

The Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.70 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 5.89 Bn by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.8% from 2025 to 2032. The market is primarily driven by the rising cases of diabetes across the globe. Strong product pipeline and increasing availability of various treatment options are proving conducive for market growth.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR11.8%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 11.8% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | Novartis, Roche, Bayer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Allergan and Among Others |
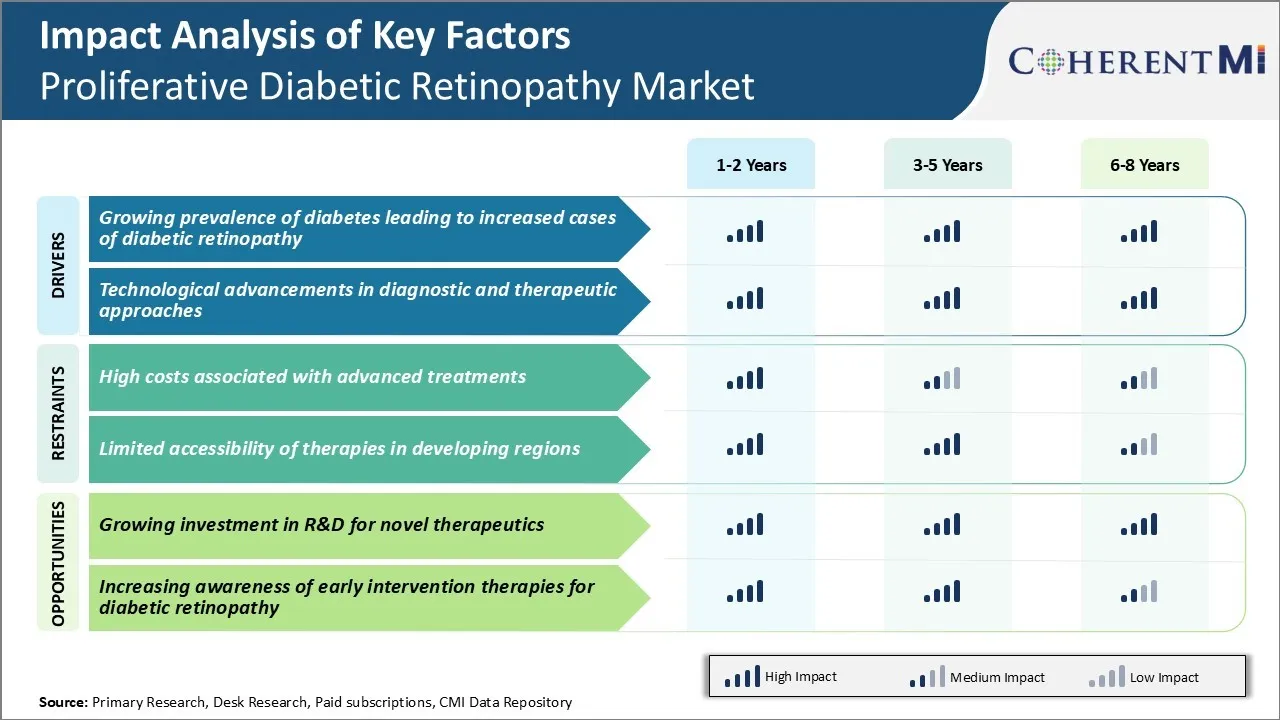
Market Driver - Growing Prevalence of Diabetes Leading to Increased Cases of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that has impacted millions worldwide over the past few decades. Both types 1 and 2 diabetes damage small blood vessels in the retina, resulting in diabetic retinopathy. It is estimated that nearly all type 1 diabetics and over 60% of type 2 diabetics develop some form of retinopathy after 20 years of living with this metabolic disease.
As more individuals are diagnosed with diabetes each year due to changing lifestyles and inadequate physical activity levels, the at-risk patient pool for developing retinal complications continues to expand rapidly.
Nearly half a billion adults were living with diabetes globally in 2019 according to the latest WHO estimates. This number has doubled since 1980 and is further expected to rise in the coming years due to aging populations and the growing prevalence of obesity. Countries with developing economies in particular have witnessed massive surges in diabetes incidence rates due to growing westernization of diets and reduced physical exertion in daily lives.
All these newly diagnosed diabetes cases will fuel the demand for retinopathy screening and treatment in the long run as retinal damage occurs years after the onset of the metabolic disease and its inadequate management.
Market Driver - Technological Advancements in Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches
Significant technological advancement is another major driver bolstering the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market. Various new diagnostic imaging systems and therapeutic drugs/devices have improved ability to detect retinopathy at early stages and deliver more targeted treatment interventions.
Wide field digital imaging such as Optos and Heidelberg retina angiography have replaced conventional mydriatic cameras for non-mydriatic and ultra-wide field retinal screening. These provide advantages of greater field of view to detect peripheral lesions, higher resolution and easier portability. In terms of therapeutics, anti-VEGF injections through innovations like Ozurdex implant and port delivery systems have made vascular ablation procedures less invasive and more effective.
Advances in laser photocoagulation including pattern scanning laser (PASCAL), navigated laser and automated variable spot size also enable more precise photocoagulation with less collateral damage. Surgical technologies have also progressed, examples being small gauge vitrectomy systems and lens sparing vitrectomy. These allow faster surgery time, sutureless closure and early visual rehabilitation.
Researchers are additionally investigating drug therapies beyond anti-VEGFs and new coating technologies for controlled drug delivery through implants inserted in the eye. Such continuous developments in retinopathy imaging, screening and therapeutics are allowing earlier detection as well as personalized treatment approaches tailored for each patient's needs.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - High Costs Associated with Advanced Treatments
One of the major challenges faced by the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market is the high costs associated with advanced treatment options such as anti-VEGF injections and laser surgery. These treatment methods require specialized equipment, regular follow-up appointments and monitoring, and frequent re-administration of drugs in some cases. This makes the overall cost of treatment quite steep.
For example, a single intravitreal injection of anti-VEGF drugs like ranibizumab or aflibercept can cost thousands of dollars. Patients are often required to receive multiple injections periodically to manage their condition. Similarly, procedures like panretinal laser photocoagulation require specialized lasers and surgical facilities that contribute significantly to the overall costs.
The economic burden of frequent and expensive treatments poses challenges in terms of access and adherence to therapy, especially in developing countries and for the uninsured population in developed markets. This high cost of care is a major limiting factor for the overall growth of this market.
Market Opportunity - Growing Investment in R&D for Novel Therapeutics
One of the key opportunities for the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market is the growing levels of investment seen in R&D for novel therapeutic drugs and technologies. Several biopharmaceutical companies and venture capital funds are investing heavily in developing new drug delivery approaches, biomarkers, and molecular targets to treat proliferative DR.
For example, significant research is ongoing to develop sustained release intraocular implants that can continuously deliver anti-VEGF drugs over longer periods, reducing the frequency of injections. Other novel avenues being explored include gene therapy, stem cell therapy, and therapies targeting new molecules like connective tissue growth factor.
The success of these development efforts can help address some of the current limitations and introduce more efficacious and cost-effective treatment options. This growing pipeline of innovative therapies and the expected approval of novel drugs in the near future present lucrative growth prospects for stakeholders in the proliferative DR market.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) is an advanced stage of diabetic eye disease where abnormal blood vessels grow into the vitreous gel. These fragile new vessels can bleed or leak fluid into the vitreous cavity, causing rapid vision loss.
The first line of treatment for PDR includes controlling blood sugar and using anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) injections directly into the eye. Common anti-VEGF drugs prescribed are ranibizumab (Lucentis) and aflibercept (Eylea). These therapies are effective in halting further development of abnormal blood vessels but require frequent monitoring and injections by an ophthalmologist.
If the disease progresses despite anti-VEGF therapy, panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) is the next line of treatment recommended. During PRP, an ophthalmologist uses a laser to apply small burns to the peripheral retina. This shrinks and seals abnormal new blood vessels by triggering scarring. Extensive PRP over multiple sittings is usually needed to treat the entire retina.
In advanced, uncontrolled PDR, surgeons may recommend vitrectomy surgery to remove the blood and scar tissue from the vitreous cavity. This helps relieve symptoms of bleeding, traction and improves chances of vision recovery. Post-surgery, medications like anti-VEGFs are continued to prevent re-proliferation of vessels.
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) is an advanced stage of diabetic eye disease characterized by the growth of new blood vessels in the retina. There are three stages of PDR - mild, moderate, and severe.
For mild to moderate PDR, the preferred first-line treatment is laser photocoagulation therapy. During this procedure, a laser is used to generate burns on the retina in order to seal off blood vessels and prevent further growth of new blood vessels. This helps reduce the risk of vision loss.
For patients who do not respond to laser therapy or have severe/high-risk PDR, anti-VEGF injections are recommended. These injections contain medications like ranibizumab (Lucentis) or aflibercept (Eylea) that inhibit Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), a protein that triggers the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. Anti-VEGF therapy is effective at halting the progression of the disease and stabilizing vision by suppressing new blood vessel growth.
In cases where PDR has led to the formation of preretinal or vitreous hemorrhage, vitrectomy surgery may be required to clear the hemorrhage and prevent further vision loss. During vitrectomy, the vitreous gel inside the eye is removed and replaced with saline or gas. This allows for better visibility of the retina and removal of any tractional retinal detachments.
Focus on advanced therapy delivery - Several leading companies are focusing on developing more advanced methods for delivering anti-VEGF therapy to patients. For example, AbbVie received FDA approval in 2018 for their Susvimo (port delivery system with ranibizumab) treatment which allows for sustained drug release over months with fewer injections required.
Strategic acquisitions and partnerships - Major players are acquiring and partnering with smaller biotechs to gain access to new and promising drug candidates. For example, Novartis acquired Roche's osteopontin gene therapy program in 2020 to accelerate its development and potential commercialization.
Geographic expansion into emerging markets - As developing countries report growing diabetes prevalence, companies are actively expanding sales and distribution networks across Asia, Latin America, Middle East and Africa. For instance, Regeneron tripled their international Eylea sales from 2016 to 2020 by commercializing in over 50 countries.
Increased R&D investment in novel technologies - Leaders are dedicating more funds towards developing gene therapies, stem cell therapies and other cutting-edge treatments. For example, Allergan invested $625 million in 2020 to support abicipar's phase 3 trials, the largest for an anti-VEGF candidate.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
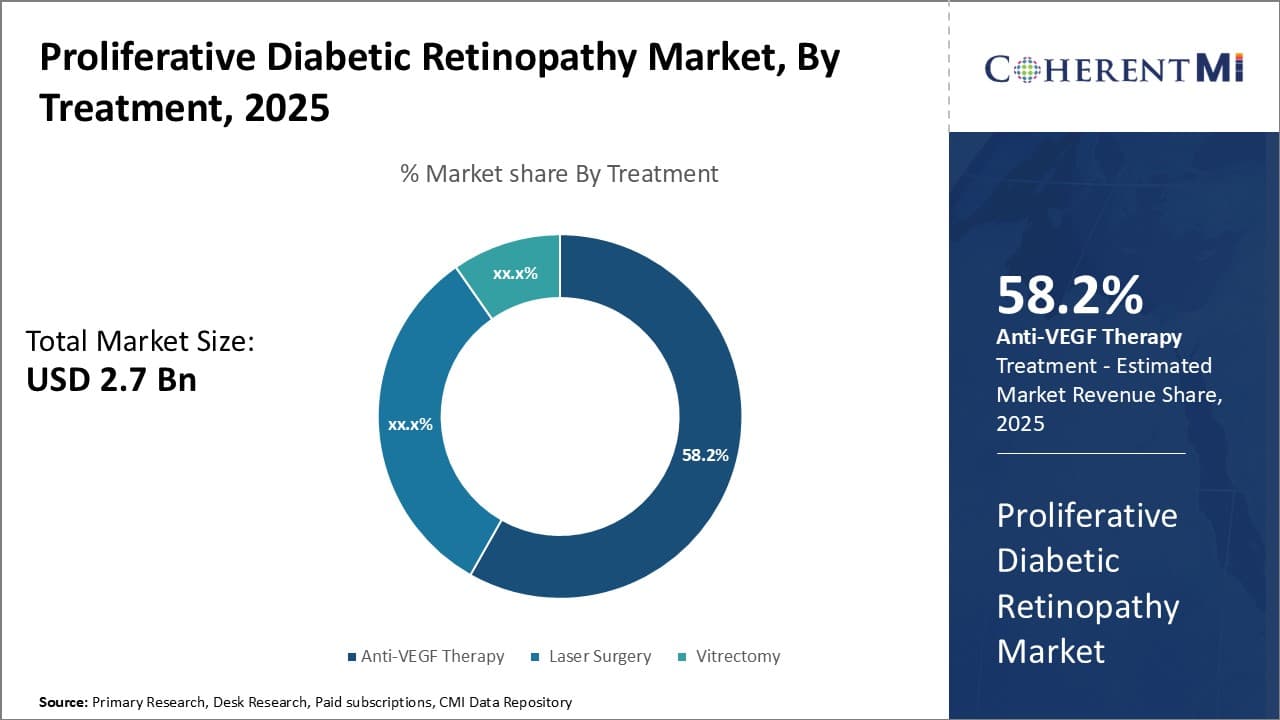
Insights, By Treatment: The Ever-Growing Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Treatment: The Ever-Growing Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy
In terms of treatment, anti-VEGF therapy is expected to hold 58.2% share of the market in 2025, owning to its effectiveness in treating abnormal blood vessel growth associated with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Anti-VEGF drugs work by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor, a protein that stimulates the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
The rising prevalence of diabetes driven by obesity, physical inactivity and poor diet has led to a corresponding surge in diabetic retinopathy cases globally. This has significantly boosted demand for anti-VEGF drugs which are considered the first line of treatment for proliferative stages of the disease.
The non-invasive nature and fewer side effects of intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF drugs make them a preferred choice over other surgical options. Continued development of improved anti-VEGF formulations with longer duration of action and high biocompatibility is also fueling their uptake.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
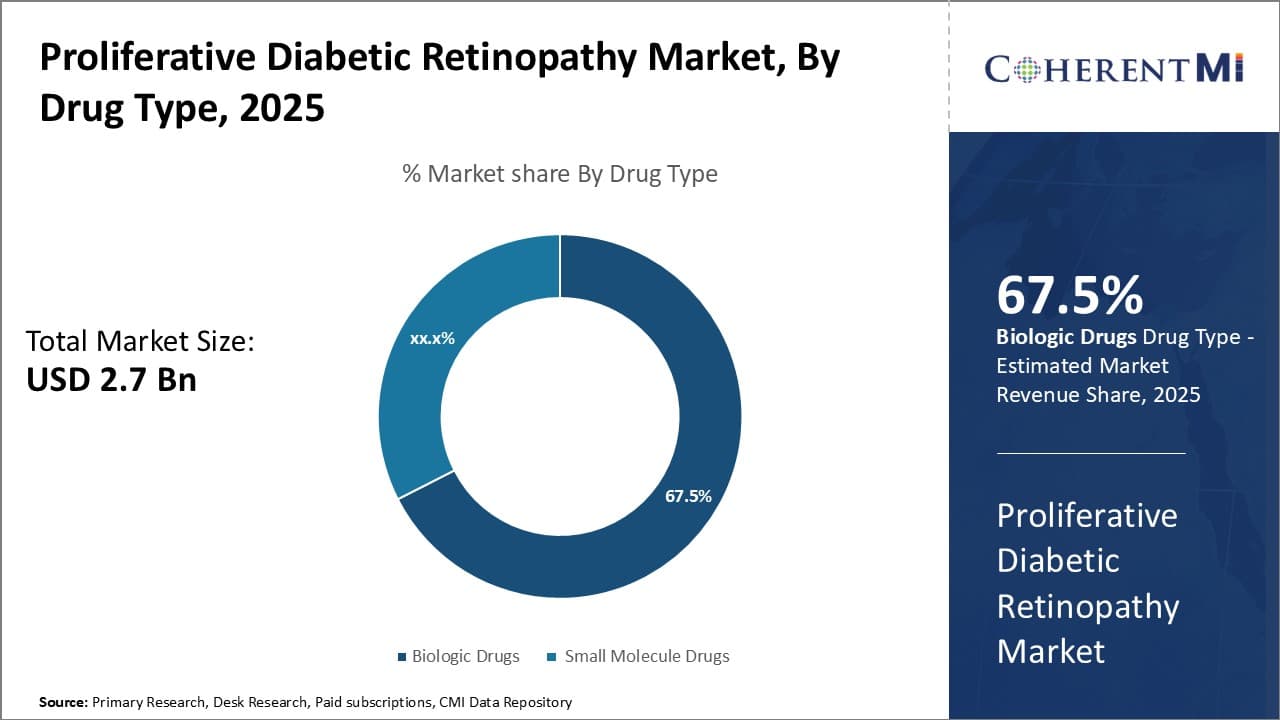
Insights, By Drug Type: Preference for Targeted Drug Delivery
In terms of drug type, biologic drugs is projected to account for 67.5% share of the market in 2025, owing to their ability to precisely target disease pathways. Unlike small molecule drugs, biologics provide greater selectivity by mimicking natural human proteins, antibodies, enzymes or receptors. They are thus able to more specifically block VEGF receptors and other growth factors elevating abnormal blood vessel formation in the retina.
Biologics also demonstrate improved pharmacokinetics over small molecules given their large molecular structure limiting non-specific distribution. Additionally, biologic drugs usually have high binding affinity and long half-lives enabling longer dosing intervals and superior management of vision threatening complications of proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Advances in monoclonal antibody and fusion protein technologies have augmented the development of novel biologic drugs with enhanced efficacy and safety profiles.
Insights, By Delivery Mechanism: Convenience and Compliance with Intraocular Delivery
In terms of delivery mechanism, intravitreal injections contribute the highest share due to the direct delivery of medications to the eye. Intravitreal injections ensure high drug concentrations are achieved at the targeted retinal tissues with minimal systemic exposure and side effects.
The one-time intraocular administration results in immediate therapeutic response without the need for frequent oral administrations associated with low patient adherence. It eliminates issues involving gastrointestinal degradation and first pass liver metabolism seen with other delivery routes.
Additionally, intravitreal injections are generally well-tolerated with a good safety profile. Such convenience and reliability factors have made intravitreal injections the preferred mode for administration of biologics for treating proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
The major players operating in the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market include Novartis, Roche, Bayer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Allergan, Ocuphire Pharma, Inc., and OcuTerra Therapeutics, Inc.
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Komal Dighe is a Management Consultant with over 8 years of experience in market research and consulting. She excels in managing and delivering high-quality insights and solutions in Health-tech Consulting reports. Her expertise encompasses conducting both primary and secondary research, effectively addressing client requirements, and excelling in market estimation and forecast. Her comprehensive approach ensures that clients receive thorough and accurate analyses, enabling them to make informed decisions and capitalize on market opportunities.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Market is segmented By Treatment (Anti-VEGF Therapy, Laser Surger...
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Market
How big is the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market?
The proliferative diabetic retinopathy market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.70 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 5.89 Bn by 2032.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market?
High costs associated with advanced treatments and limited accessibility of therapies in developing regions are the major factors hampering the growth of the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market.
What are the major factors driving the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market growth?
Growing prevalence of diabetes leading to increased cases of diabetic retinopathy and technological advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic approaches are the major factors driving the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market.
Which is the leading treatment in the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market?
The leading treatment segment is anti-VEGF therapy.
Which are the major players operating in the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market?
Novartis, Roche, Bayer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Allergan, Ocuphire Pharma, Inc., and OcuTerra Therapeutics, Inc. are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market?
The CAGR of the proliferative diabetic retinopathy market is projected to be 11.8% from 2025-2032.