Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market is segmented By Drug Class (Anticonvulsants, Antipsychotic Medications, Others), By Treatment (Medication, Respirat....
Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR6.1%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 6.1% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Recursion Pharmaceuticals, IntraBio Inc, Johnson & Johnson Services Inc, Axovant Services, Sio Gene Therapies and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market Analysis
The Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.71 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 5.17 Bn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% from 2024 to 2031. Tay-Sachs disease is a rare genetic disorder and the market size is expected to grow moderately over the forecast period.
The market is expected to witness steady growth over the next few years. Growing awareness initiatives by non-profit organizations and governments regarding rare diseases like Tay-Sachs disease are increasing the focus on developing new treatment options. Additionally, a rise in genetic screening and testing is helping in early diagnosis and improving clinical outcomes. Various pipeline drugs and gene therapies currently under development are also expected to drive the market if approved in the coming years. However, the rare disease nature and lack of treatment alternatives may continue limiting market growth potential over the forecast period.
Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market Trends
Market Driver - The Rising Prevalence of Lysosomal Storage Disorders Leading to Increased Demand for Novel Therapies
The growing number of lysosomal storage disorders worldwide has been accompanied by an increased focus on developing novel therapies. Tay-Sachs disease, a rare and fatal genetic condition caused by the deficient activity of hexosaminidase A enzyme, falls under this category. Due to impaired metabolism and accumulation of harmful GM2 ganglioside in nerve cells, affected individuals typically experience progressive neurological deterioration leading to early death.
While there is currently no cure for Tay-Sachs, researchers have made substantial headway in diagnosing and understanding the disease pathogenesis. Widespread newborn screening programs allow for early confirmation which is crucial given that symptoms generally manifest between 3-6 months of age. Further research into the genetic roots and molecular pathways disrupted by hexosaminidase A deficiency have illuminated new therapeutic targets. Foremost among them is enzyme replacement therapy which aims to supplement the missing enzyme activity intravenously. Industry leaders are working on developing recombinant forms of hexosaminidase A that can cross the blood-brain barrier, degrade toxic GM2 buildup, and stall or reverse neurological decline.
Other cutting-edge strategies in development involve gene therapy using adeno-associated viral vectors to deliver functioning hexosaminidase A genes. Initial trials have shown great promise in animal models by restoring enzyme levels, clearing storage material, and importantly, preventing symptom onset when administered pre-symptomatically. Combination therapies are also an active area of research, pairing gene therapy with molecules to facilitate widespread gene and protein distribution in the central nervous system. These novel approaches offer hope that what was previously a uniformly fatal disease by age five may eventually be treatable or even preventable. If successful, they could transform the standard of care for not only Tay-Sachs but the broader class of lysosomal storage disorders as well.
Market Driver - Signs of Progress Fuels Gene Therapy in the Long-Term
As scientific abilities to manipulate genes and access different parts of the body have rapidly advanced in recent times, gene therapy has taken center stage as a potential game-changer for numerous inherited conditions. Tay-Sachs disease is one such target where the promise of gene therapy is being actively explored. Existing mainly as a proof-of-concept, initial attempts have provided glimpses of what may be possible with further refinement.
delivered enzyme-coding genes to the brain and other tissues of animal models via AAV vectors. These trials observed partial to full correction of enzyme deficiencies, reduction of toxic substrate buildups, stabilization or recovery of lost functions—critically important signs that the approach warrants continued exploration. Excitingly, when treatment was administered presymptomatically before damage onset, symptoms did not manifest at all. Such findings have motivated larger, multi-center human studies to evaluate safety and efficacy profiles in Tay-Sachs patients.
Ongoing efforts are working to enhance gene delivery methods, develop vectors tailored for neural tissue, and combine therapies for better overall effectiveness. Meanwhile, cell-based and RNA-based therapies are other innovative avenues being investigated. Much work remains but with each passing year, the field edges closer to finally having a disease-modifying option. By overcoming hurdles of the past, gene therapy stands to revolutionize the story for Tay-Sachs disease and bring hope to families affected by this and similar genetic conditions long deemed incurable. Continued progress sustains the momentum needed to eventually translate promising preclinical signs into real clinical impact.
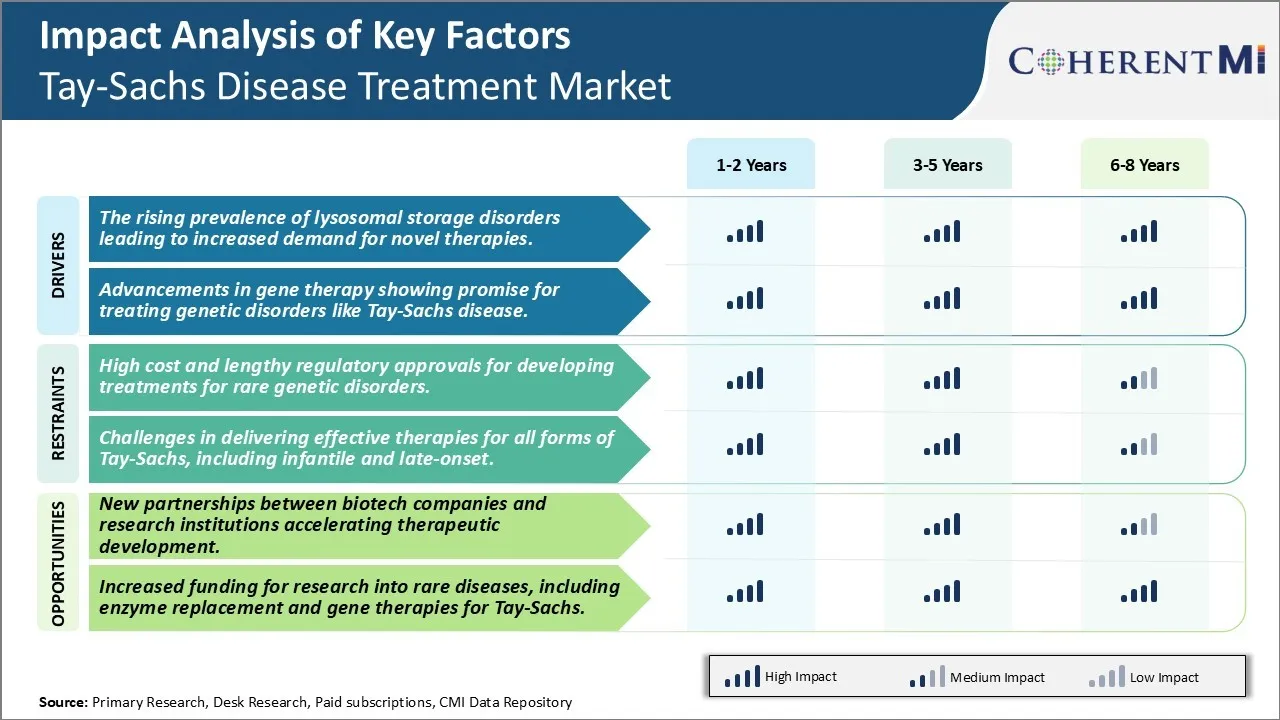
Market Challenge - High Cost and Lengthy Regulatory Approvals for Developing Treatments for Rare Genetic Disorders
Developing treatments for rare genetic disorders like Tay-Sachs disease presents significant challenges due to the high costs associated with research and development as well as lengthy regulatory approval processes. As Tay-Sachs primarily affects Ashkenazi Jewish populations, the small patient pool makes it difficult to recoup R&D investments through product sales. Clinical trials also prove challenging given the small numbers. Additionally, the rarity of these conditions means natural history is not well understood, making it harder to develop targeted therapies and validate clinical endpoints. Lengthy approval timelines further increase costs as companies must fund research programs and clinical trials over extended periods of time without guarantee of being able to market a product. These challenges collectively serve as deterrents for large biopharma companies and limit innovation in this critical therapeutic area to mostly smaller biotechs and venture-backed startups.
Opportunity: New Partnerships Accelerating Therapeutic Development
There is now an opportunity to accelerate development of novel treatments through new partnerships between biotech companies and research institutions. Increased awareness and understanding of genetic diseases have led to more funding opportunities that create incentives for partnerships. By combining their therapeutic expertise with academic research capabilities, these alliances are helping push more candidates into clinical testing faster. Partners can also share resources and patients to conduct larger or more specialized trials than what one group could achieve independently. Such collaborative models have potential to de-risk programs for biotechs while speeding the translation of promising science into therapies. If successful, these partnerships may inspire larger pharmaceutical firms to invest more heavily in orphan and rare disease research as approvability challenges are navigated through cooperative models.
Prescribers preferences of Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market
Tay-Sachs disease is a rare genetic disorder where fatty substances called gangliosides build up in the nerve cells of the brain. Prescribers follow a symptomatic treatment approach as the disease progresses through four main stages.
In the early stage, when symptoms are mild, prescribers may recommend over-the-counter medications to help manage symptoms like joint stiffness. As the disease advances to the intermediate stage, prescribers start prescribing medication to slow symptom progression. Enzyme replacement therapy drugs like alglucosidase alfa (Lumizyme) are commonly prescribed to break down gangliosides accumulating in nerve cells.
The late stage involves loss of motor skills and cognitive abilities. Prescribers focus on improving quality of life by preventing complications. Medications for seizures like levetiracetam (Keppra) are often prescribed. In the final stage, patients become wheelchair-bound and fully dependent. Prescribers utilize end-of-life care and ensure comfort.
Prescribers also consider medication cost and insurance coverage, as treatments like ERT are extremely expensive. Family preference and priorities weigh on prescribers' medication choices as the disease progresses from mild to severe. Off-label drug uses are also explored depending on the patient's specific symptoms. Overall, a staged symptomatic approach tailored to the individual patient guides prescribers' treatment decisions for Tay-Sachs disease.
Treatment Option Analysis of Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market
Tay-Sachs disease progresses through four main stages - early infantile, late infantile, juvenile, and adult. In the early stages, treatment focuses on managing symptoms.
For infants in the early infantile stage, enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) has become the standard first-line treatment. The most commonly used ERT drug is alfa-N-acetylhexosaminidase A (Naglazyme), a recombinant form of the missing enzyme. Naglazyme is administered intravenously every 14 days and has been shown to slow disease progression and extend life expectancy in clinical trials. It works by replacing the deficient enzyme to break down GM2 ganglioside buildup in neurons.
As the disease advances to the late infantile and juvenile stages, additional supportive care is needed. Seizures are treated with antiepileptic medications like vigabatrin. Physical and occupational therapy can help maintain motor skills for as long as possible. Nutritional support via feeding tubes may be needed if swallowing becomes impaired.
For adults in the final stage of Tay-Sachs, treatment shifts to symptom management and palliative care to minimize suffering. Brain degeneration is too extensive for ERT to provide meaningful benefits at this point. Caregivers provide round-the-clock support for activities of daily living. Overall, ERT with Naglazyme remains the first preference for treating early-stage Tay-Sachs due to its effectiveness in delaying neurological deterioration according to clinical evidence.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market
R&D Investments and Clinical Trial Development: Players have invested heavily in R&D to develop novel treatment options for Tay-Sachs disease. For example, Axovant Gene Therapies invested USD 40 million in 2018 to advance its gene therapy program for Tay-Sachs. In January 2022, it initiated a Phase 1/2 clinical trial to evaluate AXO-AAV-GM2 for late infantile and juvenile forms. Successful completion and approval of this trial could give Axovant the first approved therapy for these forms.
Strategic Acquisitions: Companies have acquired other players with promising Tay-Sachs programs to boost their pipeline.
Partnerships for Manufacturing and Commercialization: Given the small patient numbers, developing specialized expertise and infrastructure internally is challenging. Leading companies therefore partner - Axovant partners with GenSight Biologics for manufacture and delivery of its gene therapy, and with Advanced Bioscience Laboratories for commercial distribution if approved. Partnerships optimize development economics.
Patient Engagement: Players regularly engage with patient advocacy groups like the Tay-Sachs Disease Foundation to understand real-world needs and pain points. They work closely on awareness initiatives, clinical trial recruitment, outcomes assessment, and post-approval support - vital for ultra-rare diseases. This helps build trust and support for new therapies from the patient community.
Segmental Analysis of Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market
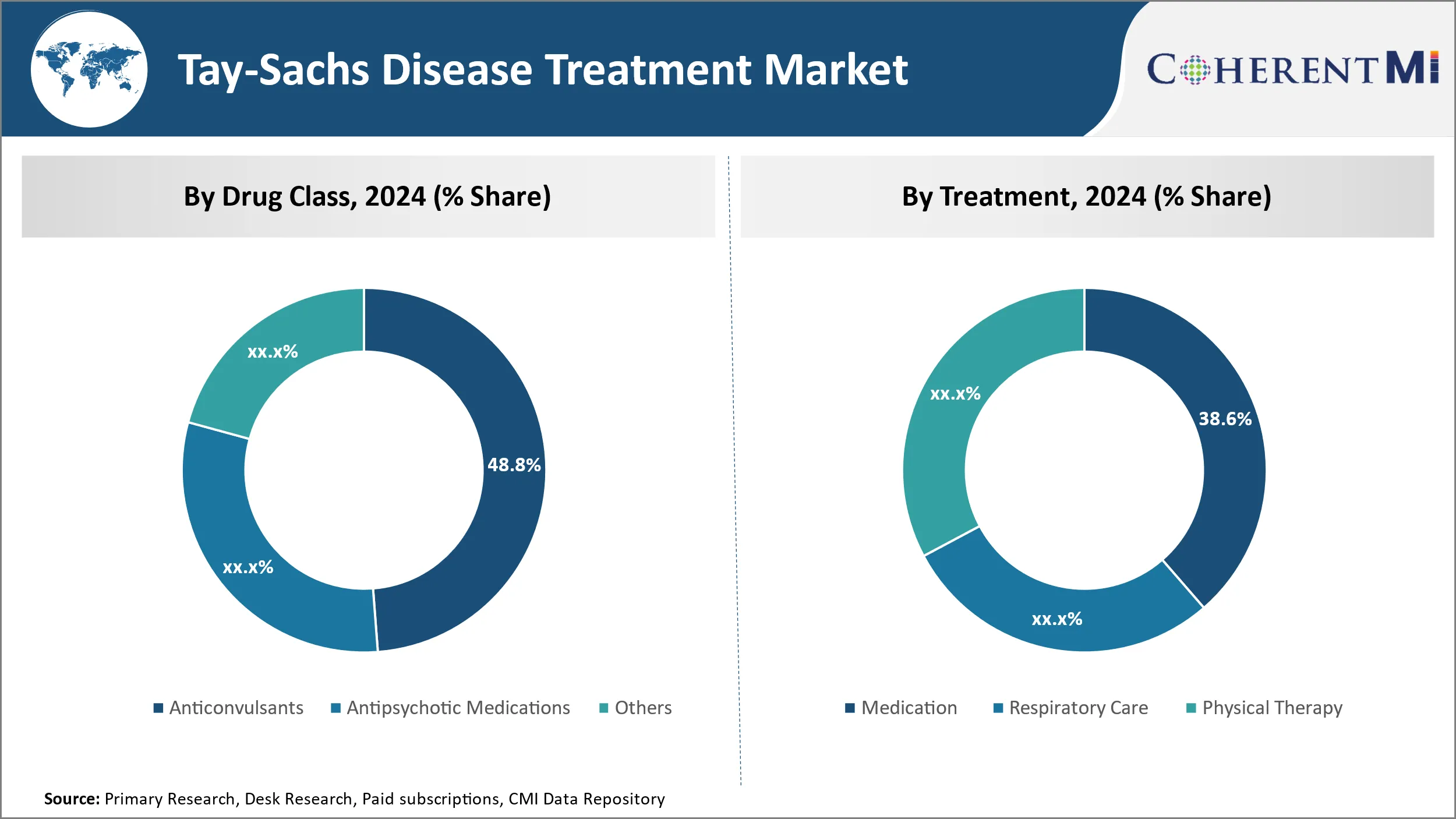
Insights, By Treatment, Medication is the Leading Segment in the Forecast Period
In terms of By Treatment, Medication is expected to contribute 38.6% share in 2024 owing to its direct effectiveness in managing symptoms. Being a potentially fatal genetic disorder with no cure, symptom management assumes utmost importance in Tay-Sachs disease. Medications not only control prominent symptoms like seizures effectively but also help reduce neurological deterioration. The reliability of pharmaceutical interventions in stabilizing patients' condition has solidified Medication's status as the front-line treatment strategy. Furthermore, self-administration of drugs at home through oral and injectable routes ensures seamless care and empowerment of families. The convenience and tangible benefits of Medication have made it the cornerstone of Tay-Sachs management protocols.
Insights, By Mode of Treatment, Injectables are Projected to Attain a Huge Demand in the Forecast Period
In terms of By Mode of Treatment, Injectable contributes the highest share of the market due to its non-oral delivery and assured absorption. As Tay-Sachs patients deteriorate neurologically over time, oral medication becomes more difficult. Injectable drugs overcome issues like inability to swallow and ensure medications reach therapeutic levels in the body. While an invasive procedure, injections eliminate concerns around incomplete drug intake. Additionally, injectable routes enable higher drug concentrations than oral while maintaining safety. This proven record of direct and uniform delivery has elevated Injectable as a preferred mode, especially for advanced stage cases. The benefits outweigh invasiveness to make it the primary administration choice as the disease progresses.
Additional Insights of Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market
The Tay-Sachs disease market is primarily focused on the development of treatments that address the underlying genetic cause of the condition. Sanofi Genzyme’s Venglustat represents a key therapeutic in this space, currently in Phase III trials, with its mechanism aimed at reducing glycosphingolipid accumulation, which is central to the pathology of Tay-Sachs. IntraBio’s IB1001 is another promising treatment that targets neuroinflammation and lysosomal dysfunction, offering a novel therapeutic approach currently in Phase II trials. The disease, which affects both children and adults, remains a significant unmet medical need, especially given the lack of curative treatments and the debilitating nature of the condition. Advances in gene therapy and targeted treatments are likely to shape the future of Tay-Sachs treatment, with a growing focus on enzyme replacement and substrate reduction therapies. Collaborations between industry and research institutions are crucial in driving forward these therapies. With rare disease funding increasing and regulatory support through orphan drug designations, the market is expected to expand as more innovative therapies reach clinical trials.
Competitive overview of Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market
The major players operating in the Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market include Recursion Pharmaceuticals, IntraBio Inc, Johnson & Johnson Services Inc, Axovant Services, Sio Gene Therapies, Pfizer Inc, AbbVie Inc, Amgen Inc, Novartis AG and Progenity Inc.
Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market Leaders
- Recursion Pharmaceuticals
- IntraBio Inc
- Johnson & Johnson Services Inc
- Axovant Services
- Sio Gene Therapies
Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market
- In May 2024, Sanofi Genzyme continues clinical trials for Venglustat, a novel oral investigational therapy aimed at inhibiting abnormal glycosphingolipid (GSL) accumulation. Venglustat has received FDA Fast Track designation for GM2 gangliosidosis and is currently in Phase III trials, targeting improved outcomes for Tay-Sachs patients by slowing disease progression.
- In May 2024, IntraBio is advancing IB1001, an oral therapy targeting lysosomal and mitochondrial dysfunction, into Phase II trials. The drug uses a novel mechanism to cross the blood-brain barrier and aims to reduce neuroinflammation and improve neuronal function in Tay-Sachs patients.
Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market Segmentation
- By Drug Class
- Anticonvulsants
- Antipsychotic Medications
- Others
- By Treatment
- Medication
- Respiratory Care
- Physical Therapy
- By Mode of Treatment
- Injectable
- Oral
- Others
- By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How Big is the Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market?
The Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.71 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 5.17 bn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.10% from 2024 to 2031.
What will be the CAGR of the Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market?
The CAGR of the Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market is projected to be 6.1% from 2024 to 2031.
What are the major factors driving the Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market growth?
The rising prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders leading to increased demand for novel therapies, and advancements in gene therapy showing promise for treating genetic disorders like Tay-Sachs disease are the major factors driving the Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market?
The high cost and lengthy regulatory approvals for developing treatments for rare genetic disorders and challenges in delivering effective therapies for all forms of Tay-Sachs, including infantile and late-onset are the major factors hampering the growth of the Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market.
Which is the leading Drug Class in the Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market?
The leading Drug Class segment is Anticonvulsants.
Which are the major players operating in the Tay-Sachs Disease Treatment Market?
Recursion Pharmaceuticals, IntraBio Inc, Johnson & Johnson Services Inc, Axovant Services, Sio Gene Therapies, Pfizer Inc, AbbVie Inc, Amgen Inc, Novartis AG, Progenity Inc are the major players.