Small Hydropower Market Size - Analysis
The small hydropower market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.33 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 3.007 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.00% from 2025 to 2032. The small hydropower market is driven by the growing demand for renewable energy sources across the world.
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR3.00%
| Study Period | 2025-2032 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2024 |
| CAGR | 3.00% |
| Market Concentration | High |
| Major Players | Andritz AG, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited, FLOVEL Energy Private Limited, GE Renewable Energy, Gilbert Gilkes & Gordon Ltd and Among Others |
please let us know !
Small Hydropower Market Trends
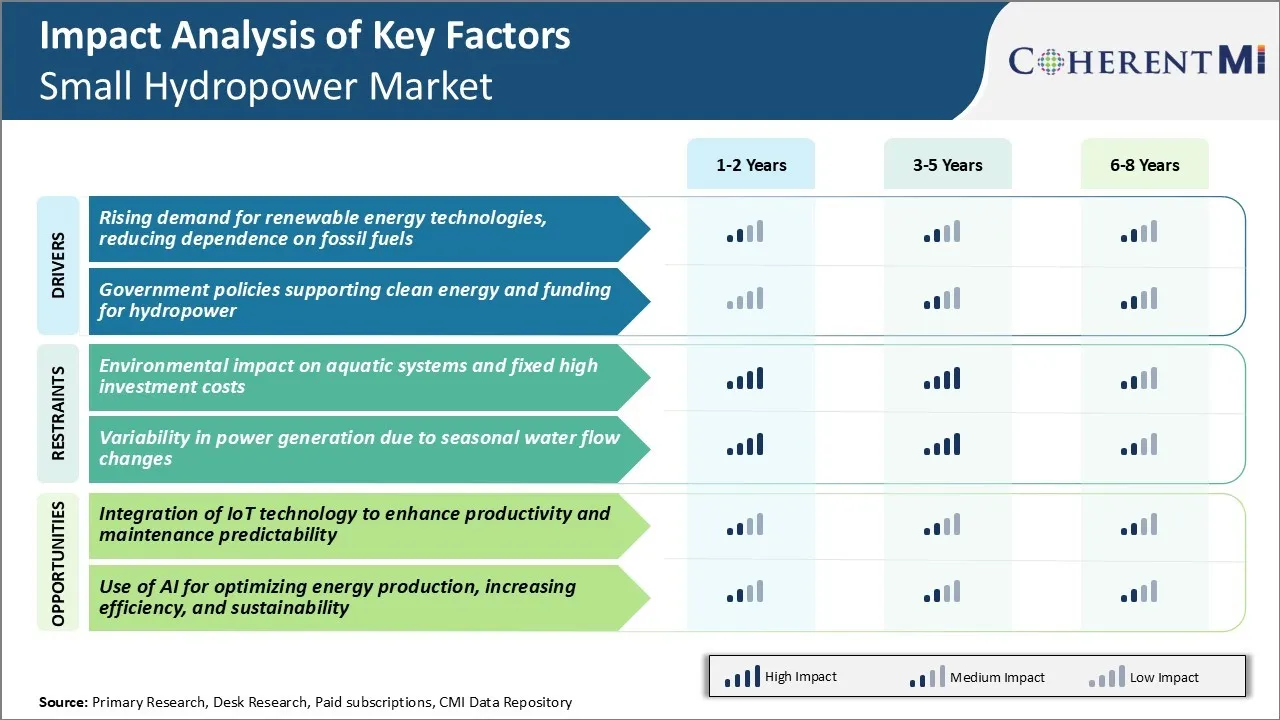
Market Driver - Rising Demand for Renewable Energy Technologies, Reducing Dependence on Fossil Fuels
The global energy landscape is undergoing a massive transformation driven by the imperatives of energy security, energy access and environmental sustainability. Countries around the world are making concerted efforts to shift towards cleaner energy sources to reduce their carbon footprint as well as diversify their energy mix away from expensive and volatile oil imports.
Small hydropower is emerging as an important part of this energy transition being a renewable, carbon-free source of energy. Many countries, especially in the developing world, still have large untapped hydropower potential which can be harnessed through small hydropower projects.
Growing emphasis on clean energy future bodes well for technologies like small hydropower which can seamlessly integrate into the grid and fulfill energy needs in a sustainable manner. Overall, the rising global momentum to transition to low carbon growth trajectory is a positive driver augmenting growth of the small hydropower market.
Market Driver - Government Policies Supporting Clean Energy and Funding for Hydropower
Many countries have formulated conducive regulatory mechanisms and rolled out attractive incentives to attract private sector investments into clean technologies. Small hydropower has been a direct beneficiary of such enabling initiatives.
Many governments offer a range of fiscal incentives for small hydropower projects such as tax breaks, subsidies, capital grants, low interest loans, feed-in-tariffs etc. This helps mini/micro hydropower achieve price competitiveness compared to conventional fuels. In addition, some nations have also instituted mandatory renewable purchase obligations which create a guaranteed market for renewable power producers.
Recognizing the immense unharnessed hydropower potential in their territories, several countries have also instituted regulatory policies reserving a certain proportion of hydropower development for small-scale projects. Some governments have gone a step further through intervention programs focused on capacity building, R&D, market intelligence, and awareness generation. These multi-pronged policy thrusts are expected to provide continued impetus to growth of affordable, scalable and environment-benign small hydropower market globally.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Market Challenge - Environmental Impact and High Investment Costs
Small hydropower projects can negatively impact local aquatic ecosystems during construction and operations. Dams disrupt the natural flow of rivers, which can harm fish populations that rely on upstream and downstream migration patterns.
The sediment build-up from damming can degrade water quality and damage habitats over time. Addressing these environmental factors requires extensive research and mitigation plans that increase initial costs.
Installing small hydropower infrastructure also has significant capital expenses for building weirs, pipes, turbines, and electrical connections. Retrofitting an existing dam for power generation still demands sizeable investment in hydroelectric equipment. Initial feasibility studies, permits, and equipment also contribute to high upfront costs.
Given the scale of individual small hydropower projects, the levelized cost of electricity generated can be comparable to large conventional power plants. High capital expenditures present a major financial challenge for companies in the small hydropower market.
Market Opportunity - Utilizing IoT Technology to Enhance Productivity and Maintenance
The small hydropower market could leverage Internet of Things (IoT) technology to optimize productivity and reduce long-term maintenance costs. Sensors installed on turbines, generators, and other critical components can remotely monitor performance data in real-time. Machine learning algorithms could then analyze operational patterns to detect any abnormal function or deterioration. This predictive monitoring capability allows issues to be identified early before major repairs are needed.
Remote asset management powered by IoT further cuts costs by decreasing unnecessary site visits. Field technicians do not need to constantly inspect equipment in-person when digital twin models provide virtual oversight. Automatic notifications of any sensor readings outside normal parameters ensures proactive maintenance.
When integrated into small hydropower infrastructure, IoT has the potential to dramatically enhance long-term productivity and reduce overall electricity costs. This will produce lucrative opportunities for players in the small hydropower market.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Small Hydropower Market
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations: Forming strategic partnerships has been a major strategy for small hydropower players to enter new markets and gain expertise. For example, in 2018, Voith partnered with China Three Gorges Corporation to develop small hydropower projects in Southeast Asia.
Focus on Emerging Markets: With saturated markets in developed nations, players have focused on high growth emerging economies in Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Africa.
Cost Leadership: Given the smaller scale of projects, controlling costs is critical. Players like Voith and Andritz have leveraged their large project experience and supply chain to offer standardized, pre-engineered solutions at lower prices.
Customer Focus: Strong localized customer support helps players better understand projects and customers' needs. For example, Gilkes focuses heavily on after-sales services through regional teams.
Segmental Analysis of Small Hydropower Market
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
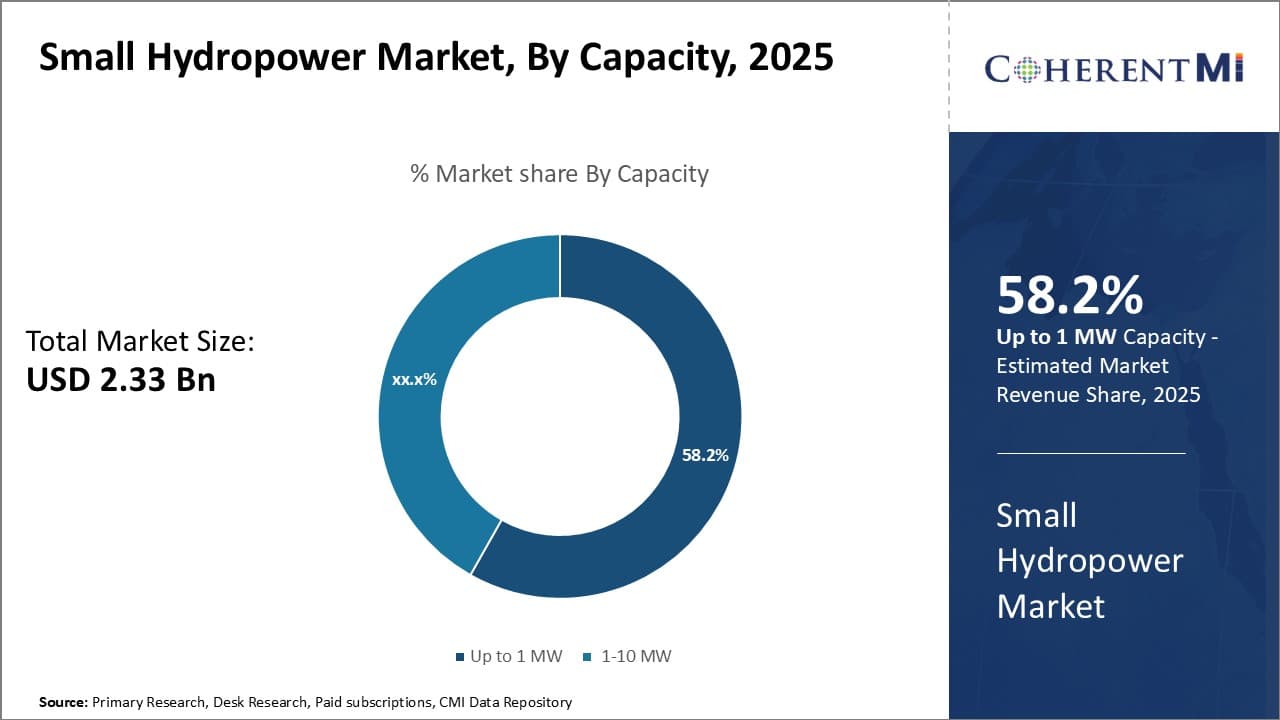
Insights, By Capacity: Up to 1 MW - Reliance on Indigenous Resources
In terms of capacity, up to 1 MW contributes 58.2% share of the small hydropower market in 2025, owning to their reliance on indigenous resources. Plants with capacity up to 1 MW tend to use smaller streams and rivers which are abundant locally. This allows them to avoid significant investments in civil infrastructure like large dams and pipelines to divert water from faraway places.
Depending on locally available water resources also ensures the project risks are relatively lower compared to large projects. These plants are suitable for decentralized power generation in remote off-grid rural communities which lack access to national power grids. Their small scale of operations also means lower environmental impacts and quicker construction times.
As many countries aim to boost rural electrification, segment Up to 1 MW is expected to grow steadily in the small hydropower market.
 To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
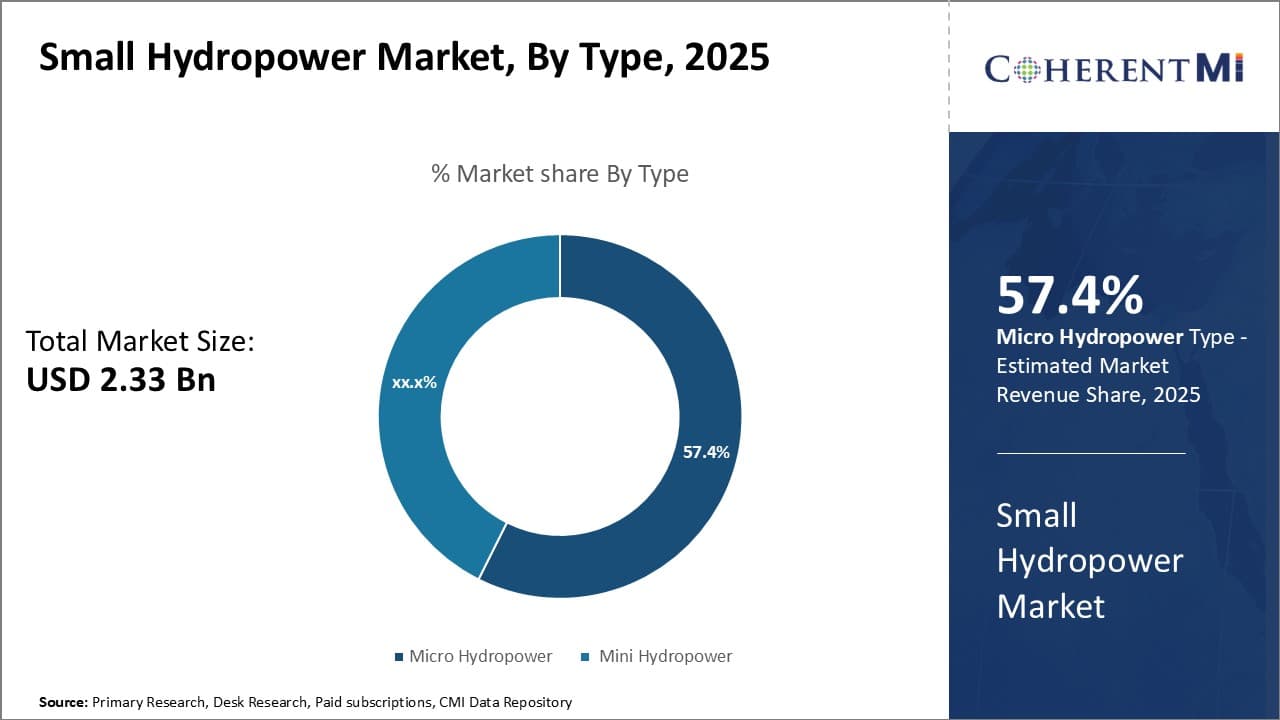
Insights, By Type: Viability in Off-Grid Areas
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Copy
Insights, By Type: Viability in Off-Grid Areas
In terms of type, micro hydropower contributes 57.4% share of the small hydropower market in 2025, owing to their high viability in serving off-grid rural areas. Micro plants with capacities below 100 kW are well-suited for distributed energy applications far from existing infrastructure. Their modular designs allow flexible installation near water resources in remote mountainous villages.
The lower investment requirements of micro plants compared to other renewables make them affordable even for poorer communities. With higher energy security and lower costs than diesel generators, they effectively meet the lighting and appliance needs of off-grid households.
In the small hydropower market, the micro hydropower segment is poised for growth through its ability to deliver clean power to unelectrified areas with minimal dependence on external infrastructure.
Insights, By Plant: Run-of-River Plants Show Consistency in Flow
In terms of plant, run-of-river plants contributes the highest share of the small hydropower market owing to their advantages in terms of consistency in flow. Run-of-river hydropower harnesses the kinetic energy of free-flowing rivers without the need for large reservoirs to store water. This ensures a steady supply of electricity throughout the year as long as the river is flowing, even during dry seasons.
The absence of huge reservoirs also reduces environmental footprints and social impacts associated with submergence of inhabited lands. Compared to reservoir-based facilities, run-of-river projects have shorter construction periods and lower capital investments. They can be conveniently set up on smaller rivers with lesser storage requirements.
With more emphasis on sustainable technologies, run-of-river plants will continue capture a major share of the small hydropower market in the future through their consistency in energy generation without disturbing natural river flows.
Additional Insights of Small Hydropower Market
- Global Renewable Energy Contribution: Small hydropower accounts for approximately 4.5% of the world's renewable energy generation.
- Regional Growth: Asia Pacific dominates the small hydropower market with over 40% share, driven by significant investments in China and India.
- Environmental Impact: Small hydropower plants have a lower ecological footprint compared to large dams, making them favorable under strict environmental regulations.
- Community-Driven Projects: In regions like Africa and Southeast Asia, local communities are initiating small hydropower projects to gain energy independence and support sustainable development.
- Retrofitting Existing Dams: There's a growing trend of adding power-generating equipment to non-powered dams, optimizing existing infrastructure for energy production without additional environmental impact.
Competitive overview of Small Hydropower Market
The major players operating in the small hydropower market include Andritz AG, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited, FLOVEL Energy Private Limited, GE Renewable Energy, Gilbert Gilkes & Gordon Ltd, Natel Energy, Siemens Energy, SNC Lavalin Group, Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation, Voith GmbH & Co. KGaA, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), Canadian Hydro Components Ltd., Mavel, a.s., and Canyon Hydro.
Small Hydropower Market Leaders
- Andritz AG
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
- FLOVEL Energy Private Limited
- GE Renewable Energy
- Gilbert Gilkes & Gordon Ltd
Recent Developments in Small Hydropower Market
- In June 2023, Voith GmbH & Co. KGaA launched a new high-efficiency micro turbine designed for low-flow water streams. This innovation allows for energy generation in previously non-viable locations, potentially increasing global small hydropower capacity.
- In May 2023, China's National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) approved the construction of a hydropower plant in the Xizang (Tibet) Autonomous Region. The project, with an investment of approximately 58.38 billion yuan (about $8.43 billion), is expected to have a total capacity of 2.6 million kilowatts and generate over 11.28 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity annually.
- In April 2023, GE Renewable Energy entered into a contract with PGE Odnawialna S.A. to modernize the 500 MW Porąbka-Żar pumped hydro storage plant in Poland. The project involves replacing four 125 MW pumped turbines and generators, aiming to extend the plant's operational life by several decades.
- In January 2023, the Ganol Hydro Power Project in Meghalaya, India, was inaugurated, adding 22.5 MW of capacity to the state's power supply. The project, valued at over ₹560 crore (approximately USD 67 million), is expected to significantly enhance the local power infrastructure.
Small Hydropower Market Segmentation
- By Capacity
- Up to 1 MW
- 1-10 MW
- By Type
- Micro Hydropower
- Mini Hydropower
- By Plant
- Run-of-River Plants
- Reservoir-Based Plants
- By Component
- Electromechanical Equipment
- Turbines
- Generators
- Electric Infrastructure
- Transformers
- Switchgears
- Civil Works
- Dams
- Canals
- Others
- Control Systems
- Monitoring Equipment
- Electromechanical Equipment
Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Sakshi Suryawanshi is a Research Consultant with 6 years of extensive experience in market research and consulting. She is proficient in market estimation, competitive analysis, and patent analysis. Sakshi excels in identifying market trends and evaluating competitive landscapes to provide actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making. Her expertise helps businesses navigate complex market dynamics and achieve their objectives effectively.
