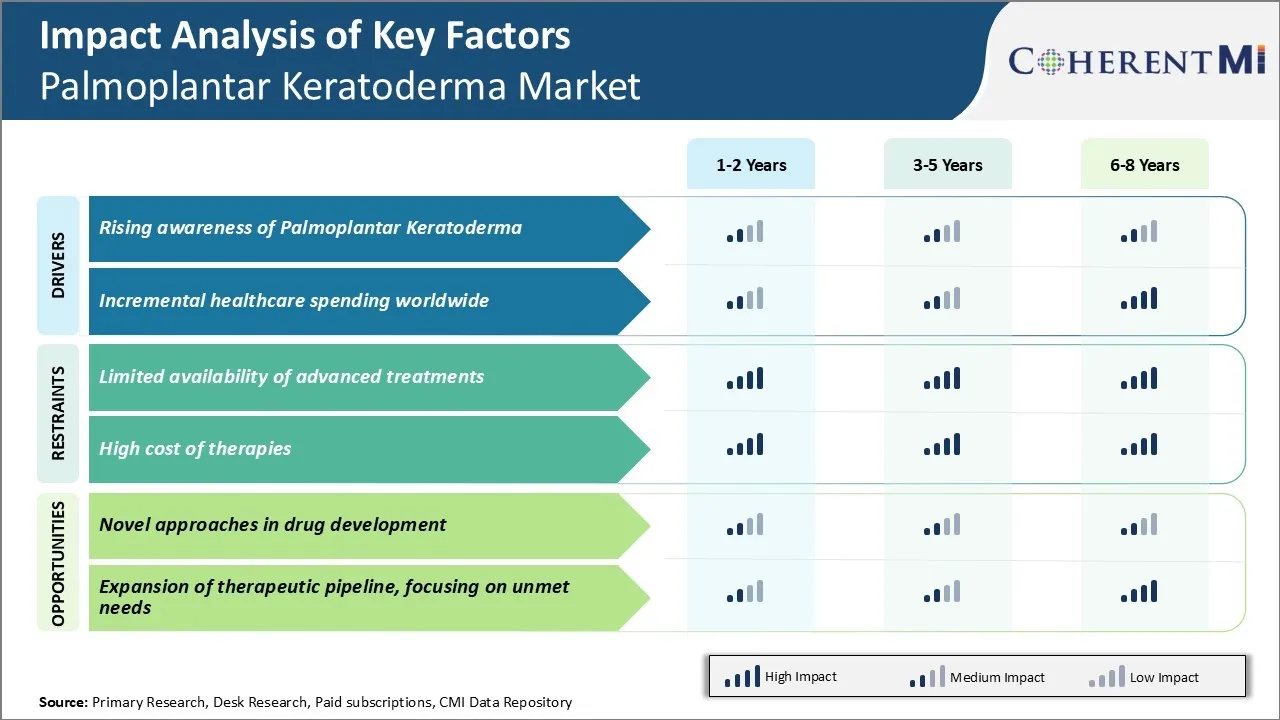
Market Challenge - Limited Availability of Advanced Treatments
One of the key challenges facing the palmoplantar keratoderma market is the limited availability of advanced treatment options. Currently, prescription medications are available but they only provide temporary relief and do not treat the underlying cause. These medications often need to be applied lifelong to manage the symptoms.
The types of medications that are available include topical creams, ointments and solutions containing keratolytic agents such as salicylic acid and urea which help soften the skin.
However, these treatments are not very effective for severe cases of palmoplantar keratoderma. There is an unmet need for more targeted treatment approaches such as gene therapies, drug therapies or other novel treatment modalities that can potentially cure this condition or at least provide longer lasting relief.
The development of such advanced treatments requires significant investments in R&D which pharmaceutical companies have been hesitant to make given the low prevalence and orphan drug status of palmoplantar keratoderma. Unless innovative therapies are brought to palmoplantar keratoderma market, patients will continue to depend upon temporary symptomatic relief with topical agents.
Market Opportunity: Novel Approaches in Drug Development
One of the key opportunities in the palmoplantar keratoderma market lies in novel approaches being explored for drug development. Researchers are working on identifying the molecular targets and pathways involved in different subtypes of palmoplantar keratoderma. This improved understanding of disease biology and etiology is opening up possibilities for targeted drug therapies that can modify disease progression.
Several biotech companies have initiated R&D programs focused on developing first-in-class oral drugs for palmoplantar keratoderma. For example, therapies based on gene silencing mechanisms like RNA interference hold promise for hereditary subtypes.
Other new modality under exploration includes gene therapies using viral vectors to replace mutated genes. Such disease-modifying treatments can potentially provide lasting benefits to patients by addressing the root cause, as opposed to temporary relief from topical treatments alone.
With continued focus on biomarker identification and clinical validation, some of these novel drug candidates may potentially enter clinical trials in the coming years. This can transform patient outcomes and drive significant growth for the palmoplantar keratoderma market.
Prescribers preferences of Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market
Palmoplantar keratoderma is typically treated via a step-wise approach depending on the severity and stage of the disease. For mild cases, physicians generally prefer to start with over-the-counter keratolytic agents that help slough off the thickened skin. Examples include Actikerall cream or Oxy 5 lotion which contain urea or salicylic acid.
If symptoms persist, prescription-strength keratolytics may be used. Common first-line medications at this stage include fluorouracil 5% cream (Efudix) and tazarotene 0.1% cream (Tazorac). For patients with wider involvement and thicker plaques, combination therapy is often favored. A popular regimen is applying Efudix in the morning and covering it with an occlusive dressing overnight, followed by Tazorac application the next evening without a dressing.
For moderate-severe PPK, especially in adults, oral retinoids such as acitretin capsules (Soriatane) may be prescribed. The starting dose is typically 0.5mg/kg with adjustments based on response and tolerability. This systemic treatment is generally very effective but monitoring is needed due to potential side effects involving mucocutaneous and musculoskeletal tissues.
Treatment Option Analysis of Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market
Palmoplantar keratoderma has varying stages of severity depending on the type. Mild cases can often be managed with over-the-counter treatments while more severe forms require prescription options.
Early stages see thickening of the skin on the palms and soles. OTC creams containing urea, salicylic acid or lactic acid help soften the skin and flakes. For moderate thickening, doctors may prescribe stronger versions of these keratolytic creams containing 5-20% concentrations.
As thickness and scaling worsens, combination therapy is favored. Popular choices include tazarotene 0.1% cream with urea or a-hydroxy acid at night, followed by emollients daily. The tazarotene accelerates skin cell turnover while acids and urea hydrate and remove scales.
In severe, cyst-like PPK, oral retinoids are considered first-line. Acitretin at 0.5mg/kg is well-tolerated and effective for most types by reducing skin cell production and inflammation. For resistant cases, narrowband UVB 2-3 times weekly alongside acitretin provides synergistic effects.
The worst affected patients may need surgical removal of thickened skin. Post-op, lifelong maintenance includes strict emollient use, keratolytic soaks, and occasional short oral retinoid courses to prevent relapse. Close monitoring is needed to select optimal, individualized long-term control based on baseline severity and response.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market
Acquisitions and partnerships have been one of the main strategies adopted by companies to gain a foothold in the palmoplantar keratoderma market. In 2021, Pfizer acquired Amplyx Pharmaceuticals, a company focused on developing treatments for invasive fungal infections and rare disease conditions like palmoplantar keratoderma. This strengthened Pfizer's portfolio of dermatologic therapies.
Focus on research and development of novel drugs targeting the underlying genetic causes is another strategy. In 2017, Axsome Therapeutics initiated Phase 2 trials for AXS-05 for palmoplantar keratoderma caused by NBDYPE genes. This drug targets underlying neurotransmitter dysfunction. The trials showed statistically significant improvements, paving the way for Phase 3 trials.
Companies are also targeting orphan drug designations to gain exclusivity in the palmoplantar keratoderma market upon approval. In 2018, Agenus received FDA orphan drug designation for AGEN2373, a clinical-stage immunotherapy treatment for monogenic keratodermas like Vohwinkel syndrome and Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia.
Partnerships with patient advocacy groups and clinical experts helps gain insights on unmet needs and improves enrollment in clinical trials. In 2020, Bellus Health partnered with the Foundation for Ichthyosis and Related Skin Types and its clinical advisors to design Phase 2 trials for BLU-5937 for palmoplantar keratoderma.
Segmental Analysis of Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market
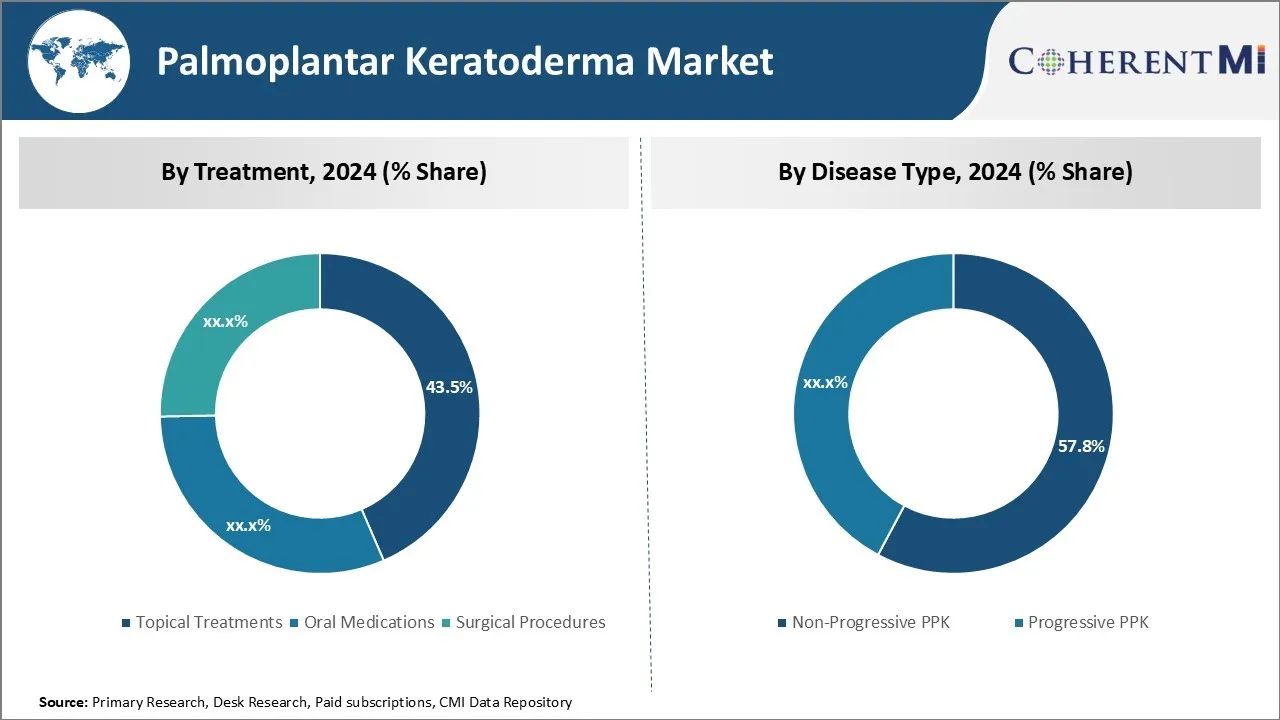
Insights, By Treatment: Ease of Application Drives Growth of Topical Treatments
In terms of treatment, topical treatments are estimated to hold 43.5% share of the palmoplantar keratoderma market in 2024, owing to their non-invasive nature and ease of application. Topical treatments such as creams, ointments and lotions provide a targeted approach to treating affected skin areas and are easy to use, requiring nothing more than periodic application onto lesions.
This simplicity makes topical treatments highly preferable over other options that may involve more complex administration methods or potential side effects. Their external application also precludes any risk of systemic absorption and associated adverse effects, increasing their safety profile.
As topical treatments do not demand visiting a specialist, they offer convenience and represent a cost-effective first-line approach for mild to moderate cases of Palmoplantar Keratoderma.
Insights, By Disease Type: Genetic Basis Drives Need for Non-Progressive Treatment
In terms of disease type, non-progressive palmoplantar keratoderma is projected to account for 57.8% share of the palmoplantar keratoderma market in 2024, since it has a predominantly genetic basis. Non-Progressive PPK is an inherited disorder caused due to mutations in genes responsible for keratinization.
Unlike Progressive PPK which has environmental triggers, Non-Progressive PPK symptoms typically remain stable over time without worsening unless improperly managed. However, effective treatment is still required to prevent discomfort, infections and maintain quality of life.
The established genetic cause of Non-Progressive PPK means patients often require lifelong management to control symptoms. This sustained need drives the palmoplantar keratoderma market for Non-Progressive PPK therapies.
Insights, By Patient Type: Higher Disease Prevalence in Pediatric Population
In terms of patient type, the pediatric segment contributes the highest share due to greater disease prevalence among children. Palmoplantar keratoderma manifests at a young age and genetics plays a role in many pediatric cases. Thickening of the skin can impair mobility and limit physical activity important for child development.
Timely therapy enables better outcomes. Additionally, parental involvement typically leads to higher treatment compliance in pediatric patients. The largely non-curative nature means therapy often continues throughout childhood. This sustained period of treatment drives the palmoplantar keratoderma market size for pediatric Palmoplantar keratoderma management.
Additional Insights of Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market
- Palmoplantar Keratoderma affects approximately 1 in every 50,000 individuals worldwide. The condition can be inherited or acquired, with genetic forms often presenting earlier in life. Due to the impact on mobility and quality of life, treatment focuses on symptomatic relief and prevention of complications.
- Palmoplantar keratoderma is characterized by thickening of the skin on the palms and soles. It often affects quality of life significantly, with symptoms like pain, cracking, and secondary infections being common. Due to its rarity, the treatment landscape has been slow to evolve, but recent advancements by companies like Novartis and Pfizer are bringing new hope to patients.
Competitive overview of Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market
The major players operating in the palmoplantar keratoderma market include LEO Pharma, Novartis AG, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), and AbbVie.
Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market Leaders
- LEO Pharma
- Novartis AG
- Pfizer
- GlaxoSmithKline (GSK)
- AbbVie
Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market
- In April 2024, LEO Pharma launched a new topical formulation aimed at treating severe PPK, significantly reducing patient discomfort and improving quality of life. LEO Pharma has been very active in dermatology, focusing on new treatments for skin conditions such as chronic hand eczema (CHE) and atopic dermatitis (AD), as seen with their recent developments involving products like delgocitinib (Anzupgo®) for chronic hand eczema.
- In August 2023, AbbVie began Phase III trials for a novel oral medication for treating progressive PPK, expected to provide an alternative to existing topical treatments. Most recent developments from AbbVie around this time are also focused on other treatments, such as upadacitinib (RINVOQ) for conditions like hidradenitis suppurativa, atopic dermatitis, Crohn's disease, and giant cell arteritis.
Palmoplantar Keratoderma Market Segmentation
- By Treatment
- Topical Treatments
- Oral Medications
- Surgical Procedures
- By Disease Type
- Non-Progressive PPK
- Progressive PPK
- By Patient Type
- Pediatric
- Adult
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the palmoplantar keratoderma market?
The palmoplantar keratoderma market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.21 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1.44 Billion by 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the palmoplantar keratoderma market?
Limited availability of advanced treatments and high cost of therapies are the major factors hampering the growth of the palmoplantar keratoderma market.
What are the major factors driving the palmoplantar keratoderma market growth?
Rising awareness of palmoplantar keratoderma and incremental healthcare spending worldwide are the major factors driving the palmoplantar keratoderma market.
Which is the leading treatment in the palmoplantar keratoderma market?
The leading treatment segment is topical treatments.
Which are the major players operating in the palmoplantar keratoderma market?
LEO Pharma, Novartis AG, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), and AbbVie are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the palmoplantar keratoderma market?
The CAGR of the palmoplantar keratoderma market is projected to be 2.5% from 2024-2031.