E-Fuel Market Size - Analysis
The e-fuel market is estimated to be valued at USD 173.90 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 553.95 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.00% from 2025 to 2032. The e-fuel market is driven by the need to decarbonize the transportation sector and achieve sustainability targets set by governments and international bodies.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR18.00%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 18.00% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Archer Daniels Midland Co., Ballard Power Systems, Inc., Ceres Power Holding Plc, Clean Fuels Alliance America, Climeworks AG and Among Others |
please let us know !
E-Fuel Market Trends
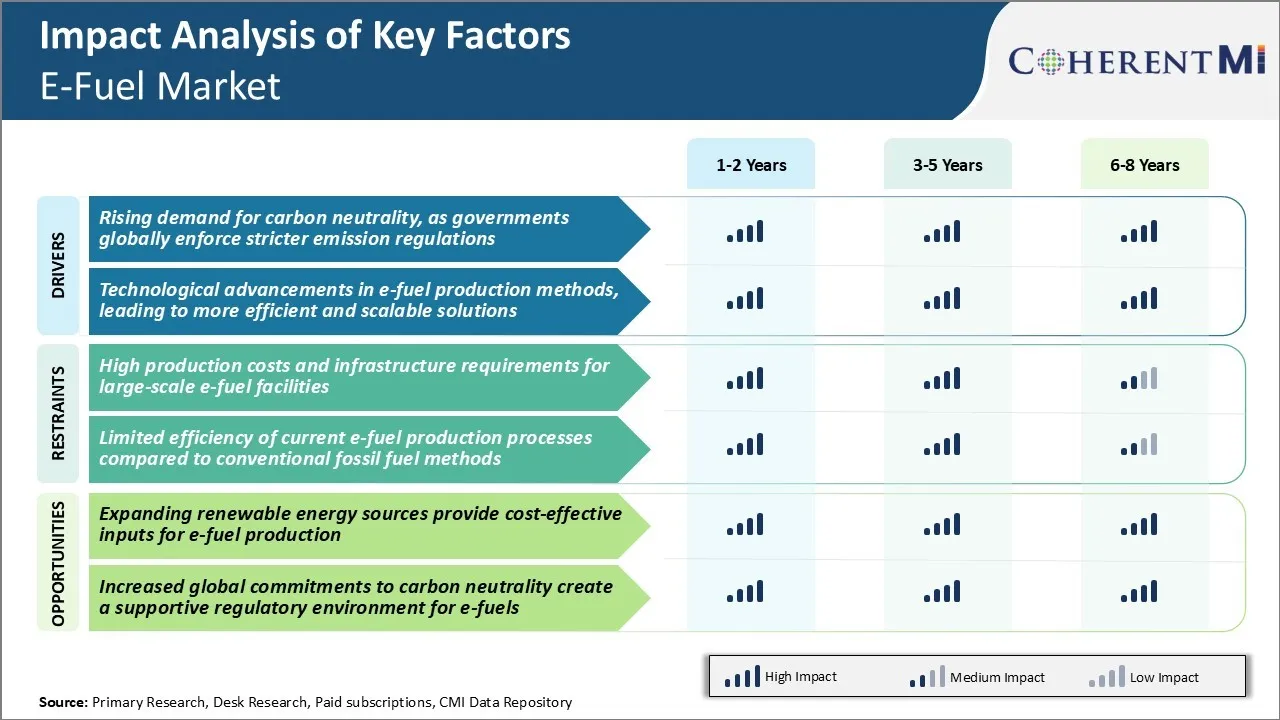
Market Driver - Rising Demand for Carbon Neutrality
Impacts of climate change have become more apparent through extreme weather events across the globe. Governments are working towards stringent emission reduction targets to curb carbon emissions. E-fuels are emerging as a promising solution for decarbonizing transportation, especially heavy-duty vehicles. E-fuels provide a convenient pathway for the transportation sector to reduce emissions without major technological changes and investments.
Many European countries are actively exploring policies to mandate the use of e-fuels and other low carbon fuels. Germany has announced an ambitious target of becoming carbon neutral by 2045 and is working on a regulation to blend e-fuels in conventional fuels. Other nations like France, UK and Nordic countries are also working on formulations to blend e-fuels to reduce emissions from hard-to-abate transportation segments.
Additionally, corporate fleets and logistics companies are committing to transitioning their fleets to low carbon alternatives to meet their own carbon neutral goals. This growing regulatory push and commitment from large corporates is expected to drive demand for carbon neutral fuels, boosting growth of the e-fuels market in the coming years.
Market Driver - Technological Advancements in E-Fuel Production Methods
The concept of producing liquid hydrocarbon fuels from renewable electricity via power-to-X pathways has been around for some time. However, technological scalability and high production costs had hindered mass adoption. Nevertheless, recent years have seen substantial progress in developing more cost-effective and efficient production methods.
Large pilot projects are exploring various production pathways and evaluating different renewable energy sources. Most efforts are focused on using the abundant solar and wind power available in sunny, windy regions to power carbon neutral e-fuel production plants.
Furthermore, innovative business models are exploring co-locating e-fuel production plants with renewable energy farms to optimize resource utilization further. Standardization of production techniques and fuel specifications is also ongoing to enable the global e-fuel market. This will encourage investment in new production facilities worldwide and scale up e-fuel supply chains. Consequently, e-fuels are expected to play a key role in supplying carbon neutral renewable liquid fuels for transportation in the future.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Production Costs and Infrastructure Requirements for Large-scale E-fuel Facilities
One of the major challenges currently faced by the e-fuel market is the high production costs associated with building large-scale e-fuel production facilities. Producing e-fuels requires significant amounts of renewable energy and hydrogen to power the synthesis process. This makes the initial infrastructure investment cost very high.
Additionally, these large-scale plants need ample land area and require a stable supply of renewable energy and water. The high capital intensity poses risks for investors and makes e-fuels less competitive compared to conventional fossil fuels on an unsubsidized cost basis. Remote locations also increase the costs of transporting the inputs and outputs to and from the production sites.
Developing the necessary infrastructure especially in regions with large potential for e-fuel production like Australia, Africa and the Middle East remains a challenge. Overcoming the economic hurdles of establishing large, capital-intensive plants is a major roadblock for the e-fuel market currently.
Market Opportunity - Expanding Renewable Energy Sources Provide Cost-effective Inputs for E-fuel Production
One of the key opportunities for the e-fuel market is the declining costs of renewable energy sources which are needed as inputs for the production process. Solar and wind energy costs have fallen by over 60-70% in the last decade owing to technology innovations, mass manufacturing of components, improved efficiencies and economies of scale.
The abundant availability of low-cost renewable power in regions with high solar irradiation and wind potential provides a strategic advantage for establishing e-fuel production sites. As renewable capacity further ramps up to meet decarbonization targets, excess renewable energy available at lower costs can be utilized for e-fuel synthesis using power-to-x technology routes. This helps improve the economics of e-fuel production and strengthens the business case for large-scale projects.
The plummeting renewable energy prices worldwide is a significant opportunity that e-fuel market players can leverage for facilitating mass adoption.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of E-Fuel Market
Partnerships and Collaboration: One of the most effective strategies adopted by major e-fuel market players has been collaborating with other players in the ecosystem. For example, Porsche partnered with Siemens Energy and other investors in 2021 to establish e-Fuel production plants in Chile.
Early Mover Advantage: Companies like Clean Fuels Development Coalition and Porsche that started developing e-fuel technologies in early 2010s have established an early mover advantage. For example, Porsche's partnership with fuel suppliers in 2017-18 to supply racecars gave it a 3–4-year head-start over others.
Government Policy Support: E-fuel producers have successfully lobbied governments to introduce mandates and incentives supporting the development of e-fuels. Sweden, for example, introduced a blend mandate for aviation fuel in 2021 with the goal of using 1% e-fuel by 2030.
Focus on Hard to Electrify Applications: Major players are targeting applications which are difficult to electrify like aviation, shipping etc. through offtake agreements.
Segmental Analysis of E-Fuel Market
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
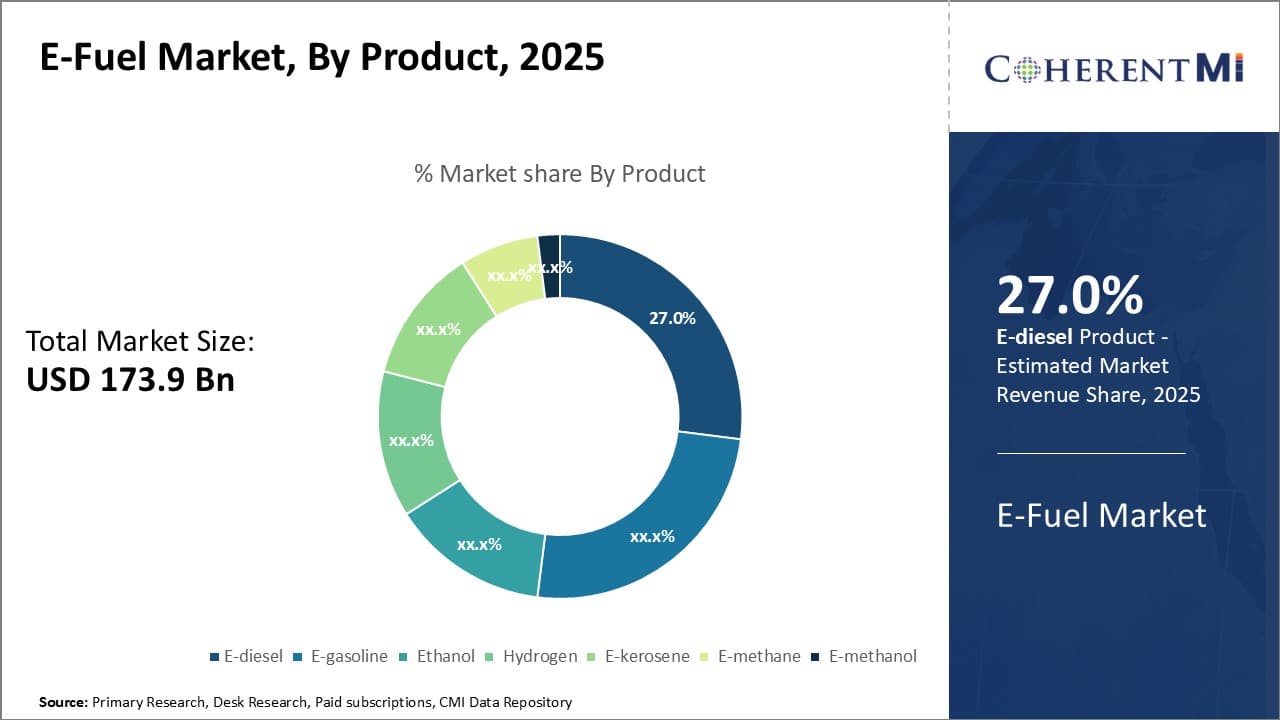
Insights, By Product: E-diesel Fueling Transportation Sector
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Product: E-diesel Fueling Transportation Sector
In terms of product, e-diesel contributes 27% share of the e-fuel market in 2025, owning to high demand from automotive and maritime industries. E-diesel is considered as one of the most viable and compatible substitutes for conventional diesel fuel. It can be directly used in diesel engines without any engine modifications, which makes it attractive for automobiles and ships.
A large fleet of trucks, buses, construction equipment and cargo ships heavily rely on diesel fuel. E-diesel is emerging as a sustainable drop-in replacement for them. Its widespread adoption can help decarbonize transportation - a major goal for many countries.
Moreover, commercial vehicles have longer replacement cycles than passenger cars, giving e-diesel more runway for penetration. As the transportation sector seeks solutions to reduce carbon footprint, e-diesel is expected gain significant traction in the foreseeable future, driving its share in the e-fuel market.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
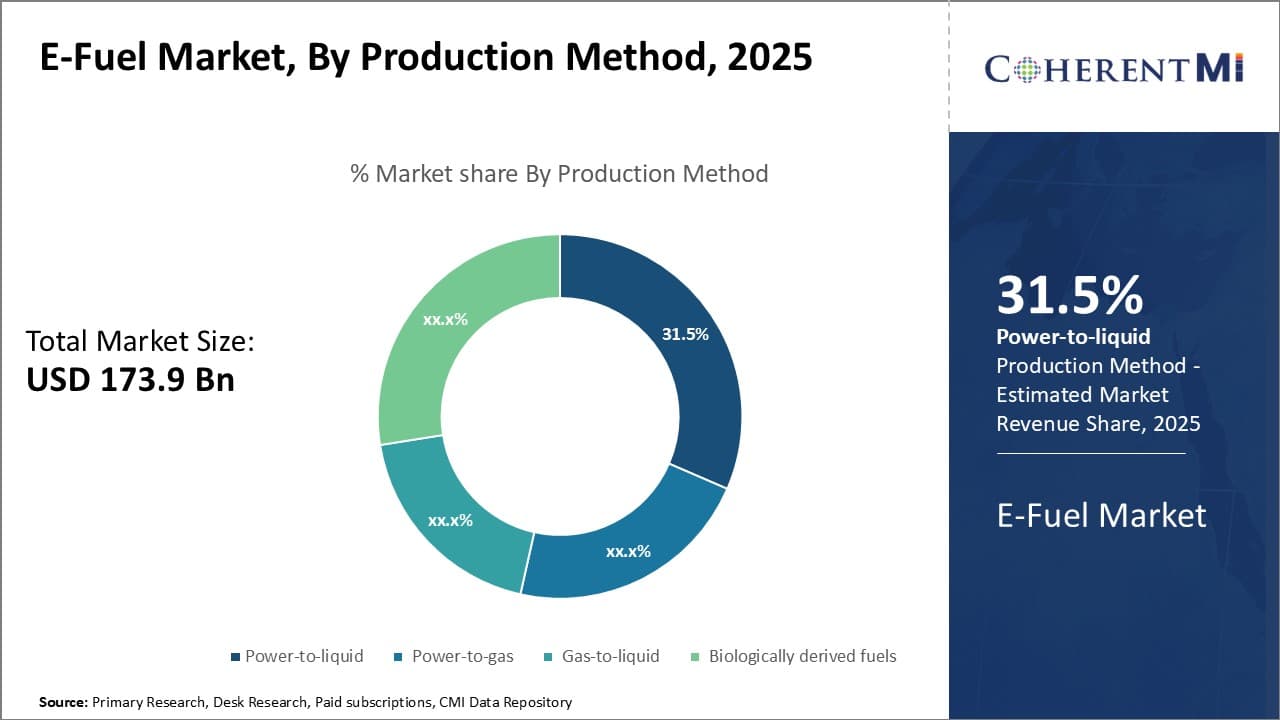
Insights, By Production Method: Power-to-liquid Method Powering Sustainable Pathways
In terms of production method, power-to-liquid method contributes the highest share of the e-fuel market owing to its promising potential. Power-to-liquid utilizes renewable electricity to produce carbon-neutral liquid fuels like e-gasoline and e-kerosene through steps involving electrolysis and methanation. Since renewable power sources like solar and wind are intermittent, their excess and off-peak energy can be stored in the form of liquid fuels using power-to-liquid technology. This offers grid balancing benefits.
Additionally, Power-to-liquid process can leverage established oil infrastructure for distribution and use of e-fuels in vehicles. This reduces economic barriers for production compared to other methods requiring new infrastructure. Given focus on integrating high shares of renewables worldwide, power-to-liquid is well-positioned to power sustainable energy pathways.
Insights, By Application: Automotive Sector Fueling Future Mobility
In terms of application, automotive segment contributes the highest share to the e-fuel market owing to active effort by automakers to electrify their fleets and pursue carbon neutrality. Both passenger electric vehicles and fuel-cell vehicles rely on e-fuels to operate. Whereas battery EVs can use e-gasoline and e-diesel, fuel-cell vehicles require e-methanol or hydrogen. Major automakers have already started producing battery as well as fuel-cell electric vehicles and expanding and promoting their models. Meanwhile, e-fuels provide compatibility with existing car designs and infrastructure. Therefore, the broad thrust towards greening the entire automotive fleet plays a crucial role in driving demand for e-fuels from this application segment. Looking ahead, widespread EV adoption combined with climate action commitment will likely propel the automotive application of e-fuels.
Additional Insights of E-Fuel Market
- Projected Demand Increase: The automotive sector is expected to account for over 40% of e-fuel demand by 2031 due to the rise of eco-friendly vehicles.
- Europe’s E-Fuel Market: Driven by stringent EU climate regulations and commitments to carbon neutrality, Europe dominates with a 47% revenue share in 2023.
- North America’s Growth: Expected to experience the fastest growth, supported by regulatory frameworks like the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) in the U.S. and Canada’s Clean Fuel Standard (CFS).
- Commercial Adoption by Airlines: Several airlines have begun testing e-kerosene to reduce their carbon footprint, signaling a significant shift in the aviation industry toward sustainable fuels.
- Government Subsidies: Some governments are offering subsidies and tax incentives to companies investing in e-fuel production, encouraging industry growth.
Competitive overview of E-Fuel Market
The major players operating in the e-fuel market include Archer Daniels Midland Co., Ballard Power Systems, Inc., Ceres Power Holding Plc, Clean Fuels Alliance America, Climeworks AG, E-Fuel Corporation, eFuel Pacific Limited, Hexagon Agility, Neste Oyj, Norsk e-Fuel AS, Siemens AG, Audi AG, Sunfire GmbH, and Carbon Recycling International.
E-Fuel Market Leaders
- Archer Daniels Midland Co.
- Ballard Power Systems, Inc.
- Ceres Power Holding Plc
- Clean Fuels Alliance America
- Climeworks AG
Recent Developments in E-Fuel Market
- In March 2024, IndiaOil launched ETHANOL 100 as an alternative automotive fuel in India to reduce fossil fuel dependency. IndianOil, along with the Indian government, has been actively promoting ethanol blending in petrol to reduce fossil fuel dependency and curb emissions.
- In June 2023, Siemens Energy partnered with Porsche to launch an e-fuel production pilot project in Chile. Utilizing wind energy, the project aims to produce synthetic fuels, potentially reducing CO2 emissions in the automotive sector.
- In June 2023, Norwegian Air Shuttle ASA announced a collaboration with Norsk e-Fuel to establish a plant in Mosjøen, Norway. The facility aims to produce sustainable synthetic aviation fuel, commonly known as e-fuel, starting in 2026.
- In April 2023, Audi AG invested in Sunfire GmbH to advance the development of high-temperature electrolysis technology. This collaboration seeks to enhance e-fuel production efficiency.
E-Fuel Market Segmentation
- By Product
- E-diesel
- E-gasoline
- Ethanol
- Hydrogen
- E-kerosene
- E-methane
- E-methanol
- By Production Method
- Power-to-liquid
- Power-to-gas
- Gas-to-liquid
- Biologically derived fuels
- By Application
- Automotive
- Aviation
- Maritime
- Power Generation
- By State
- Liquid
- Gas
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Sakshi Suryawanshi is a Research Consultant with 6 years of extensive experience in market research and consulting. She is proficient in market estimation, competitive analysis, and patent analysis. Sakshi excels in identifying market trends and evaluating competitive landscapes to provide actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making. Her expertise helps businesses navigate complex market dynamics and achieve their objectives effectively.
