Nuclear Reactor Market Size - Analysis
The nuclear reactor market is estimated to be valued at USD 48.32 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 62.31 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7% from 2025 to 2032. The nuclear reactor market is expected to witness positive growth over the forecast period, driven by factors such as rising concerns regarding climate change and need for low-carbon energy sources.
The nuclear reactor market is estimated to be valued at USD 48.32 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 62.31 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7% from 2025 to 2032.
The nuclear reactor market is expected to witness positive growth over the forecast period, driven by factors such as rising concerns regarding climate change and need for low-carbon energy sources.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR3.7%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 3.7% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Alstom, Areva S.A., BWX Technologies, Inc., Dongfang Electric Corp., Ltd., Doosan Corporation and Among Others |
please let us know !
Nuclear Reactor Market Trends
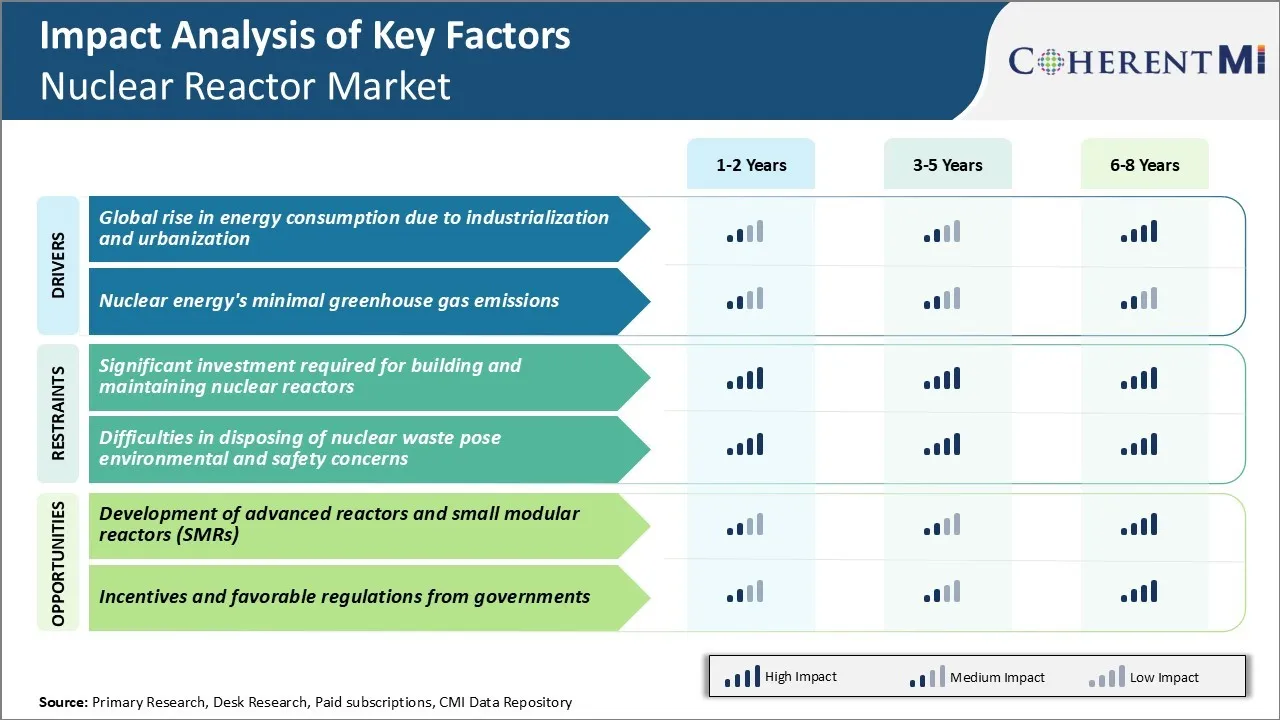
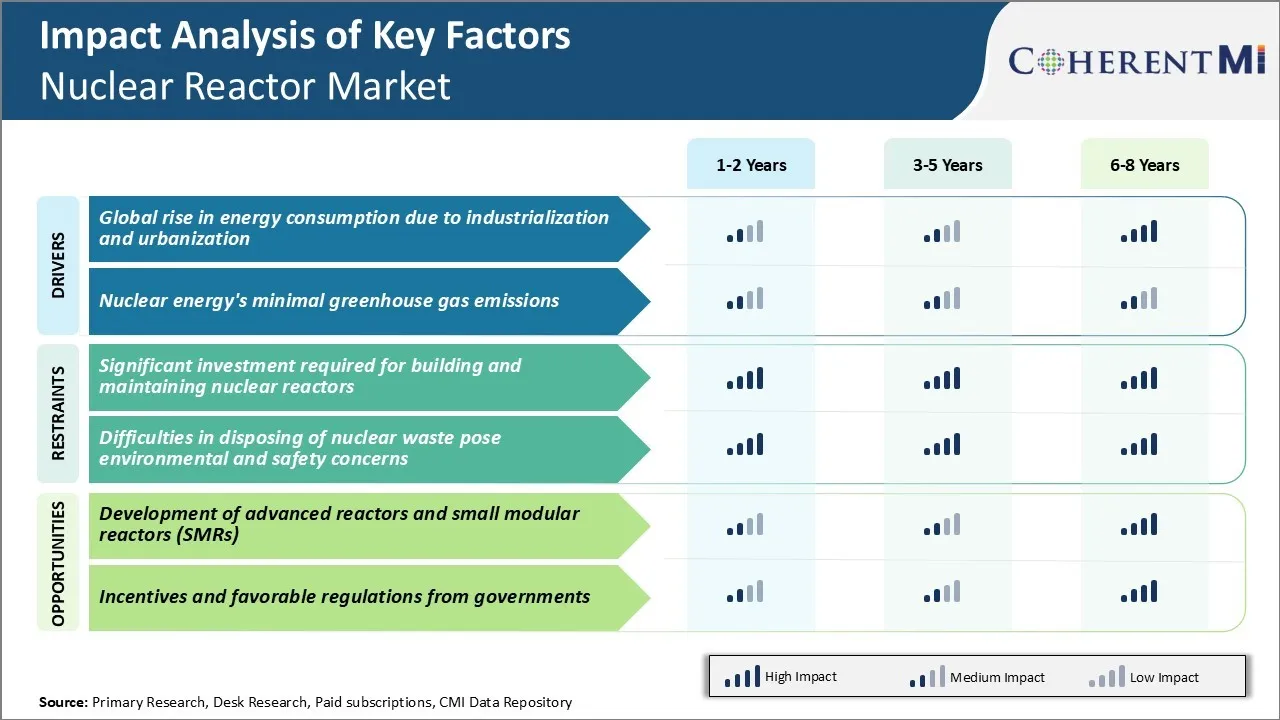
Market Driver - Global Rise in Energy Consumption due to Industrialization and Urbanization
As industrialization and urbanization picks up pace around the world, global energy consumption is also increasing at a dramatic rate to support this growth. At the same time, developed nations require growing amounts of energy to fuel their large industrial bases and power modern amenities in homes and offices with rising living standards.
With escalating energy consumption projected to continue well into the future, there is an urgent need for reliable and sustainable energy sources that can meet large-scale power needs consistently over the long-term. Nuclear power with its high energy density has emerged as one viable option to fulfill mounting electricity demands while reducing emissions. Though nuclear plants involve high upfront investment costs, once constructed they can generate massive amounts of steady base-load power for decades to come. Their operation also does not emit greenhouse gases and most nations have sufficient domestic uranium resources or can import them to fuel reactors.
New nuclear reactor designs also aim to address concerns around safety, cost and waste management. Overall, nuclear energy's potential to deliver carbon-free electricity at gigawatt scales, accelerating growth prospects for the nuclear reactor market.
Market Driver – Nuclear Reactors: A Greenhouse Gas Friendly Option
While the world grapples with the threatening impacts of climate change caused by heat-trapping emissions, transitioning to low-carbon sources of energy is paramount. Fossil fuels which currently account for over 80% of the global energy mix are the single largest contributor to climate change.
However, reducing dependence on coal, oil and gas is incredibly difficult given how deeply entrenched they are across power infrastructure, transportation and various industries. Rapid economic growth in emerging markets has also led to a steep rise in their fossil fuel consumption levels in recent decades.
As per various studies, the use of nuclear energy has already avoided emitting billions of tons of carbon into the environment. Scaling up nuclear power capacity can significantly aid emission reduction targets of nations as per the Paris Agreement on climate change. Besides providing clean energy on a utility-scale, nuclear can also help diversify the energy mix and boost energy security by reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels. Newer reactor designs promise even more sustainable operations with minimal waste. Overall, nuclear reactors’ almost zero-emission attribute makes it a key component of transitioning to a low-carbon economy.
 To learn more about this report,Request Sample Copy
To learn more about this report,Request Sample Copy
Market Challenge - Significant Investment Required for Building and Maintaining Nuclear Reactors
The nuclear reactor market faces significant challenges related to the massive investments required for building and maintaining nuclear power facilities. Setting up a new nuclear power plant demands billions of dollars’ worth of capital investments. For instance, the Hinkley Point C project in the UK which is currently under construction is expected to cost around £20 billion.
Existing nuclear plants also require heavy and consistent investments to ensure safety standards are met through the facilities’ operational lifetimes that can stretch over decades. Regular maintenance, repair, refueling and upgrades of outdated equipment add to operational expenses.
The high fixed costs associated with nuclear power make the energy less competitive compared to other renewable sources such as solar and wind, whose installation and maintenance costs have reduced significantly in recent years.
Overall, the long payback periods and risky investments needed for building and sustaining nuclear infrastructure pose serious economic challenges to the growth of the nuclear reactor market.
Market Opportunity - Development of Advanced Reactors and Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
The nuclear reactor market is witnessing opportunities arising from the development of advanced reactor designs as well as small modular reactors. Advances in reactor technologies aim to enhance safety features, reduce costs of building and operating facilities, increase fuel efficiency and address challenges of nuclear waste disposal.
For instance, molten salt and sodium-cooled fast reactor concepts promise enhanced efficiency compared to existing light water reactor technologies. Researchers are also working on designs of small modular reactors that can be factory-fabricated and transported to sites as ready-to-install modules rather than huge conventional reactors.
SMRs have lower upfront capital requirements for installation and hold promise for decentralized off-grid energy production. Their modular design also allows incremental capacity additions matching growing power demands. It is expected that innovative advanced and small modular reactor technologies will help open up new markets for nuclear energy in the coming decades. This emerges as a significant opportunity for companies involved in the nuclear reactor supply chain.
As industrialization and urbanization picks up pace around the world, global energy consumption is also increasing at a dramatic rate to support this growth.
At the same time, developed nations require growing amounts of energy to fuel their large industrial bases and power modern amenities in homes and offices with rising living standards.
With escalating energy consumption projected to continue well into the future, there is an urgent need for reliable and sustainable energy sources that can meet large-scale power needs consistently over the long-term.
Nuclear power with its high energy density has emerged as one viable option to fulfill mounting electricity demands while reducing emissions.
Though nuclear plants involve high upfront investment costs, once constructed they can generate massive amounts of steady base-load power for decades to come.
Their operation also does not emit greenhouse gases and most nations have sufficient domestic uranium resources or can import them to fuel reactors.
New nuclear reactor designs also aim to address concerns around safety, cost and waste management.
Overall, nuclear energy's potential to deliver carbon-free electricity at gigawatt scales, accelerating growth prospects for the nuclear reactor market.
While the world grapples with the threatening impacts of climate change caused by heat-trapping emissions, transitioning to low-carbon sources of energy is paramount.
Fossil fuels which currently account for over 80% of the global energy mix are the single largest contributor to climate change.
However, reducing dependence on coal, oil and gas is incredibly difficult given how deeply entrenched they are across power infrastructure, transportation and various industries.
Rapid economic growth in emerging markets has also led to a steep rise in their fossil fuel consumption levels in recent decades.
As per various studies, the use of nuclear energy has already avoided emitting billions of tons of carbon into the environment.
Scaling up nuclear power capacity can significantly aid emission reduction targets of nations as per the Paris Agreement on climate change.
Besides providing clean energy on a utility-scale, nuclear can also help diversify the energy mix and boost energy security by reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
Newer reactor designs promise even more sustainable operations with minimal waste.
Overall, nuclear reactors’ almost zero-emission attribute makes it a key component of transitioning to a low-carbon economy.
The nuclear reactor market faces significant challenges related to the massive investments required for building and maintaining nuclear power facilities.
Setting up a new nuclear power plant demands billions of dollars’ worth of capital investments.
For instance, the Hinkley Point C project in the UK which is currently under construction is expected to cost around £20 billion.
Existing nuclear plants also require heavy and consistent investments to ensure safety standards are met through the facilities’ operational lifetimes that can stretch over decades.
Regular maintenance, repair, refueling and upgrades of outdated equipment add to operational expenses.
The high fixed costs associated with nuclear power make the energy less competitive compared to other renewable sources such as solar and wind, whose installation and maintenance costs have reduced significantly in recent years.
Overall, the long payback periods and risky investments needed for building and sustaining nuclear infrastructure pose serious economic challenges to the growth of the nuclear reactor market.
The nuclear reactor market is witnessing opportunities arising from the development of advanced reactor designs as well as small modular reactors.
Advances in reactor technologies aim to enhance safety features, reduce costs of building and operating facilities, increase fuel efficiency and address challenges of nuclear waste disposal.
For instance, molten salt and sodium-cooled fast reactor concepts promise enhanced efficiency compared to existing light water reactor technologies.
Researchers are also working on designs of small modular reactors that can be factory-fabricated and transported to sites as ready-to-install modules rather than huge conventional reactors.
SMRs have lower upfront capital requirements for installation and hold promise for decentralized off-grid energy production.
Their modular design also allows incremental capacity additions matching growing power demands.
It is expected that innovative advanced and small modular reactor technologies will help open up new markets for nuclear energy in the coming decades.
This emerges as a significant opportunity for companies involved in the nuclear reactor supply chain.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Nuclear Reactor Market
Focus on innovation and advanced technologies
One of the major strategies adopted by leading players such as Westinghouse Electric Company and General Electric has been to focus heavily on research and development to bring innovative nuclear reactor designs and advanced technologies to the nuclear reactor market.
For example, GE-Hitachi has focused on developing smaller, modular reactors that can be factory-built and transported to customer sites for rapid deployment. Its BWRX-300 design received early site permit from the US NRC in 2020. The focus on innovative solutions has helped these players position themselves at the cutting-edge of the nuclear reactor market.
Strategic international partnerships and collaborations
Many vendors in the nuclear reactor market have adopted a strategy of forging strategic international partnerships and collaboration agreements to win large nuclear plant construction contracts globally.
One of the major strategies adopted by leading players such as Westinghouse Electric Company and General Electric has been to focus heavily on research and development to bring innovative nuclear reactor designs and advanced technologies to the nuclear reactor market.
For example, GE-Hitachi has focused on developing smaller, modular reactors that can be factory-built and transported to customer sites for rapid deployment.
Its BWRX-300 design received early site permit from the US NRC in 2020.
The focus on innovative solutions has helped these players position themselves at the cutting-edge of the nuclear reactor market.
Many vendors in the nuclear reactor market have adopted a strategy of forging strategic international partnerships and collaboration agreements to win large nuclear plant construction contracts globally.
Segmental Analysis of Nuclear Reactor Market
 To learn more about this report,Request Sample Copy
To learn more about this report,Request Sample Copy
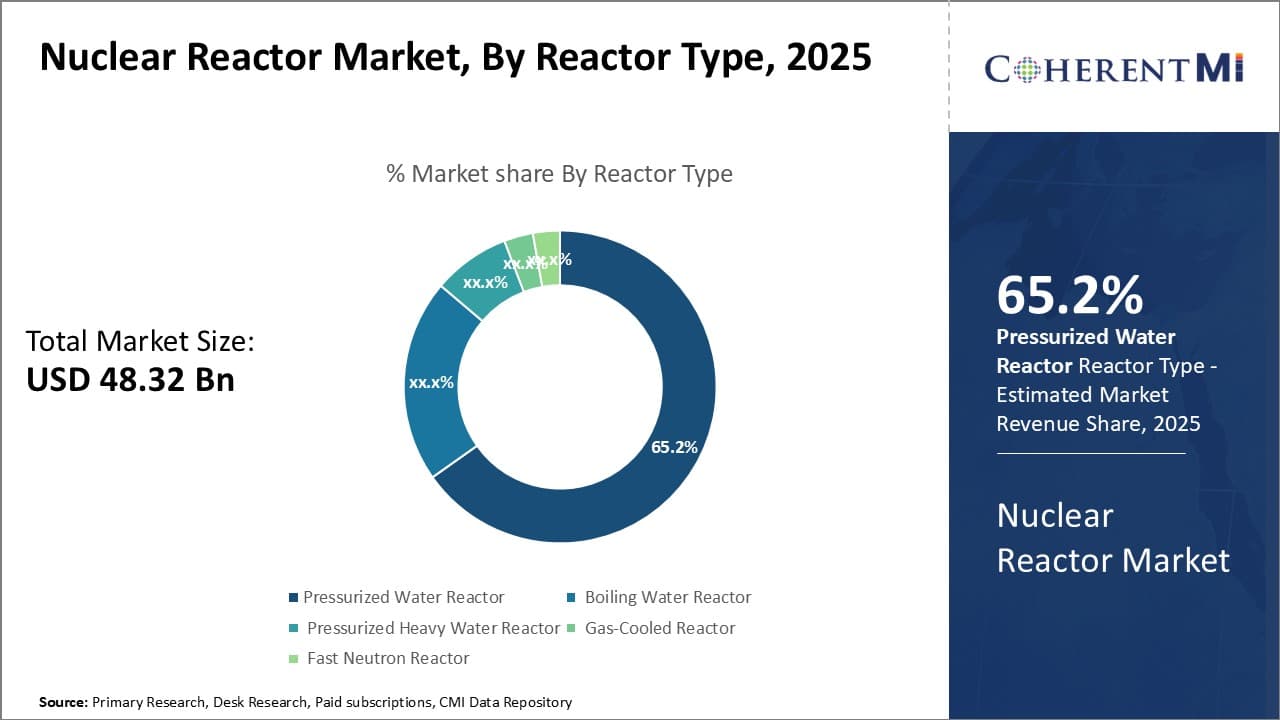
Insights, By Reactor Type: Streamlined Operations Drive PWR Adoption
In terms of reactor type, pressurized water reactor (PWR) is expected to 65.2% share of the nuclear reactor market in 2025. This is due to its relatively streamlined design and operations compared to other reactors. The conventional PWR design utilizes a primary loop where highly pressurized water transfers heat from the reactor core to a steam generator.
This separates the radioactive primary coolant from the non-radioactive secondary system where steam is generated to drive the turbine. Such a dedicated heat transfer system allows for safer, more efficient energy production without risk of radioactive steam exposure.
Advanced PWR models have further optimized the basic design through features like lower enriched fuel, passive safety systems and modular construction. Standardized passive safety systems in particular can trigger emergency cooling without external power or operator action, offering robust protection against accidents. Thereby, this segment is expected to influence the nuclear reactor market trends in coming years.
 To learn more about this report,Request Sample Copy
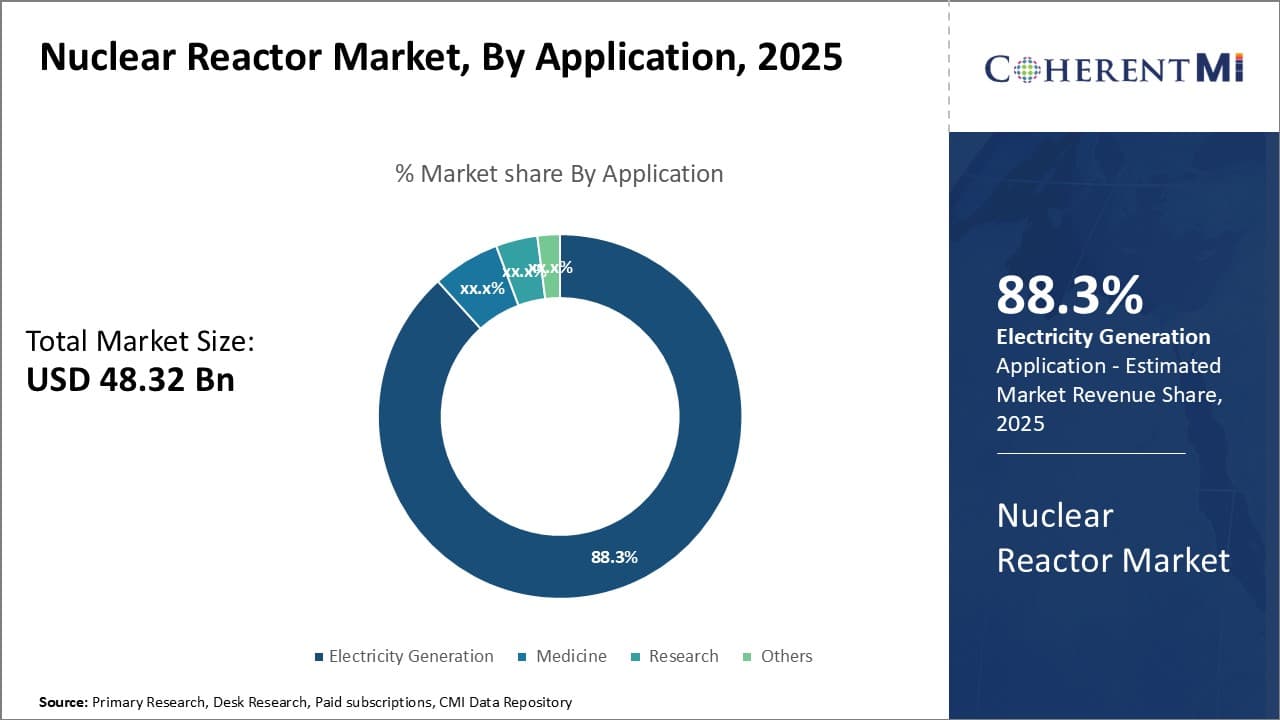
Insights, By Application: Wide Range of Uses Increase BWR Popularity
To learn more about this report,Request Sample Copy
Insights, By Application: Wide Range of Uses Increase BWR Popularity
In terms of application, electricity generation contributes 88.3% share of the nuclear reactor market in 2025. This is due to the flexibility of boiling water reactors (BWR) to not only produce base-load power but supplement peak demand as well. Unlike some reactor designs tightly coupled to large-scale grid output, BWRs can efficiently operate across a spectrum of power levels. Plant operators have precise control over steam flow and pressure to quickly match electricity needs.
This varied output profile makes BWRs highly suitable for diverse grid requirements. As intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind proliferate grids, nuclear fleets need flexibility to balance their intermittency. BWR versatility supports reliable integration of such variable generation.
Resulting revenue streams beyond just power sales enhance BWR project economics. Their multi-purpose energy delivery leads utilities and independent power producers to favor BWR fleets for balanced, resilient grid provision well into the coming decades.
Insights, By End User: Reliable Output Favors Commercial Sector
In terms of end user, the commercial sector contributes the highest share in the nuclear reactor market due to nuclear energy's unmatched reliability in supplying baseload power. Petrochemical facilities also depend on uninterrupted electricity to run delicate refining and separation equipment. Unplanned outages risk safety incidents or environmental damage.
Nuclear energy's near-100% capacity factors give commercial clients certainty that power will flow rain or shine. No concerns over fuel price volatility or interruptions from weather events like hurricanes disrupting gas pipelines or transmission lines as with fossil alternatives.
Even for utilities, nuclear energy's reliable, zero-emission attributes help satisfy emission targets while ensuring power customers never want for power even during extreme conditions. Hospitals, data centers and other sensitive commercial loads receive quality power continuously without risk of blackouts from fuel supply problems or extreme weather.
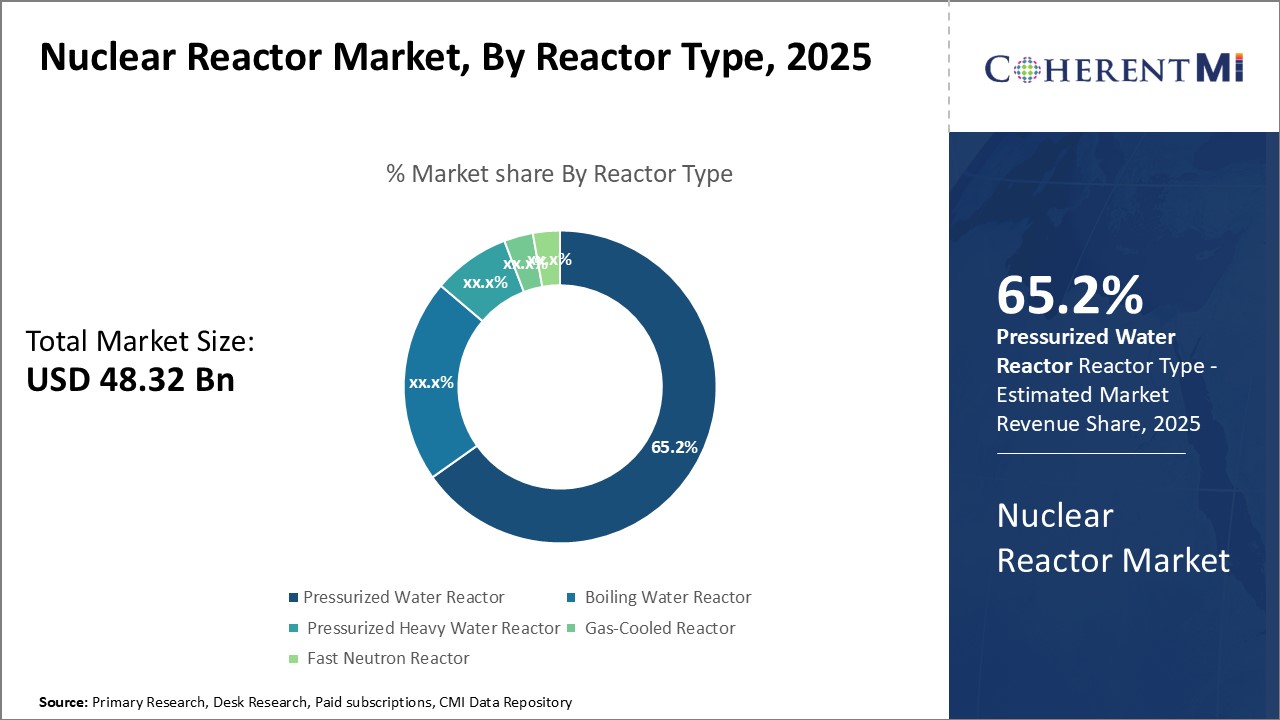
In terms of reactor type, pressurized water reactor (PWR) is expected to 65.2% share of the nuclear reactor market in 2025.
This is due to its relatively streamlined design and operations compared to other reactors.
The conventional PWR design utilizes a primary loop where highly pressurized water transfers heat from the reactor core to a steam generator.
This separates the radioactive primary coolant from the non-radioactive secondary system where steam is generated to drive the turbine.
Such a dedicated heat transfer system allows for safer, more efficient energy production without risk of radioactive steam exposure.
Advanced PWR models have further optimized the basic design through features like lower enriched fuel, passive safety systems and modular construction.
Standardized passive safety systems in particular can trigger emergency cooling without external power or operator action, offering robust protection against accidents.
Thereby, this segment is expected to influence the nuclear reactor market trends in coming years.
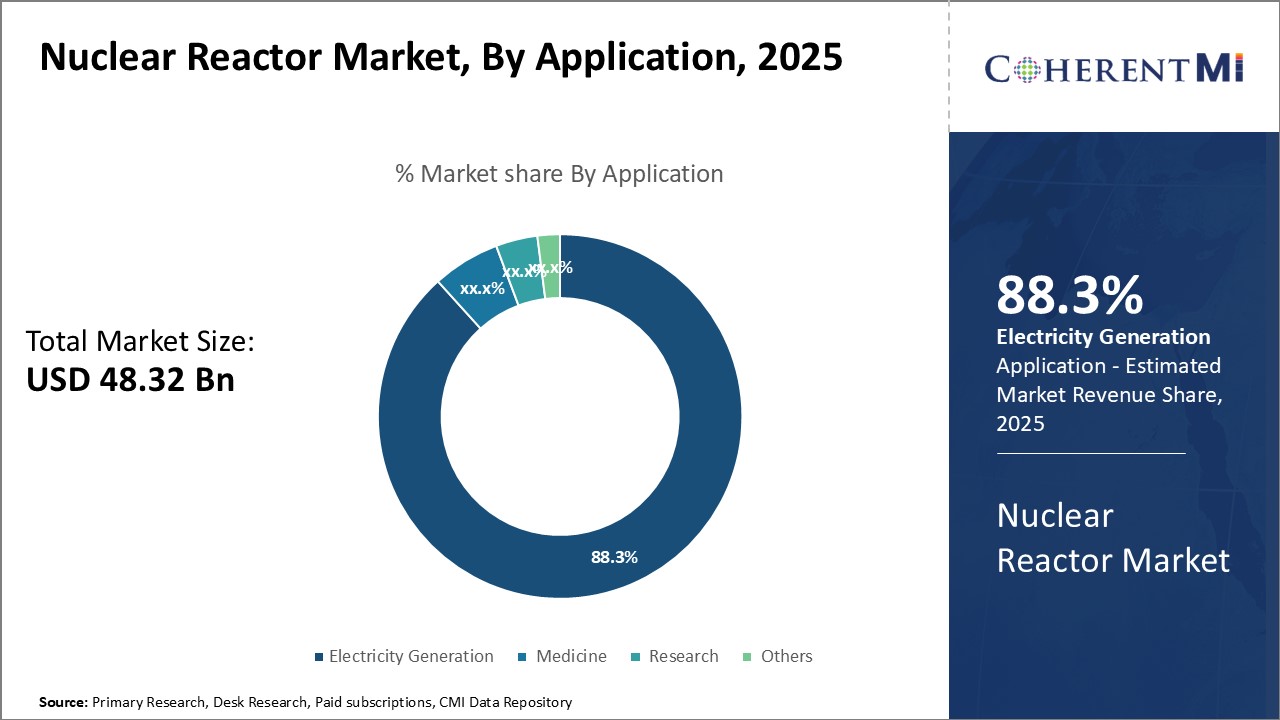 Insights, By Application: Wide Range of Uses Increase BWR Popularity
Insights, By Application: Wide Range of Uses Increase BWR PopularityIn terms of application, electricity generation contributes 88.3% share of the nuclear reactor market in 2025.
This is due to the flexibility of boiling water reactors (BWR) to not only produce base-load power but supplement peak demand as well.
Unlike some reactor designs tightly coupled to large-scale grid output, BWRs can efficiently operate across a spectrum of power levels.
Plant operators have precise control over steam flow and pressure to quickly match electricity needs.
This varied output profile makes BWRs highly suitable for diverse grid requirements.
As intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind proliferate grids, nuclear fleets need flexibility to balance their intermittency.
BWR versatility supports reliable integration of such variable generation.
Resulting revenue streams beyond just power sales enhance BWR project economics.
Their multi-purpose energy delivery leads utilities and independent power producers to favor BWR fleets for balanced, resilient grid provision well into the coming decades.
In terms of end user, the commercial sector contributes the highest share in the nuclear reactor market due to nuclear energy's unmatched reliability in supplying baseload power.
Petrochemical facilities also depend on uninterrupted electricity to run delicate refining and separation equipment.
Unplanned outages risk safety incidents or environmental damage.
Nuclear energy's near-100% capacity factors give commercial clients certainty that power will flow rain or shine.
No concerns over fuel price volatility or interruptions from weather events like hurricanes disrupting gas pipelines or transmission lines as with fossil alternatives.
Even for utilities, nuclear energy's reliable, zero-emission attributes help satisfy emission targets while ensuring power customers never want for power even during extreme conditions.
Hospitals, data centers and other sensitive commercial loads receive quality power continuously without risk of blackouts from fuel supply problems or extreme weather.
Additional Insights of Nuclear Reactor Market
- Asia Pacific’s Dominance: The region holds the largest share in 2023 in the nuclear reactor market due to significant investments in nuclear energy, particularly in China and India.
- Europe's Growth: Expected to be the fastest-growing region in the nuclear reactor market due to rising investments in nuclear technology and long-term development plans by EU nations.
- Nuclear power contributes about 9% of the world's electricity, with a significant increase expected as nuclear infrastructure grows.
- 440 operational nuclear reactors worldwide are driving global electricity generation, marking an important nuclear reactor market trend.
- Following historical nuclear incidents, there has been a global emphasis on improving nuclear reactor safety. The adoption of passive safety systems and rigorous regulatory frameworks has become standard practice in the nuclear reactor market.
- Asia Pacific’s Dominance: The region holds the largest share in 2023 in the nuclear reactor market due to significant investments in nuclear energy, particularly in China and India.
- Europe's Growth: Expected to be the fastest-growing region in the nuclear reactor market due to rising investments in nuclear technology and long-term development plans by EU nations.
- Nuclear power contributes about 9% of the world's electricity, with a significant increase expected as nuclear infrastructure grows.
- 440 operational nuclear reactors worldwide are driving global electricity generation, marking an important nuclear reactor market trend.
- Following historical nuclear incidents, there has been a global emphasis on improving nuclear reactor safety. The adoption of passive safety systems and rigorous regulatory frameworks has become standard practice in the nuclear reactor market.
Competitive overview of Nuclear Reactor Market
The major players operating in the nuclear reactor market include Alstom, Areva S.A., BWX Technologies, Inc., Dongfang Electric Corp., Ltd., Doosan Corporation, General Electric Company (GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy), Korea Electric Power Corporation, Larsen & Toubro Limited, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, LTD., Shanghai Electric, The State Atomic Energy Corporation, Toshiba Corporation, Rosatom State Atomic Energy Corporation, Electricité de France S.A. (EDF), China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC), China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC), and Westinghouse Electric Company LLC.
The major players operating in the nuclear reactor market include Alstom, Areva S.A., BWX Technologies, Inc., Dongfang Electric Corp., Ltd., Doosan Corporation, General Electric Company (GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy), Korea Electric Power Corporation, Larsen & Toubro Limited, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, LTD., Shanghai Electric, The State Atomic Energy Corporation, Toshiba Corporation, Rosatom State Atomic Energy Corporation, Electricité de France S.A.
(EDF), China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC), China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC), and Westinghouse Electric Company LLC.
Nuclear Reactor Market Leaders
- Alstom
- Areva S.A.
- BWX Technologies, Inc.
- Dongfang Electric Corp., Ltd.
- Doosan Corporation
Recent Developments in Nuclear Reactor Market
- In June 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) issued a request for proposals (RFP) to purchase low-enriched uranium (LEU) from domestic sources. This initiative is backed by $2.7 billion as part of President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, aimed at enhancing the domestic nuclear fuel supply chain.
- In March 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi witnessed the commencement of core loading at India’s first indigenous Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) located in Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu. This event marks a significant milestone in India's nuclear energy development, as the reactor is a key part of the country's three-stage nuclear power program aimed at achieving energy self-sufficiency.
- In April 2021, GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH) partnered with Synthos Green Energy (SGE) to advance the deployment of small modular reactors (SMRs) in Poland, specifically the BWRX-300 design. This collaboration aims to facilitate the construction of at least 10 BWRX-300 reactors in Poland, targeting operational readiness by 2029.
- In June 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) issued a request for proposals (RFP) to purchase low-enriched uranium (LEU) from domestic sources. This initiative is backed by $2.7 billion as part of President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, aimed at enhancing the domestic nuclear fuel supply chain.
- In March 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi witnessed the commencement of core loading at India’s first indigenous Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) located in Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu. This event marks a significant milestone in India's nuclear energy development, as the reactor is a key part of the country's three-stage nuclear power program aimed at achieving energy self-sufficiency.
- In April 2021, GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH) partnered with Synthos Green Energy (SGE) to advance the deployment of small modular reactors (SMRs) in Poland, specifically the BWRX-300 design. This collaboration aims to facilitate the construction of at least 10 BWRX-300 reactors in Poland, targeting operational readiness by 2029.
Nuclear Reactor Market Segmentation
- By Reactor Type
- Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)
- Conventional PWR
- Advanced PWR
- Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)
- Conventional BWR
- Advanced BWR
- Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR)
- CANDU Reactors
- Advanced PHWR
- Gas-Cooled Reactor (GCR)
- Magnox Reactors
- Advanced Gas-Cooled Reactors (AGR)
- Fast Neutron Reactor (FNR)
- Sodium-Cooled Fast Reactors
- Lead-Cooled Fast Reactors
- Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)
- By Application
- Electricity Generation
- Base Load Power
- Peak Load Power
- Medicine
- Radioisotope Production
- Radiation Therapy
- Research
- Scientific Research
- Material Testing
- Others
- Desalination
- Space Applications
- Electricity Generation
- By End User
- Commercial
- Utility Companies
- Independent Power Producers
- Residential
- District Heating
- Community Power Supply
- Industrial
- Manufacturing Plants
- Petrochemical Industries
- Commercial
- By Reactor Type
- Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)
- Conventional PWR
- Advanced PWR
- Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)
- Conventional BWR
- Advanced BWR
- Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR)
- CANDU Reactors
- Advanced PHWR
- Gas-Cooled Reactor (GCR)
- Magnox Reactors
- Advanced Gas-Cooled Reactors (AGR)
- Fast Neutron Reactor (FNR)
- Sodium-Cooled Fast Reactors
- Lead-Cooled Fast Reactors
- Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)
- By Application
- Electricity Generation
- Base Load Power
- Peak Load Power
- Medicine
- Radioisotope Production
- Radiation Therapy
- Research
- Scientific Research
- Material Testing
- Others
- Desalination
- Space Applications
- Electricity Generation
- By End User
- Commercial
- Utility Companies
- Independent Power Producers
- Residential
- District Heating
- Community Power Supply
- Industrial
- Manufacturing Plants
- Petrochemical Industries
- Commercial

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Sakshi Suryawanshi is a Research Consultant with 6 years of extensive experience in market research and consulting. She is proficient in market estimation, competitive analysis, and patent analysis. Sakshi excels in identifying market trends and evaluating competitive landscapes to provide actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making. Her expertise helps businesses navigate complex market dynamics and achieve their objectives effectively.