Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market is segmented By Treatment (Pharmacological Therapy, Gene Therapy, Supportive Care), By Diagnostic Tool (Genetic Test....
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market Size
Market Size in USD Mn
CAGR5.5%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 5.5% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Parion Sciences, ReCode Therapeutics, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Reata Pharmaceuticals, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market Analysis
The primary ciliary dyskinesia market is estimated to be valued at USD 538.2 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 784.5 Mn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% from 2024 to 2031. The market is witnessing positive trends with many pharmaceutical companies actively working on developing targeted treatments for primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD).
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Awareness of Rare Diseases like PCD
For too long, primary ciliary dyskinesia flew under the radar of even many physicians. Studies have shown that delay in diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia averages around 7 years from initial presentation of symptoms. A lack of awareness among some specialists has meant missed opportunities for patients to access specialized treatment sooner.
However, with greater prominence of primary ciliary dyskinesia in medical literature and conferences, more doctors are learning about its signs and learning how to test for it properly. Major teaching hospitals have also established dedicated rare disease clinics where primary ciliary dyskinesia is now routinely considered in the differential diagnosis of children with recurrent wet coughs or issues like sinusitis and infertility that don't respond to usual treatments.
The growing recognition of the disease will help drive the primary ciliary dyskinesia market as improved diagnosis allows for earlier interventions. As awareness continues to spread to even more rural primary care physicians, earlier diagnosis rates for PCD will climb significantly. This factor is an important driver of increased demand in the primary ciliary dyskinesia market.
Market Driver - Advances in Genetic Research and Gene Therapy
Researchers have made major strides in recent years towards better understanding the genetics underlying primary ciliary dyskinesia. Advancing genome sequencing technologies have accelerated the discovery of new PCD-causing genes. To date, genetic testing can detect a definitive mutation in approximately 70% of patients clinically diagnosed with PCD. However, annually more candidate genes are identified through collaborations between research centers globally.
At the same time, progress in cellular and animal models of PCD allows scientists to closely study the effects of specific gene mutations. Among the most promising approaches are gene therapy and gene editing techniques like CRISPR. As the first gene therapy clinical trials for PCD get underway, this will energize the primary ciliary dyskinesia market and attract more investment funding for additional trials.
A definitive treatment restoring cilia function could profoundly impact patients' quality of life and reduce healthcare costs from years of management instead of cure. The primary ciliary dyskinesia market will grow substantially on the back of continued genetic research bringing forth new diagnostics and therapies closer to reality for this orphan disease population.
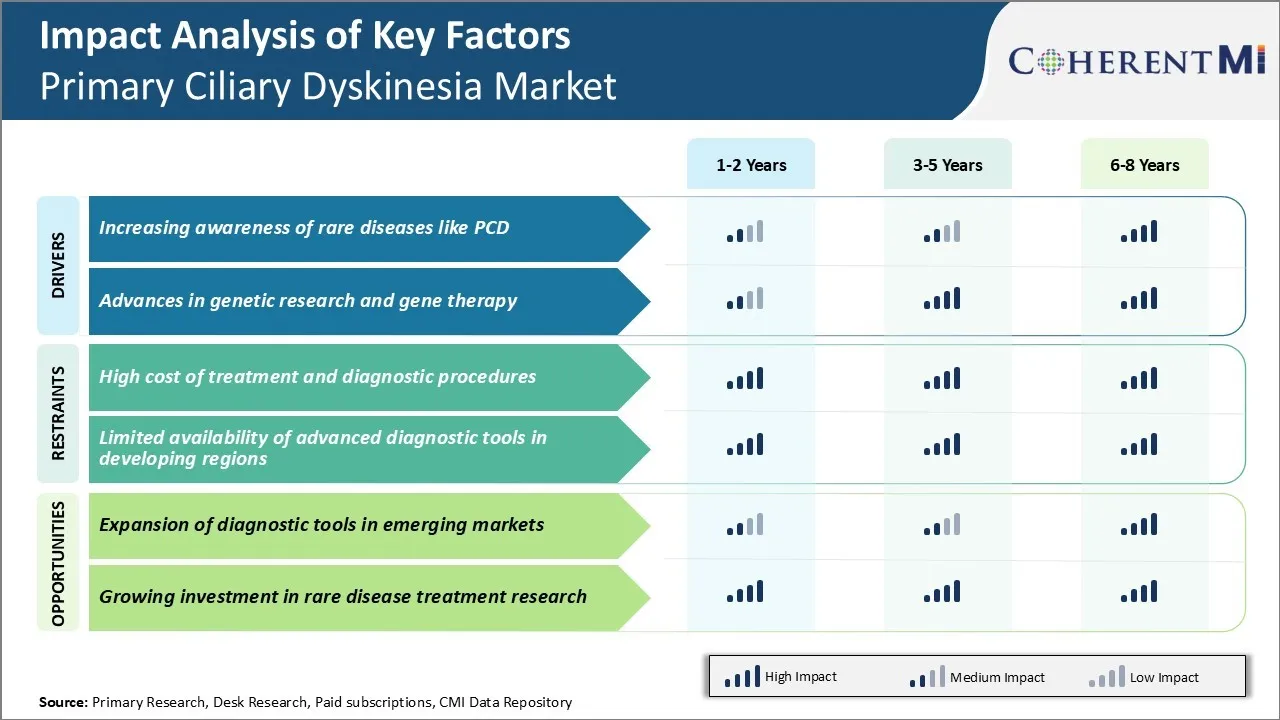
Market Challenge - High Cost of Treatment and Diagnostic Procedures
One of the major challenges being faced in the primary ciliary dyskinesia market is the high cost associated with treatment and diagnostic procedures. Currently, the treatment involves lifelong medication and airway clearance techniques to manage symptoms like chronic infections, bronchiectasis and sinusitis. These therapies come at a substantial recurring cost to patients.
Diagnosing PCD also requires specialized tests and equipment that are available only in select research centers. The tests include nasal or bronchial biopsy to examine cilia structure under electron microscopy. Special scanning electron microscopes capable of magnifying cilia are required which adds to the cost.
The tests are also time-consuming requiring samples to be sent to research labs. All these factors contribute to the high cost of diagnosis ranging between $5000 to $10000 in developed markets. This financial burden prevents many patients from getting timely and accurate diagnosis, creating a major challenge for players in the primary ciliary dyskinesia market.
Market Opportunity - Expansion of Diagnostic Tools in Emerging Markets
One of the key opportunities for growth in the primary ciliary dyskinesia market lies in expanding diagnostic capabilities to emerging countries. Currently, specialized diagnostic tests and infrastructure are concentrated only in developed nations of North America and Western Europe. This limits diagnosis to a small proportion of the global population.
Major diagnostic players in the primary ciliary dyskinesia market are focusing on developing portable, easy-to-use, and more affordable diagnostics tools. For example, development of molecular diagnostics tests based on genetic mutations can be performed in any clinical laboratory without the need for electron microscopy.
Similarly, handheld devices utilizing dark-field microscopy imaging of mucus samples allow point-of-care diagnostic screening. Expanding availability of such tools in regions like Asia, Latin America and Eastern Europe will help diagnose larger patient pools in the primary ciliary dyskinesia market. It will also reduce the time and costs involved in centralized testing. Incoming technologies are well positioned to tap into the sizable untreated patient population in emerging economies and drive the next phase of growth for primary ciliary dyskinesia market.
Prescribers preferences of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market
Primary ciliary dyskinesia is a rare genetic disorder where cilia are either absent or have abnormal structure and function. Prescribers' treatment approaches vary depending on the stage and severity of the disease.
In mild early-stage cases, airway clearance techniques are usually the first line of treatment to help clear mucus from the lungs. Devices like the Aerobika and Acapella may be prescribed to help loosen and thin secretions. Prescribers may also recommend inhaled medications like Pulmozyme (dornase alfa) and hypertonic saline to aid drainage.
For moderate cases, antibiotics are often prescribed prophylactically to prevent chronic lung infections. Azithromycin (Zithromax) is a commonly used brand due to its tolerability. As the disease progresses, inhaled or oral steroids like Flovent or Pulmicort may be added to reduce inflammation.
In more severe later-stage PCD, physicians frequently prescribe bronchodilators in conjunction with other therapies. Brands such as Spiriva (tiotropium bromide) and Symbicort (budesonide/formoterol) help make breathing easier. Lung transplant evaluation may also be considered, depending on pulmonary function tests.
Treatment Option Analysis of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market
Primary ciliary dyskinesia has four main stages - mild, moderate, severe, and life-threatening - based on symptoms and lung function.
For mild PCD, airway clearance techniques like active cycle of breathing and modified postural drainage are preferred first-line treatments to help clear mucus from the lungs. Antibiotics are used short-term during respiratory infections to prevent exacerbations.
In moderate PCD, the addition of inhaled therapies is common. Bronchodilators such as albuterol help open airways, while inhaled hypertonic saline and medications like Pulmozyme thin and loosen mucus to ease clearance. Corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation during flare-ups.
For severe PCD, newer airway clearance devices that use high-frequency chest wall oscillation via vests are often used along with inhaled treatments mentioned above. Chronic antibiotics are sometimes needed long-term to suppress frequent infections.
In life-threatening PCD cases where lung function is very poor, systemic corticosteroids, immunosuppressants or biologics may be tried to control inflammation and slow disease progression as a bridge to lung transplantation. This is currently the only treatment option once the lungs are severely damaged and non-transplant therapies are no longer effective.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market
Focus on treatments targeting underlying causes:
Knowing the genetic cause of PCD is crucial for developing targeted therapeutics. Vertex Pharmaceuticals acquired exclusive rights to Ivacaftor, a CFTR potentiator drug, in 2014. Several clinical trials showed Ivacaftor significantly improved lung function in patients with specific genetic mutations causing PCD.
Expand indications through additional clinical trials:
After the initial approval for certain mutations, Allergan continued clinical trials in 2019 to expand Ivacaftor's label to include more genetic variants causing PCD. This allowed the drug to treat a larger patient subset. Additional trials also explored Ivacaftor's use in younger pediatric patients.
Acquisitions to enhance capabilities:
In 2021, Takeda Pharmaceutical acquired exclusive rights to research and develop novel gene therapies for PCD from Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute. This gave Takeda access to SBPMDI's expertise and research pipeline in gene therapy.
Segmental Analysis of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market
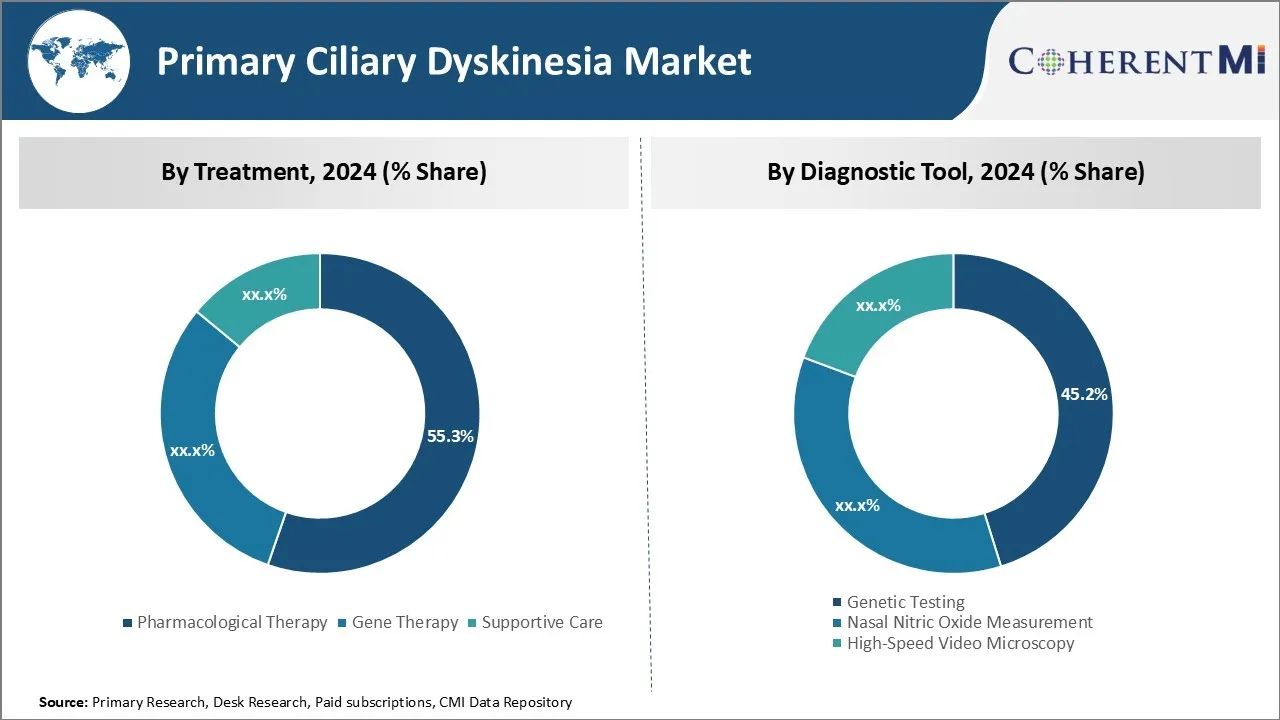
Insights, By Treatment: Dominance of Emerging Treatment Therapies Drives Pharmacological Therapy Segment
In terms of treatment, pharmacological therapy contributes 55.3% share of the primary ciliary dyskinesia market in 2024. This is due to emergence of novel drug candidates targeting the underlying pathogenesis of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Several pharmaceutical companies are developing drugs that can repair or replace defective cilia.
For example, Vertex Pharmaceuticals is evaluating corrector compounds that enhance cilia function by correcting folding defects in CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) proteins. Other therapies under research aim to reduce tissue damage caused by impaired mucociliary clearance.
Researchers are also focusing on gene therapies such as editing defective genes or supplementing functional copies. Although pharmacological therapy dominates currently, gene therapy is expected grow at a higher pace over the long-run due to its potential to provide permanent cure.
Insights By Diagnostic Tool: Rising Awareness Boosts Genetic Testing Segment
In terms of diagnostic tool, genetic testing contributes 45.2% share of the primary ciliary dyskinesia market in 2024, owing to increasing awareness and diagnostic rates of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Traditionally, primary ciliary dyskinesia was under-diagnosed due to non-specific symptoms mimicking other conditions like asthma and sinusitis. However, initiatives by patient advocacy groups and medical experts to educate healthcare providers as well as public have enhanced screening and detection rates.
More patients are undergoing genetic testing to confirm diagnosis. Technologies like next-generation sequencing allow screening of multiple genes simultaneously, improving efficiency and turnaround time of tests. While genetic testing dominates presently, high-speed video microscopy could garner greater acceptance in future with ongoing automation and data analytics advances.
Insights, By Disease Manifestation: Focus on Pulmonary Issues Drives Pulmonary Disease Segment
In terms of disease manifestation, pulmonary disease contributes the highest share of the primary ciliary dyskinesia market as it is the most prevalent and severe manifestation of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Impaired mucociliary clearance in lungs predisposes patients to recurrent respiratory infections from early childhood.
Chronic inflammation and damage lead to bronchiectasis and respiratory failure in advanced stages. Majority of treatment and research efforts focus on lung-related conditions. Drugs enhancing mucus clearance, airway clearance techniques through chest physiotherapy, and antibiotics reducing infection exacerbations aid pulmonary management. Gene therapies endeavor to correct cilia motility defects specifically in lungs.
Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment of pulmonary involvement aims to prevent disease progression. While other manifestations exist, pulmonary disease remains the dominant focus area due to its clinical significance and impact on quality of life in primary ciliary dyskinesia patients.
Additional Insights of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market
- In 2023, the United States had nearly 1,800 diagnosed prevalent cases of PCD, with the highest cases in the 6-20 age group.
- Treatment strategies for PCD largely focus on managing respiratory symptoms and preventing infections, often borrowing approaches from cystic fibrosis treatment protocols.
- Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia is frequently under-recognized and misdiagnosed, leading to significant delays in treatment. Experts emphasize the need for increased awareness to ensure early diagnosis and effective management.
- Pulmonary diseases represent the largest category of clinical manifestations in PCD patients, with early intervention needed to manage symptoms and improve patient quality of life.
Competitive overview of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market
The major players operating in the primary ciliary dyskinesia market include Parion Sciences, ReCode Therapeutics, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Reata Pharmaceuticals, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, and Celgene Corporation.
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market Leaders
- Parion Sciences
- ReCode Therapeutics
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals
- Reata Pharmaceuticals
- Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market
- In September 2024, Vertex Pharmaceuticals initiated a new clinical trial phase for a CFTR modulator therapy adapted for primary ciliary dyskinesia patients, aiming to treat the underlying cause of the disease. This could revolutionize treatment approaches.
- In July 2024, Parion Sciences announced progress in their gene therapy trials for PCD, showing promise for long-term treatment efficacy. This development is expected to reduce the burden of lifelong supportive care for PCD patients. In September 2023, they published Phase 2 results for their investigational therapy, idrevloride in hypertonic saline, which showed significant improvements in lung function for PCD patients.
- In June 2024, the U.S. FDA granted Orphan Drug Designation to RCT1100, a gene therapy developed by ReCode Therapeutics. This therapy is designed to target primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), a rare genetic disorder that affects respiratory function due to defective cilia. The designation aims to support the development of therapies for rare diseases by providing incentives such as tax credits and potential market exclusivity, accelerating the development process.
- In April 2023, Parion Sciences announced that it had received a positive opinion from the Paediatric Committee (PDCO) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the Paediatric Investigation Plan (PIP) for its Idrevloride Inhalation Solution. This solution, an epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) inhibitor, is under development for the treatment of primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), a rare genetic disorder. This positive opinion helps expand treatment options for children with PCD in the EU, broadening the potential market for this therapeutic.
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Market Segmentation
- By Treatment
- Pharmacological Therapy
- Gene Therapy
- Supportive Care
- By Diagnostic Tool
- Genetic Testing
- Nasal Nitric Oxide Measurement
- High-Speed Video Microscopy
- By Disease Manifestation
- Pulmonary Disease
- Situs Abnormality
- Infertility
- Eye disorders
- By Patient Age Group
- 0-5 Years
- 6-20 Years
- 21-40 Years
- 40+ Years

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the primary ciliary dyskinesia market?
The primary ciliary dyskinesia market is estimated to be valued at USD 538.2 Mn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 784.5 Mn by 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the primary ciliary dyskinesia market?
High cost of treatment and diagnostic procedures and limited availability of advanced diagnostic tools in developing regions are the major factors hampering the growth of the primary ciliary dyskinesia market.
What are the major factors driving the primary ciliary dyskinesia market growth?
Increasing awareness of rare diseases like PCD and advances in genetic research and gene therapy are the major factors driving the primary ciliary dyskinesia market.
Which is the leading treatment in the primary ciliary dyskinesia market?
The leading treatment segment is pharmacological therapy.
Which are the major players operating in the primary ciliary dyskinesia market?
Parion Sciences, ReCode Therapeutics, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Reata Pharmaceuticals, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, and Celgene Corporation are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the primary ciliary dyskinesia market?
The CAGR of the primary ciliary dyskinesia market is projected to be 5.5% from 2024-2031.