PROTAC Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
PROTAC Market is segmented By Type (Heterobifunctional PROTAC, Molecular Glues, Others), By Application (Drug Discovery and Development, Cancer Resear....
PROTAC Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR25.1%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 25.1% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Arvinas, Celgene, Nurix Therapeutics, Hinova Pharmaceuticals, Dialectic Therapeutics and Among Others |
please let us know !
PROTAC Market Analysis
The Global PROTAC Market is estimated to be valued at USD 0.40 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.59 billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.1% from 2024 to 2031.
The PROteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) market is rapidly growing, driven by its innovative approach to targeted protein degradation, offering new therapeutic strategies for diseases that are difficult to treat with traditional drugs. PROTACs are bifunctional molecules that use the body’s natural protein degradation system to remove disease-causing proteins, presenting a novel mechanism of action compared to conventional therapies. The market has been witnessing significant growth over the past few years due to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders, where conventional therapies often fail due to drug resistance. PROTAC technology provides a promising solution by enabling the selective degradation of target proteins, which can help overcome resistance mechanisms. Investments from major pharmaceutical companies and advancements in drug discovery platforms further propel the market growth.
PROTAC Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Clinical Trials and Research in PROTAC technology.
PROTAC technology continues to garner significant interest from both academic and industrial researchers due to its ability to induce targeted protein degradation. Over the past decade, the number of research publications and patents related to PROTACs has grown exponentially as scientists work to better understand the technology's applications and potential. This increasing focus is further driving innovation that could help realize PROTACs' clinical and commercial potential.
On the clinical front, lead optimization efforts are maturing PROTAC candidates for various therapeutic areas. For example, several oncology-focused programs are now in Phase-1 trials to evaluate the safety, tolerability and initial efficacy of PROTAC degraders against well-validated cancer targets like androgen receptor and estrogen-related receptor alpha. Results so far have been promising and help validate the technology's translatability. In addition to oncology, areas like immunology-inflammation, neurology and cardiometabolic diseases are attracting PROTAC development interest due to opportunities to safely target disease pathways not amenable to traditional inhibition. All this clinical momentum is expected to continue expanding the technology's evidence base in patients.
On the discovery and research side, most big pharma and several medium-sized biotech companies have now established internal PROTAC discovery units or partnered with specialist startups. They recognize that PROTACs could allow access to currently difficult to drug or non-druggable protein targets linked to various diseases. This level of committed investment from industry is spurring broader scientific understanding of critical design properties like optimal linker design and E3 ligase recruitment. It is also increasing the pace at which PROTACs against new target classes progress from conceptualization through lead optimization stages into preclinical development candidates. Several of these preclinical candidates are projected to enter clinical trials in the coming years.
Market Driver - The Ability of PROTACs to Target Disease-Causing Proteins Previously Considered “Undruggable.”
One of the most exciting aspects of PROTAC technology is their ability to target protein classes traditionally viewed as "undruggable." The mechanism of induced protein degradation circumvents many of the limitations constraining traditional small molecule inhibition approaches. By recruiting the inherent multi sub-unit E3 ligase enzyme complexes that normally turnover proteins inside cells, PROTACs can effectively eliminate the problem target protein without necessarily requiring high-affinity binding at catalytic or regulatory sites on the target.
This property has opened up entirely new target families and disease pathways for therapeutic exploration. Receptors like ER alpha that lack traditional enzyme active sites become amenable to small molecule modulation through PROTACs. Transcription factors critical for disease progression but lacking traditional orthosteric sites can potentially be suppressed at the protein level instead of requiring direct binding. Even membrane proteins challenging to target with cell-permeable agents may find PROTACs provide an alternative solution.
Early research successes like the first-ever extracellular protein degradation demonstrate PROTACs can functionally complement traditional modalities. By breaking free from the constraints of orthosteric binding requirements, PROTACs promise to enable novel therapies against diseases where the molecular drivers were simply thought impossible to directly target with small molecules. Now proteins linked to intractable conditions are under active investigation as PROTAC drug discovery programs.
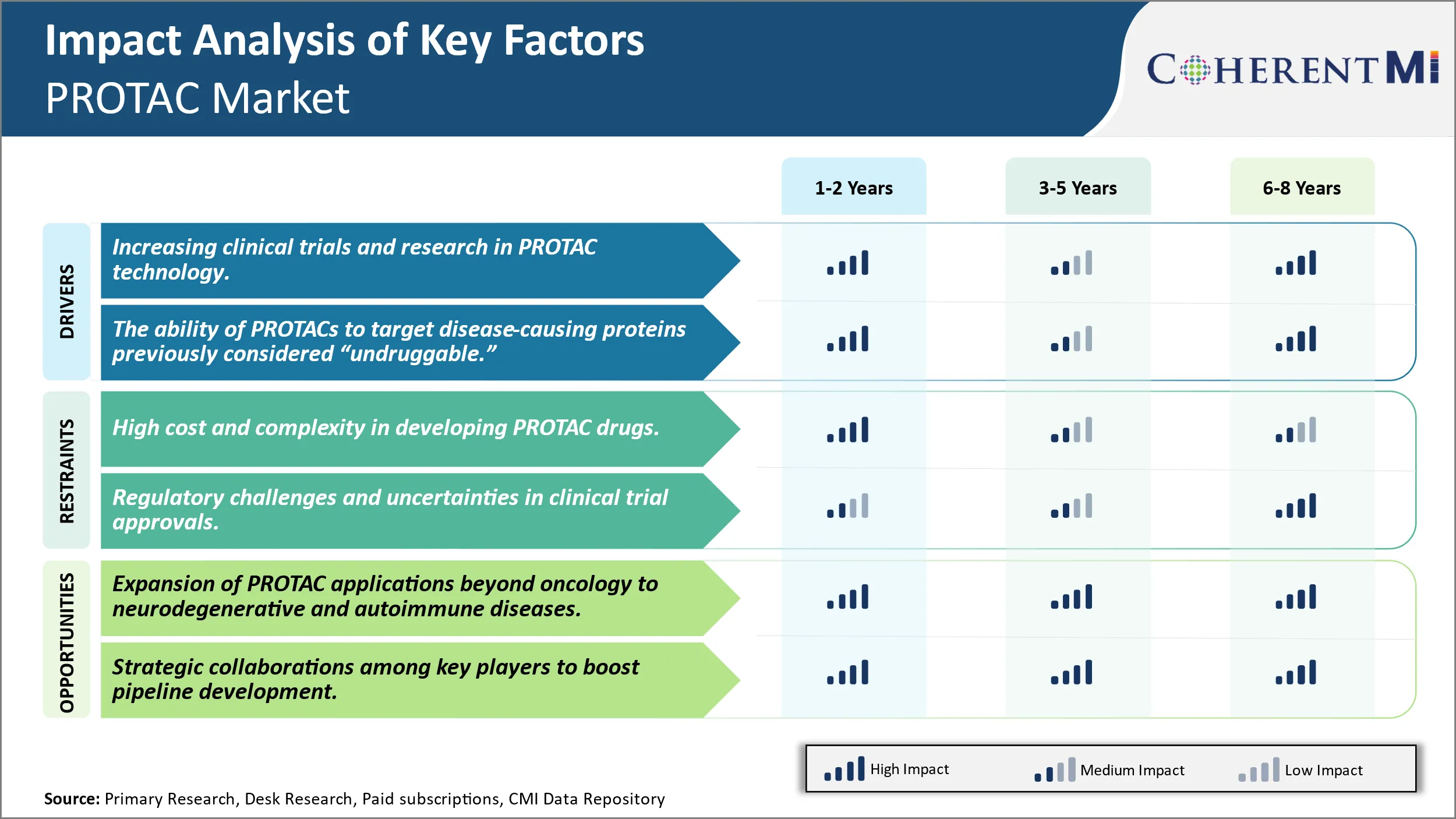
Market Challenge - High Cost and Complexity in Developing PROTAC Drugs.
One of the major challenges faced by the PROTAC drug market is the high cost and complexity associated with the research and development of PROTAC drugs. Developing a successful PROTAC candidate requires identifying a target protein for degradation, designing bifunctional molecules that can recruit the target protein to an E3 ligase for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, and optimizing the drug candidates for adequate potency and selectivity. This drug discovery process is highly specialized and resource-intensive. It often requires interdisciplinary expertise in protein biology, chemical synthesis, pharmacology, and medicinal chemistry. Considerable financial investment is also needed to set up the required infrastructure and conduct the extensive preclinical and clinical validation studies. While the promise of PROTACs to drug previously undruggable targets is tremendous, the technical barriers and high costs mean only a handful of companies currently have the capability and funding to actively pursue PROTAC research programs. This limits innovation and slows the growth of the overall PROTAC market currently dominated by just a few pipeline candidates.
Market Opportunity: Expansion Of PROTAC Applications Beyond Oncology to Neurodegenerative and Autoimmune Diseases.
A major opportunity for the PROTAC market lies in expanding its therapeutic applications beyond oncology into other disease areas with high unmet needs like neurodegeneration and autoimmunity. Many of the proteins implicated in neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's were previously not amenable to conventional small molecule or biologic drugs due to their biochemical properties and cellular functions. PROTACs offer a unique approach for the selective degradation of such "undruggable" disease targets. Similarly, selective immunomodulation by PROTAC-induced degradation of certain immune cell surface receptors and signaling proteins holds promise for the treatment of autoimmune conditions. While oncology remains the near-term focus for most PROTAC companies, exploring new disease applications can help drive future growth. It also attracts interest and investment from pharmaceutical partners to support early clinical studies, thereby accelerating the clinical validation and uptake of the PROTAC modality beyond cancer.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of PROTAC Market
Product Innovation: One of the most successful strategies adopted by players has been continuous investment and focus on product innovation.
Strategic Acquisitions: Companies have strengthened their market position and product portfolio through strategic acquisitions. In 2024, Novartis spent USD 150 million to acquire Arvinas phase-3 ready protein degrader that has the capability to treat a wide range of prostate cancer.
Focus on Emerging Markets: Players have succeeded by identifying high growth emerging markets and customizing offerings to those regions.
These strategic moves around continuous innovation, value-added acquisitions and prioritizing high growth regions have helped key companies in the PROTAC market like Olam, ADM and Cargill strengthen their competitive position and outperform competitors over the long run. Data shows that companies deploying such strategies have consistently gained market share over the past decade.
Segmental Analysis of PROTAC Market
Insights, By Type, Molecular Design Drives adoption of Heterobifunctional PROTACs
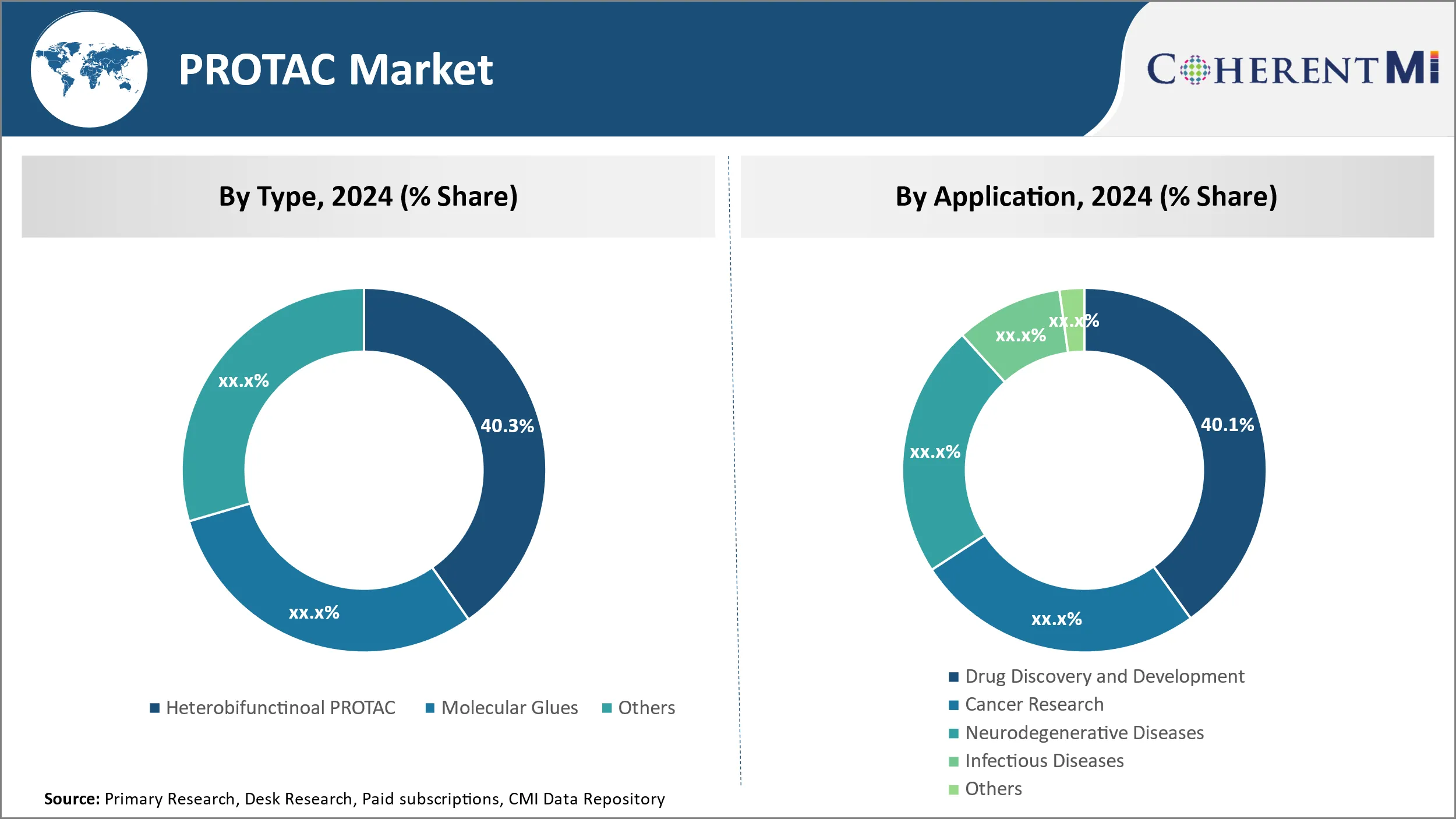
By therapeutic type, heterobifunctional PROTACs lead the market share at 40.27% in 2024 due to their adaptable molecular structure. These molecules comprise three key components - a ligand that binds the target protein for degradation, a ligand that binds an E3 ubiquitin ligase for recruitment to the proteasome, and a linker uniting the two. This modular design grants scientists’ considerable flexibility in selecting ligands and tailoring the linker to optimize target engagement and degradation. Researchers can readily modify heterobifunctional PROTACs to probe various disease-related proteins without requiring new ligand discovery. The ability to repurpose existing ligands speed development and lowers costs. Further, optimizing the linker composition influences intracellular trafficking and proteasomal clearance, allowing degradation kinetics to be refined. Heterobifunctional PROTACs' tunable structure proves invaluable for studying protein functions and validating targets, driving their popularity in drug discovery.
Insights, By Application, Speeding Drug Development Drives PROTAC adoption in Discovery and Development
By application, drug discovery and development accounted for 40.10% in 2024 and leads PROTAC usage due to the technology's ability to accelerate the process. Using PROTACs, researchers can rapidly profile compound activity against multiple disease-related proteins. They leverage existing chemical matter rather than relying solely on new compound synthesis. PROTACs also offer temporal control over protein depletion to efficiently validate targets at certain stages. Studying a target's dependency on expression levels aids go/no-go decisions and identifies optimal therapeutic windows. As PROTACs can eliminate both wild-type and mutant forms of a protein, they help establish a target's druggability. Such insights at early stages optimize resource allocation and shorten development timelines. Further, PROTACs support robust pharmacodynamic profiling and enable proof-of-mechanism studies in animal models to expedite clinical translation. Overall, PROTACs' target validation and mechanistic capabilities clearly accelerate discovery and development workflows.
Insights, By Therapeutic Area, Targeting Oncogenic Drivers Fuels PROTAC Adoption in Oncology
By therapeutic area, oncology tops PROTAC usage given cancer's dependence on specific drivers. Harnessing the ubiquitin-proteasome system's critical role in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis, PROTACs eliminate oncoproteins central to tumor growth and survival. Examples include degrading the androgen receptor to treat prostate cancer, BRD4 to combat leukemia, or VHL to address renal cell carcinoma. Compared to conventional inhibitors, inducing protein degradation offers stronger antitumor activity by fully removing neomorphic or gain-of-function drivers. PROTACs can also thwart resistance arising from target mutations by destroying both mutant and wild-type forms equally. As newer oncogenes emerge, PROTACs' ability to rapidly validate novel targets and probes cancer dependencies empowers precision oncology. Their exquisite selectivity for the disease context further minimizes toxicity. Taken together, oncology presents prime opportunities to harness PROTACs’ degradation capabilities against some of medicine’s most challenging diseases.
Additional Insights of PROTAC Market
- Over 90 PROTAC-based leads are currently under evaluation, with around 20% in clinical development.
- PROTACs account for more than 30% of pipeline drugs under research.
- PROTAC technology represents a paradigm shift in drug discovery by targeting and degrading disease-inducing proteins within cells. The market is set to grow significantly due to the increasing number of PROTAC drugs under clinical trials. The absence of currently approved therapies highlights the market's potential for new entrants, driving innovation and development in oncology and other therapeutic areas.
Competitive overview of PROTAC Market
The major players operating in the PROTAC Market include Arvinas, Celgene, Nurix Therapeutics, Hinova Pharmaceuticals, Dialectic Therapeutics, Accutar Biotech, Kymera, Sanofi, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) and Pfizer.
PROTAC Market Leaders
- Arvinas
- Celgene
- Nurix Therapeutics
- Hinova Pharmaceuticals
- Dialectic Therapeutics
PROTAC Market - Competitive Rivalry

PROTAC Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in PROTAC Market
- February 2024: Arvinas announced the first-in-human dosing of ARV-102, targeting neurodegenerative disease by crossing the blood-brain barrier
- February 2024: Vepdegestrant received FDA Fast Track Designation for ER+/HER2- breast cancer.
PROTAC Market Segmentation
- By Type
- Heterobifunctional PROTAC
- Molecular Glues
- Others
- By Application
- Drug Discovery and Development
- Cancer Research
- Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Infectious Diseases
- Others
- By Therapeutic Area
- Oncology
- Neurology
- Infectious Diseases
- Cardinology
- Endocrinology
- By End-user
- Pharmaceutical
- Academic and Research Institutes
- Contract Research Organizations

Would you like to explore the option of buyingindividual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the PROTAC Market?
The Global PROTAC Market is expected to be valued at USD 0.40 billion in 2024 and reach USD 2.59 billion in 2031.
What will be the CAGR of the PROTAC Market?
The CAGR of the PROTAC Market is projected to be 25.1% from 2024-2031.
What are the major factors driving the PROTAC Market growth?
The increasing clinical trials and research in PROTAC technology and the ability of PROTACs to target disease-causing proteins previously considered “undruggable” are the major factor driving the PROTAC Market.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the PROTAC Market?
The high cost and complexity in developing PROTAC drugs and regulatory challenges and uncertainties in clinical trial approvals are the major factor hampering the growth of the PROTAC Market.
Which is the leading Type segment in the PROTAC Market?
Heterobifunctional PROTAC is the leading segment.
Which are the major players operating in the PROTAC Market?
Arvinas, Celgene, Nurix Therapeutics, Hinova Pharmaceuticals, Dialectic Therapeutics, Accutar Biotech, Kymera, Sanofi, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Pfizer are the major players.