Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market SIZE AND SHARE ANALYSIS - GROWTH TRENDS AND FORECASTS (2024 - 2031)
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market is segmented By Drug (Monoclonal Antibody, Small Molecule, Peptide), By Route of Administration (Oral, Parente....
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market Size
Market Size in USD Bn
CAGR8.36%
| Study Period | 2024 - 2031 |
| Base Year of Estimation | 2023 |
| CAGR | 8.36% |
| Market Concentration | Medium |
| Major Players | AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Merck & Co., Novartis, Basilea Pharmaceutica and Among Others. |
please let us know !
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market Analysis
The pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.3 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.28 Bn by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.36% from 2024 to 2031. Increased investment in research and development of novel drugs and vaccines for treatment and prevention is driving the market. Growing geriatric population who are more susceptible to bacterial infections also contributes to market growth.
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market Trends
Market Driver - Increasing Incidence of Multidrug-resistant Bacterial Strains
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is regarded as a notorious bug due to its intrinsic resilience that allows it to resist a variety of antimicrobial agents. The rising prevalence of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections poses a significant threat in both healthcare and community settings. Treatment failure and mortality associated with such infections has increased manifold. Multidrug-resistant strains spread rapidly between patients especially in crowded healthcare facilities with poor infection control practices.
Outbreaks due to these "superbugs" have become common and widespread across geographies. Moreover, biofilm formation on indwelling medical devices allows the bacteria to persist for longer durations, leading to chronic resistant infections that are more difficult to eradicate.
The growing resistance underscores the urgent need for novel drugs that can effectively tackle strains resistant to frontline antimicrobials. Traditional drug discovery approaches need to be supplemented with newer strategies focused on modulating bacterial virulence, inhibiting biofilm formation and disrupting efflux mechanisms.
Combination therapies as well as alternative treatment methods such as phage therapy also hold promise in overcoming resistance. Overall, the pervasiveness of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains has increased the clinical imperative for more effective therapies, thereby driving growth in this market.
Market Driver - Rising Demand for Novel Therapies that Address Resistant Infections
The inability to effectively treat multidrug-resistant pseudomonas aeruginosa infections with existing antimicrobial armamentarium has led to increased demand for newer treatment paradigms. Conventional antibiotics are failing against these "superbugs" and the dwindling drug pipeline calls for innovative non-antibiotic therapies that can address resistance. Additionally, there is a need to develop new drugs that can specifically target Pseudomonas aeruginosa without facing cross-resistance issues.
Traditional small-molecule antibiotics are proving increasingly inefficient amidst continuously evolving resistance mechanisms. Novel therapeutic approaches such as monoclonal antibodies, anti-virulence drugs, biofilm-disrupting agents, and phage therapies have garnered significant research interest in recent times. These alternative modalities aim to curb bacterial pathogenesis through non-antibiotic mechanisms, thereby slowing down the emergence of resistance.
Immunotherapies that leverage the body's natural defenses are also being explored. Monoclonal antibodies represent an attractive immunotherapy approach with potential to confer protection against virulent strains. Agents targeting critical virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa like type III secretion system and associated toxins hold promise.
In addition, combination regimens leveraging synergies between drug classes show ability to restore antimicrobial activity against resistant strains. Alternative therapies involving phage endolysins, bacteriophage therapy, and engineered synergy are generating optimism.
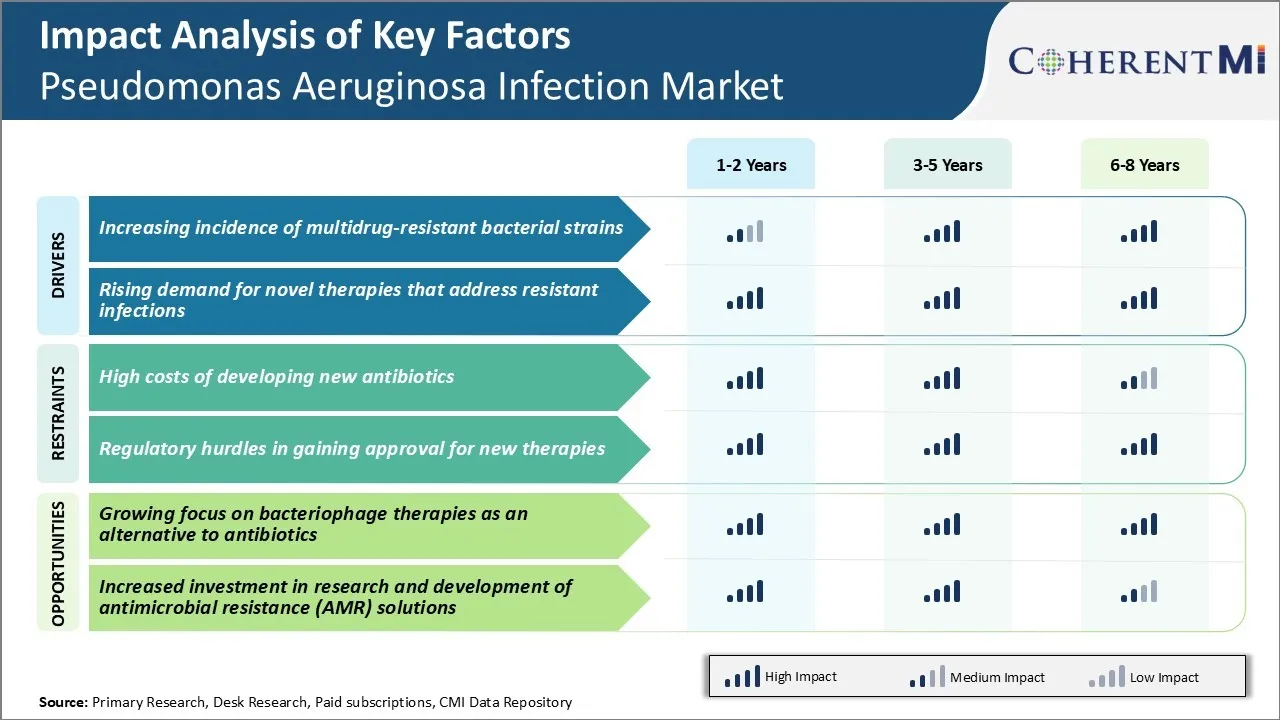
Market Challenge - High Costs of Developing New Antibiotics
One of the major challenges facing the Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market is the extremely high costs associated with developing new antibiotics. Developing a brand-new antibiotic can cost well over $1 billion USD due to the lengthy research and clinical trial process required to get FDA approval.
Given these high costs, pharmaceutical companies have little incentive to invest in developing treatments for multidrug-resistant pathogens like P. aeruginosa that typically have smaller patient populations. Additionally, once a new antibiotic is approved there are mounting pressures to reserve its use as a “last resort” option, limiting its potential sales revenue compared to broader-use antibiotics.
These combined factors of high development costs and smaller market sizes mean new antibiotic research and approval rates have significantly dropped in recent years, leaving few treatment innovations in the pipeline for serious Gram-negative infections like P. aeruginosa.
Unless regulatory incentives or public-private partnerships can help offset these financial barriers, drug-resistant threats like P. aeruginosa may continue rendering our existing antibiotics obsolete faster than replacements can be created.
Market Opportunity - Growing Focus on Bacteriophage Therapies as an Alternative to Antibiotics
One promising opportunity in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market is the growing focus on developing bacteriophage therapies as an alternative to traditional antibiotics. Bacteriophages are viruses that selectively target and kill specific bacterial strains without harming human cells.
Due to their ability to self-amplify, phage therapies may circumvent many of the challenges facing new antibiotic development by having significantly lower associated research and manufacturing costs. Several biotech and pharmaceutical companies are now conducting clinical trials on phage therapies for difficult-to-treat infections like P. aeruginosa, encouraged by their potential as living drugs customizable to different antibiotic-resistant strains.
As more evidence emerges on their safety and efficacy compared to antibiotics, phage therapies could open up new treatment options for P. aeruginosa and other multidrug-resistant pathogens. Their ability to self-perpetuate also alleviates the selective pressure driving further bacterial resistance. If ongoing research continues validating their promise, bacteriophage therapies may represent a breakthrough in our ongoing battle against antibiotic resistance.
Prescribers preferences of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic pathogen known to cause both acute and chronic lung infections. Treatment usually involves a combination of antibacterial drugs, with choices dependent on the stage and severity of infection.
For mild to moderate acute infections, monotherapy with a fluoroquinolone such as ciprofloxacin (Ciprobay) or levofloxacin (Tavanic) is often first-line. More severe cases typically require dual therapy combining a beta-lactam like piperacillin-tazobactam (Zosyn) with an aminoglycoside like tobramycin (Nebcin). Chronically infected patients may be prescribed an inhaled formulation of an anti-pseudomonal drug such as colistin methanesulfonate (Coly-Mycin M).
As the infection progresses and becomes more resistant, combination IV therapy is favored. Popular options include beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations - for example, ceftazidime (Fortaz) with avibactam (Avycaz) - or a carbapenem like imipenem-cilastatin (Primaxin). Last-line multidrug resistance often leads to the use of newer inhaled antibiotics like levofloxacin (Arikayce) or the polymyxin antibiotic aztreonam (Cayston).
Other factors that influence choice include a patient's comorbidities, compliance history, infection site (e.g. wound vs. lung), and results of culture/sensitivity testing for individual pathogen drug resistance patterns. Close monitoring of treatment response and resistance development over time also drives prescribers' sequential therapy decisions.
Treatment Option Analysis of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa infection can range from mild to severe depending on the patient's immune status and site of infection. Treatment involves targeted antimicrobial therapy and control of associated risk factors.
For mild infections, oral antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin are first-line options. They achieve adequate concentrations in respiratory and urinary tract sites. However, resistance often develops quickly requiring stronger agents.
More severe infections involve multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas strains. The first intravenous option is usually a piperacillin-tazobactam combination. Its broad spectrum and bactericidal activity make it effective against a variety of Gram-negative rods including Pseudomonas.
For infections resistant to piperacillin-tazobactam or in severely ill patients, the treatment of choice is an antipseudomonal carbapenem like imipenem or meropenem. These administer reliable coverage against many resistant strains. Cefepime is an alternative but resistance has been increasing in recent years.
For patients who cannot receive systemic therapy or have chronic lung infections, inhaled tobramycin is beneficial. Its high dosage at the infection site helps overcome poor lung tissue penetration of other drugs. Combination therapy using an antipseudomonal agent with an aminoglycoside may also be tried in life-threatening situations.
Key winning strategies adopted by key players of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market
Product innovation through R&D: Developing novel drugs and treatment options has helped companies gain an edge over competitors and capture more market share. For example, Merck launched SIVEXTRO (tedizolid phosphate) in 2014, the first oxazolidinone antibacterial approved for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections.
Strategic acquisitions: Companies have strengthened their product pipeline and market position through strategic acquisitions of firms with complementary assets and technologies. For instance, in 2018, Pfizer acquired Array BioPharma to gain access to its pipeline of targeted cancer medicines, including the BRAF inhibitor BRAFTOVI approved for colon cancer.
Partnerships and licensing deals: Pharmaceutical players form partnerships with biotech companies to share development costs and risks. In 2019, Novartis entered a collaboration with Entasis Therapeutics to develop ETX2514, a novel fixed-dose combination antibacterial drug.
Focus on emerging markets: Given market potential, companies focus on expanding in high-growth emerging markets of Asia, Africa and Latin America through local manufacturing and marketing partnerships. For example, AstraZeneca established a subsidiary in China and partnered with several local pharma firms for manufacturing and distributing its inhaled antibiotic Tobramycin.
Segmental Analysis of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market
Insights, By Drug: Rising prevalence of chronic infections drives Monoclonal antibody segment growth
In terms of drug, monoclonal antibody segment is expected to hold 45.7% share of the market in 2024, owning to its targeted therapeutic approach against chronic P. aeruginosa infections. Monoclonal antibodies are highly specific proteins that can restore, enhance or mimic the immune system's attack on pathogens like P. aeruginosa. Their specificity allows them to neutralize microbial virulence factors and toxins more precisely with minimal off-target toxicity compared to other drugs.
As chronic respiratory infections and therapy-resistant UTIs caused by P. aeruginosa are on the rise, the antibody drugs are gaining prominence. Their ability to combat biofilms and inhibit quorum sensing mechanisms employed by the bacteria help clear stubborn infections.
Many leading drug makers are investing heavily in developing humanized monoclonal antibodies against key virulence factors of P. aeruginosa. The segment growth is further fueled by the rising adoption of combination therapies pairing antibodies with other anti-microbials to attain synergistic efficacy.

Insights, By Route of Administration: Oral Route Drives Market Led by Patient Compliance and Convenience
In terms of route of administration, oral administration is expected to account for 50.4% share of the market in 2024, owing to better patient acceptance and compliance. Treating chronic P. aeruginosa infections requires long term administration of anti-microbial drugs. The oral route provides distinct advantages over parenteral drugs in this context, as oral medications are less invasive, more convenient to self-administer and fit better into patients' daily routines. This improves adherence to treatment regimens significantly.
Oral drugs also allow for outpatient care as opposed to in-hospital intravenous therapies. This eases the burden on healthcare systems and lowers the overall cost of care. Pharmaceutical companies thus focus more R&D efforts on developing novel oral anti-pseudomonal drugs and formulations to leverage the high-growth oral segment.
Insights, By Infection: Rising ICU Admissions and Immunosuppression Fuel Respiratory Infections Segment
In terms of infection, respiratory infections contribute the highest share owing to the opportunistic pathogen's propensity to cause ventilator-associated and nosocomial pneumonias. The elderly population which is more susceptible to chronic lung conditions like COPD, the rise in ICU admissions worldwide and increased use of mechanical ventilation devices provide an ideal niche for P. aeruginosa to infect lungs. Likewise, prolonged corticosteroid therapy or diseases like cystic fibrosis that weaken the lungs predispose patients to life-threatening respiratory infections by the bacterium. Growing cancer patient pool undergoing chemotherapy or bone marrow transplants also face high risk of pulmonary pseudomonal infections due to induced immunosuppression. This has prompted healthcare providers and drug developers to prioritize innovative therapies targeting P. aeruginosa respiratory diseases.
Additional Insights of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa is responsible for a significant proportion of hospital-acquired infections globally. It is a major cause of pneumonia, UTIs, and wound infections, particularly in immunocompromised patients. The rise of resistant strains has made it one of the most challenging infections to treat.
- The rising prevalence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, particularly in healthcare-associated settings, is a major concern. An estimated 51,000 healthcare-associated Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections occur in the U.S. each year, contributing significantly to the growing demand for new therapeutics.
- Armata Pharmaceuticals and Spexis lead in the development of therapeutic phages and antibiotics targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa, reflecting the industry's focus on addressing the rising antimicrobial resistance.
Competitive overview of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market
The major players operating in the pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market include AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Merck & Co., Novartis, Basilea Pharmaceutica, Armata Pharmaceuticals, Spexis, AvidBiotics Corp, Polyphor AG, and Phico Therapeutics.
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market Leaders
- AstraZeneca
- Pfizer
- Merck & Co.
- Novartis
- Basilea Pharmaceutica
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market - Competitive Rivalry, 2024

Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market
(Dominated by major players)
(Highly competitive with lots of players.)
Recent Developments in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market
- In June 2024, Armata Pharmaceuticals announced the completion of Phase II clinical trials for AP PA02, which targets respiratory infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The results indicated promising efficacy in cystic fibrosis patients, potentially paving the way for future treatment approvals. The company also stated that the final patient follow-up is scheduled for August 2024, and the topline results from the trial are expected to be available in the second half of 2024. The trial is a multi-center, double-blind, placebo-controlled study focusing on patients with Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis (NCFB), aiming to assess the safety and efficacy of inhaled AP-PA02
- In March 2024, AstraZeneca announced positive results from Phase III trials of its new antibiotic targeting multidrug-resistant strains of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, which significantly reduced the infection duration in hospitalized patients. AstraZeneca is involved in multiple collaborations and development efforts related to antibiotics and antimicrobial resistance. Also, there are ongoing significant developments in the antibiotic field, such as Pfizer’s new antibiotic combination that targets multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other Gram-negative bacteria, which could offer critical new treatments for such infections.
- In late 2023, Spexis revealed the initiation of Phase I trials for Murepavadin, an inhaled antibiotic aimed at multi-drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The drug is expected to address unmet needs in cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis patients. The Phase I clinical trial tested the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of inhaled murepavadin (iMPV) in healthy volunteers. The results showed that iMPV was well-tolerated at all dose levels, with no serious adverse events. The study also demonstrated that murepavadin achieved effective concentrations in the lung tissue while maintaining low systemic bioavailability, which is essential for targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients.
In August 2023, Pfizer launched a new antimicrobial peptide therapy aimed at treating hospital-acquired respiratory infections caused by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. This therapy is expected to improve patient outcomes by targeting bacterial resistance mechanisms. Pfizer has been active in developing new antimicrobial therapies for hospital-acquired infections, including treatments like Zavicefta (a combination of ceftazidime and avibactam). Zavicefta is designed to treat severe infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, particularly in cases of hospital-acquired pneumonia.
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection Market Segmentation
- By Drug
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Small Molecule
- Peptide
- By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Parenteral
- Topical
- By Infection
- Respiratory Infections
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- By Patient Type
- Hospital-acquired Infections
- Community-acquired Infections

Would you like to explore the option of buying individual sections of this report?
Frequently Asked Questions :
How big is the pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market?
The pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.3 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.28 Bn by 2031.
What are the key factors hampering the growth of the pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market?
High costs of developing new antibiotics and regulatory hurdles in gaining approval for new therapies are the major factors hampering the growth of the pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market.
What are the major factors driving the pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market growth?
Increasing incidence of multidrug-resistant bacterial strains and rising demand for novel therapies that address resistant infections are the major factors driving the pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market.
Which is the leading drug in the pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market?
The leading drug segment is monoclonal antibody.
Which are the major players operating in the pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market?
AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Merck & Co., Novartis, Basilea Pharmaceutica, Armata Pharmaceuticals, Spexis, AvidBiotics Corp, Polyphor AG, and Phico Therapeutics are the major players.
What will be the CAGR of the pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market?
The CAGR of the pseudomonas aeruginosa infection market is projected to be 8.36% from 2024-2031.